142
5 SEQUENCE INSTRUCTIONS
5.6 Termination Instructions
Ending the sequence program
END
This instruction indicates the end of a program.
• This instruction indicates the end of all programs including the main routine program, subroutine program, and interrupt
program. When this instruction is executed, the CPU module ends execution of the currently executing program.
• The first time the RUN is started, execution begins from this instruction.
• This instruction cannot be programmed midway during the main sequence program. When this processing is required
midway during the program, use the FEND instruction.
• When programming is performed using the engineering tool in ladder edit mode, the END instruction is automatically input
and cannot be edited.
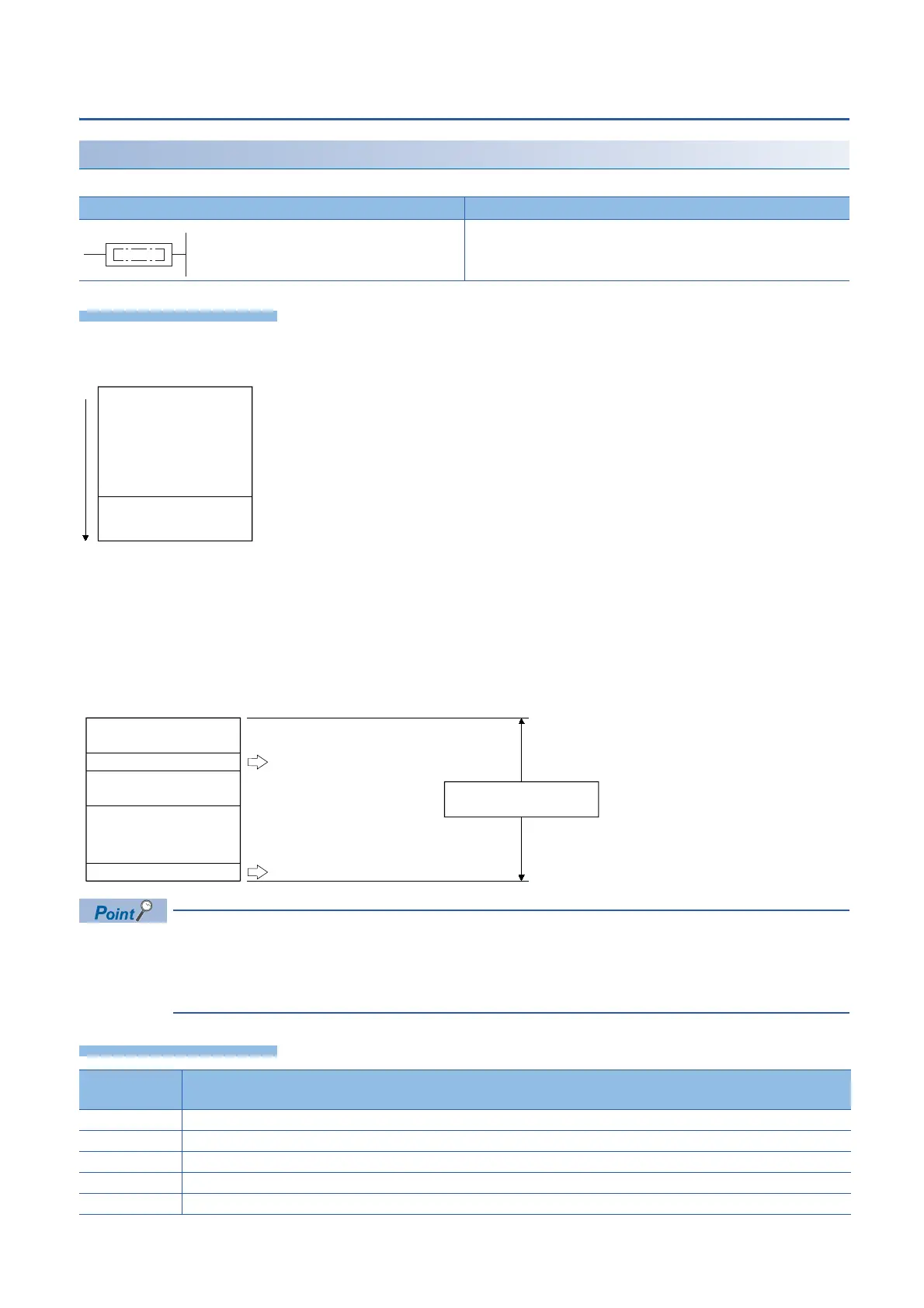
• The following illustrates how the END and FEND instructions are used properly when a program contains a main routine
program, subroutine program, and interrupt program.
The END instruction executed while a program is divided into multiple program blocks indicates the end of a
program block.
The END instruction executed for END processing is executed at the end of the last executed program
registered in the program settings.
Ladder diagram Structured text
Not supported.
Error code
(SD0/SD8067)
Remarks
3340 The END instruction is executed before the NEXT instruction after the FOR instruction is executed.
3381 The END instruction is executed before the RET instruction after the CALL(P) instruction is executed.
33E3 The END instruction is programmed between FOR-NEXT.
33E4 The END instruction is programmed between MC-MCR.
33E7 The END instruction is programmed between I-IRET.
END
0
Sequence program
FEND
END
Main routine program
Interrupt Program
Main sequence
program area
Subroutine program
(FEND instruction is required.)
(END instruction is required.)

 Loading...
Loading...











