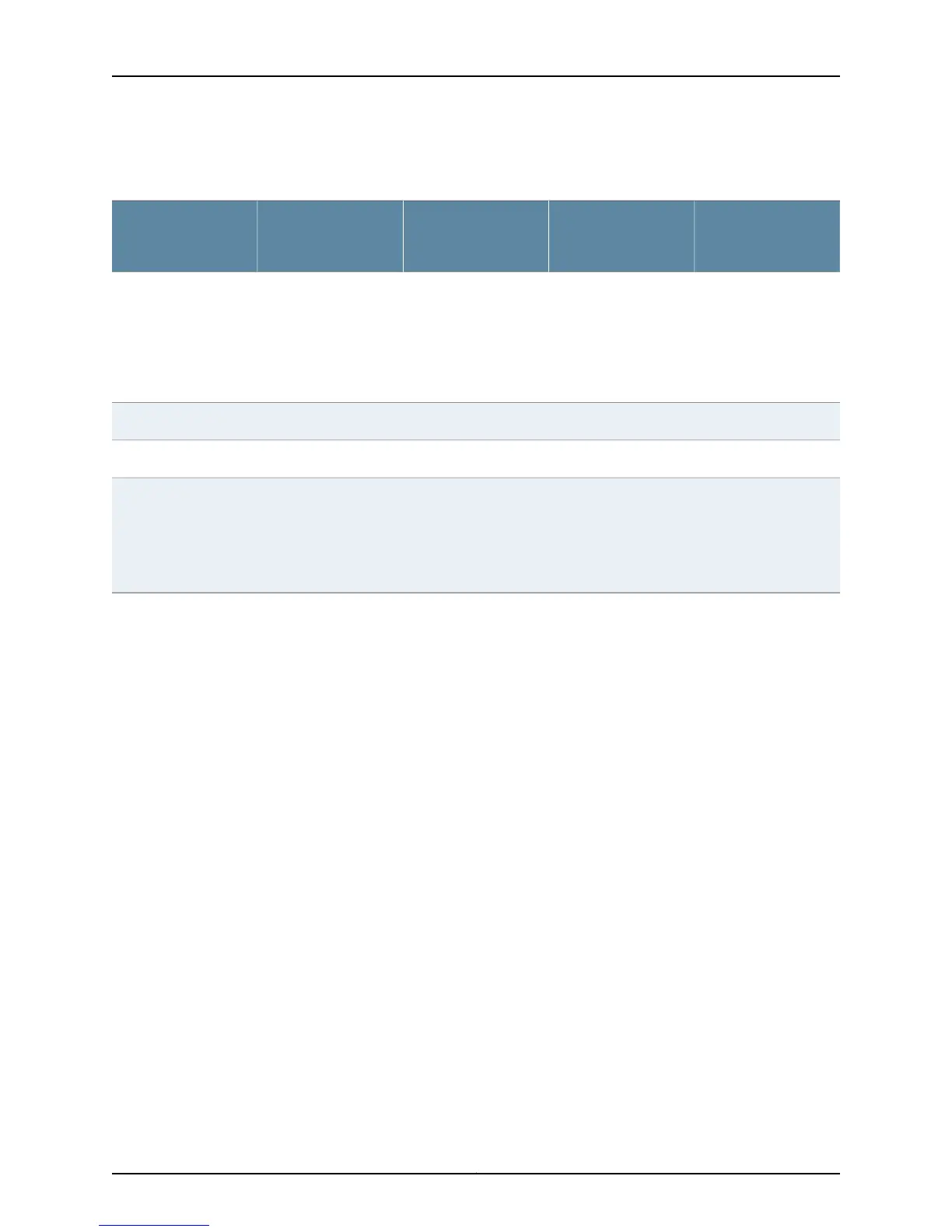
Table 13: Source Addresses and Default Next Hop Addresses for Various Configurations
(continued)
Default Next Hop
Value for IPv6
Prefixes
Default Next Hop
Value for IPv4
Prefixes
Source Address used
for TCPv4 and TCPv6
Connection
Configured Update
Source Address
Configured Neighbor
Address
IPv6 address of the
interface. If the
interface does not have
an IPv6 address, then
the IPv4 address of the
interface is mapped to
an IPv6 address.
IPv4 address of the
interface
IPv4 address of the
interface. If the
interface does not have
an IPv4 address, then
the session does not
come up.
Interface nameIPv4 neighbor address
IPv6 source address0.0.0.0IPv6 source addressIPv6 source addressIPv6 neighbor address
Not allowedNot allowedNot allowedIPv4 source addressIPv6 neighbor address
IPv6 address of the
interface
IPv4 address of the
interface. If the
interface does not have
an IPv4 address, then
0.0.0.0.
IPv6 address of the
interface. If the
interface does not have
an IPv6 address, then
the session does not
come up.
Interface nameIPv6 neighbor address
You can override a native IPv6 next-hop address with either the neighbor update-source
command or an outbound route map.
When you specify an interface with the neighbor update-source command, the
IPv4-mapped IPv6 address of the interface is used instead of the native IPv6 address
for the next hop.
host1(config)#interface loopback 0
host1(config-if)#ip address 10.1.1.1/32
host1(config-if)#exit
host1(config)#router bgp 100
host1(config-router)#neighbor 2::2 update-source loopback 0
In this example, the IPv4-mapped IPv6 address of the loopback 0 interface is the next-hop
address sent when IPv6 prefixes are advertised. However, if loopback 0 has an IPv6
address, then that address is used as the default next hop for advertising IPv6 prefixes.
Specifying Peers That Are Not Directly Connected
Normally, EBGP speakers are directly connected. When you cannot connect EBGP
speakers directly, you can use the neighbor ebgp-multihop command to specify that
the neighbor is more than one hop away. You generally need static routes to configure
multihop connections. By default, the one-hop limitation per EBGP peers is enforced by
the time-to-live attribute. You can override this default limit by using the ttl variable to
specify the maximum number of hops to the peer.
In Figure 12 on page 33, router Boston and router LA are connected together through
router NY, rather than by a direct connection. Routers Boston and LA are configured as
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.32
JunosE 11.2.x BGP and MPLS Configuration Guide

 Loading...
Loading...