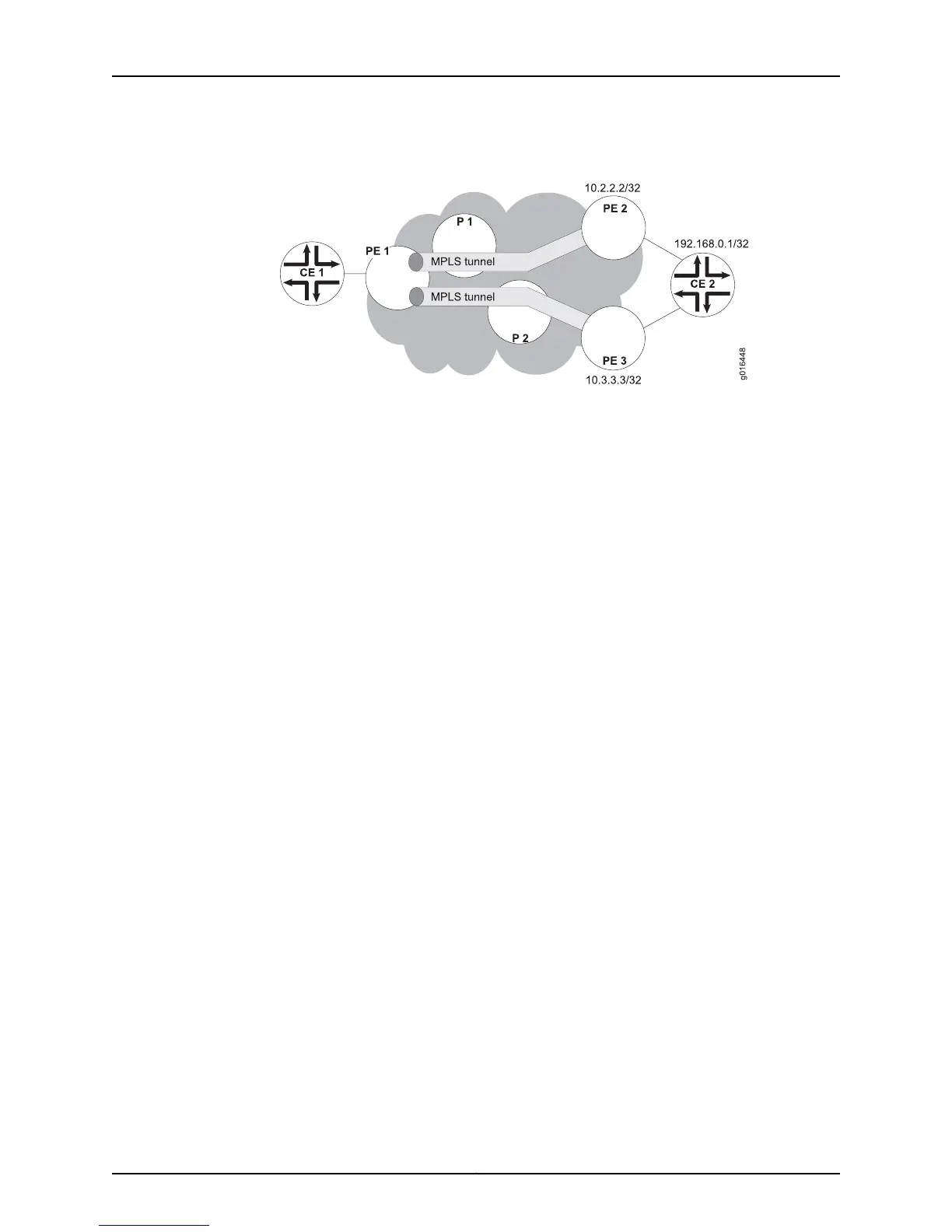
Figure 68: ECMP BGP/MPLS VPN Scenario
With respect to PE 1, this network has an ECMP set of two equal-cost legs for the VPN
prefix of CE 2, 192.168.0.1/32:
•
PE 1 -> P 1 -> PE 2 -> CE 2
•
PE 1 -> P 2 -> PE 3 -> CE 2
The details of these routes are displayed by the following command:
host1:pe1:pe1-ce1#show ip route 192.168.0.1 detail
192.168.0.1/32 Type: Bgp Distance: 200 Metric: 0 Tag: 0 Class: 0
MPLS next-hop: 741, ECMP next-hop, leg count 2
MPLS next-hop: 389, label 17, VPN traffic, resolved by MPLS next-hop 376
MPLS next-hop: 376, resolved by MPLS next-hop 385, peer 10.3.3.3
MPLS next-hop: 385, label 24 on GigabitEthernet1/1/0.2
(ip19000002.mpls.ip [V:pe1]), nbr 10.3.2.2
MPLS next-hop: 740, label 18, VPN traffic, resolved by MPLS next-hop 729
MPLS next-hop: 729, resolved by MPLS next-hop 737, peer 10.2.2.2
MPLS next-hop: 737, label 27 on GigabitEthernet1/1/0.1
(ip19000001.mpls.ip [V:pe1]), nbr 10.3.1.2
If the connection to PE 2 fails, BGP marks the MPLS next hop 729 as a failed indirect next
hop as soon as BGP is notified of the loss of connectivity. However, some traffic continues
to be forwarded to CE 2 through PE 2; this traffic is lost. BGP quickly prunes the failed
route from the FIB, stopping this traffic loss, and then recalculates the routes to CE 2.
During this period, traffic for CE 2 is forwarded only through PE 3. When the new routes
are installed in the FIB, traffic is forwarded to CE 2 by means of the newly installed route.
BGP/MPLS VPN Components
If you have specified the VPN-IPv4 address family, you can configure virtual private
networks across an IP backbone. BGP carries routing information for the network and
MPLS labels, whereas MPLS transports the data traffic. Figure 69 on page 387 shows a
typical scenario.
The service provider backbone comprises two types of routers:
•
Provider edge routers (PE routers)
•
Provider core routers (P routers)
PE routers are situated at the edge of the service provider core and connect directly to
customer sites. These routers must run BGP-4, including the BGP/MPLS VPN extensions.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.386
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...