MPLS uses the EXP bits in the shim header to support differentiated services. The JunosE
Software supports both statically configured and signaled mapping between the EXP
bits and the PHB of traffic.
In a signaled environment, you can configure on the ingress node the set of PHBs that a
tunnel supports, and then the set of PHBs is signaled end to end.
To support differentiated services, MPLS employs two types of LSPs: E-LSPs and L-LSPs.
The two types differ in how their PHB is determined. In the JunosE Software, the PHB is
a combination of traffic class (also called per-hop scheduling class, or PSC) and drop
precedence (color).
•
E-LSPs (EXP-inferred-PSC LSP) can transport as many as eight BAs. For E-LSPs, the
traffic’s PHB is learned from the MPLS shim header.
•
L-LSPs (Label-only-inferred-PSC LSP) transport a single PSC. The PHB is determined
from a combination of the packet’s label, which indicates the traffic class, and the EXP
field of the shim header, which indicates the drop precedence.
•
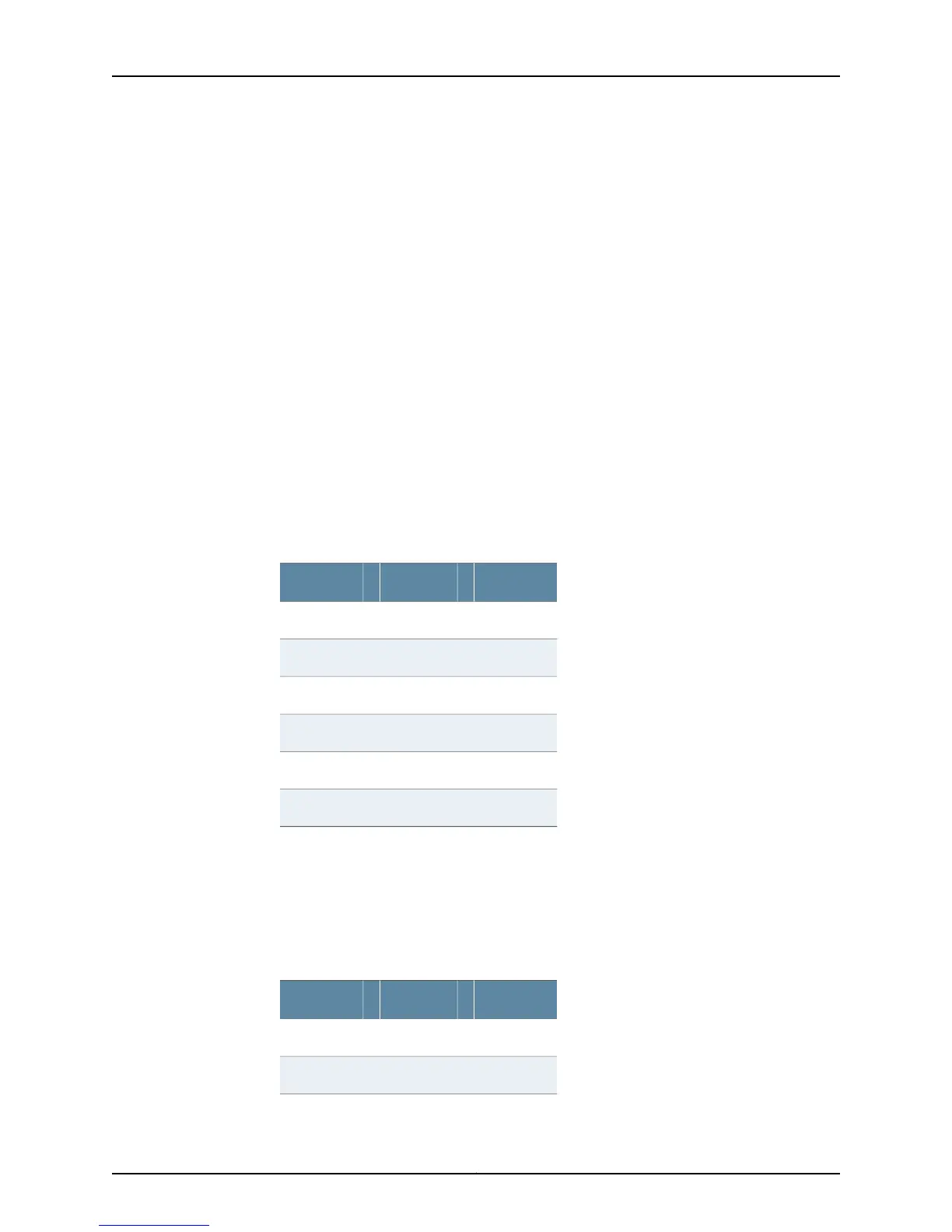
Table 56 on page 308 indicates how the PSC (column 1) is combined with the EXP
field (column 2) to determine the PHB for incoming traffic on L-LSPs.
Table 56: Incoming L-LSP PHB Determination
PHB=EXP Field+PSC
BE000BE
CSn000CSn
AFn1001AFn
AFn2010AFn
AFn3011AFn
EF000EF
For nonstandard PHBs (any that are not listed in Table 56 on page 308), the JunosE
Software uses mapping similar to AFn mapping; EXP 001 is mapped to color green,
EXP 010 is mapped to yellow, and EXP 011 is mapped to red.
Table 57 on page 308 presents three examples that indicate how the PSC and the
EXP field are combined to determine the PHB for traffic on incoming L-LSPs.
Table 57: Examples of Incoming L-LSP PHB Determination
PHB=EXP Field+PSC
AF22010AF2
AF32010AF3
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.308
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...