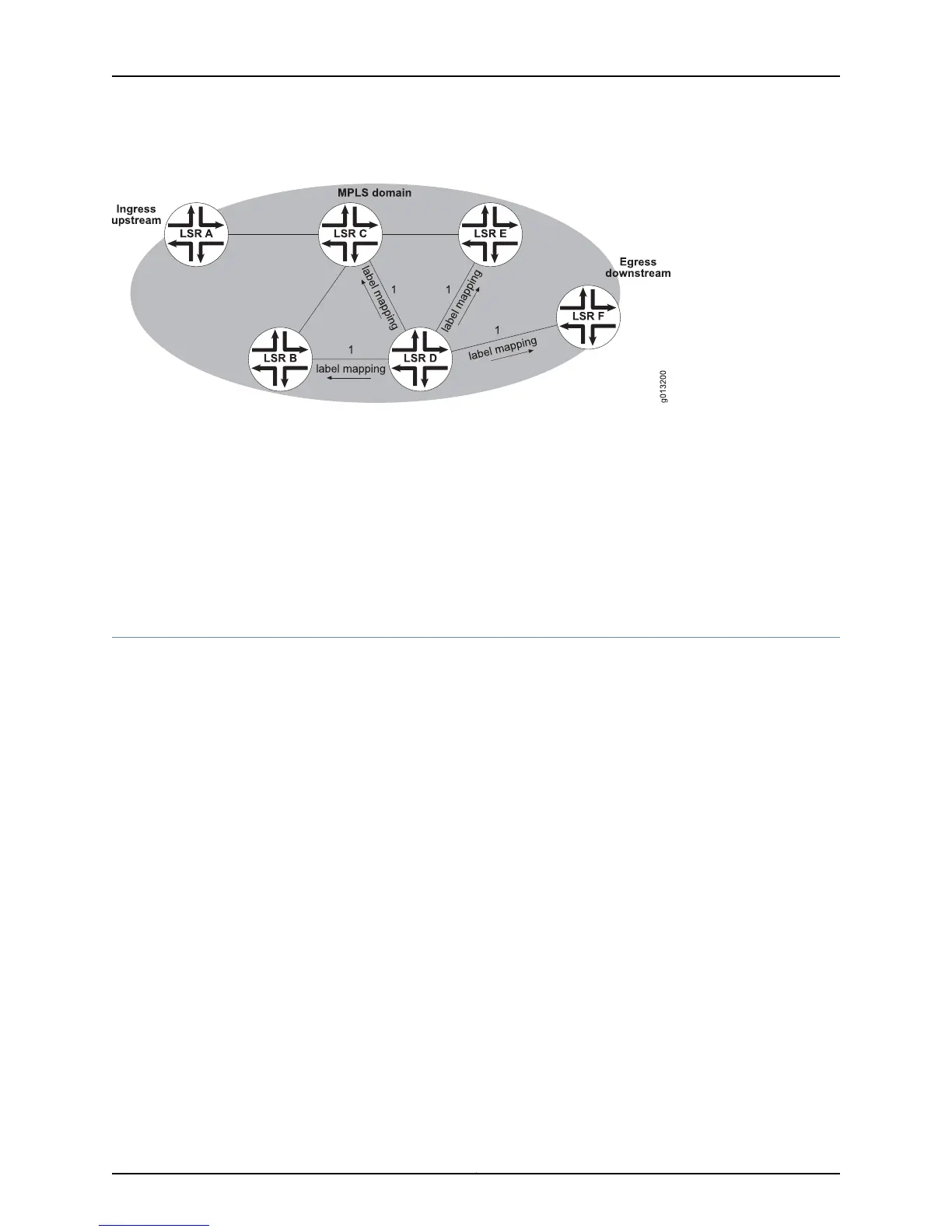
Figure 54: LSP Creation, Downstream-Unsolicited, Independent Control
Related Topics TTL Processing in the Platform Label Space Overview on page 222•
• IP Data Packet Mapping onto MPLS LSPs Overview on page 229
• MPLS Label Switching and Packet Forwarding Overview on page 218
• MPLS Forwarding and Next-Hop Tables Overview on page 233
• MPLS Interfaces and Interface Stacking Overview on page 236
• Topology-Driven LSPs Overview on page 255
IP Data Packet Mapping onto MPLS LSPs Overview
IP packets are mapped onto LSPs by one of the following methods:
•
RSVP-TE tunnels can be referenced directly by static routes that you configure. You
can determine which routes (routes destined for which subnets) to direct through the
LSP and issue the appropriate ip route commands, as shown in the following example:
host1(config-if)#ip route 10.15.21.16 tunnel mpls:1
You cannot create any static routes until the tunnel interface has been created.
However, the tunnel does not have to be active before you create the static routes.
•
RSVP-TE tunnels are announced to IS-IS and OSPF; the IGP then uses the tunnels as
next hop interfaces for its SPF calculations. For this method, you must issue the tunnel
mpls autoroute announce command. When the LSP is established, the ingress LSR
announces the LSP endpoint to the IGP. This is also referred to as registering the LSP.
The IGP then recalculates the shortest path for all routes destined for or beyond that
endpoint. You can choose to register endpoints with both IS-IS and OSPF. The following
is an example registration command:
host1(config-if)#tunnel mpls autoroute announce isis
•
For topology-driven LSPs, LDP can modify the IP routing table to use MPLS next hops
in the routing table, replacing the regular IP next hops for the corresponding routes.
•
For labeled BGP routes, BGP adds routes with MPLS next hops to the appropriate VR
or VRF routing table.
229Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 3: MPLS Overview

 Loading...
Loading...