18 BIT SHIFT FUNCTIONS
18.2 n-bit Right Shift
793
18
18.2 n-bit Right Shift
SHR(_E)
These functions shift an input value rightward by (n) bits and output the result.
■Descriptions, types, and data types
■Operation processing
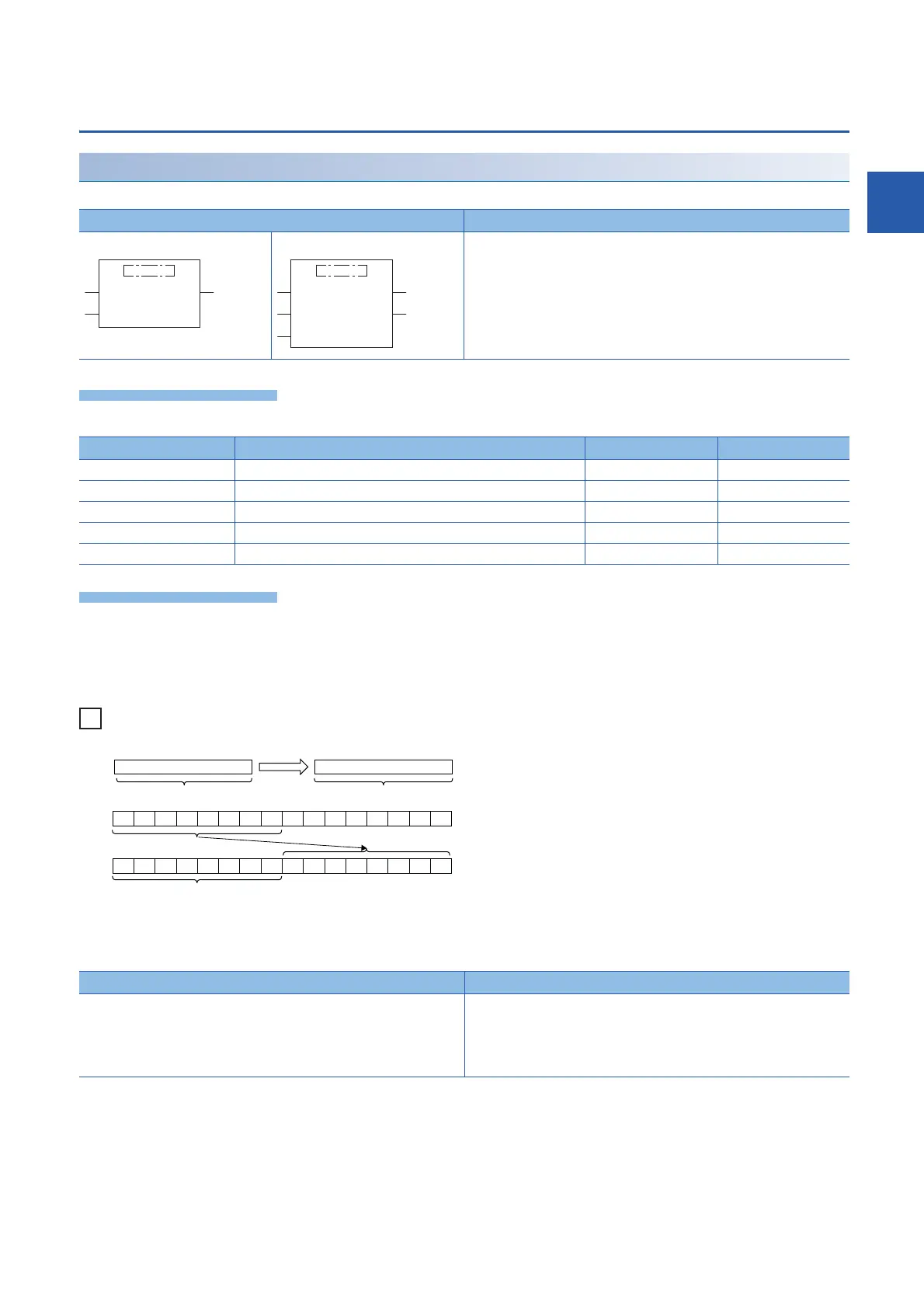
• These functions shift the WORD or DWORD type data input to (s) right by (n) bits and output the result in the same data
type as (s) from (d).
• The number input in (n) is used as the number of right-shift bits.
When the data type of (s) is WORD and 8 is input in (n)
• "0" is set to "n" bits from the most significant bit.
• A value input to (n) is the WORD or DWORD type data value.
• A value input to (n) (Number of shift bits) is the INT type data value and within the following range.
Ladder diagram Structured text
[Without EN/ENO] [With EN/ENO] [Without EN/ENO]
d:=SHR(s,n);
[With EN/ENO]
d:=SHR_E(EN,ENO,s,n);
Argument Description Type Data type
EN Execution condition (TRUE: Execution, FALSE: Stop) Input variable BOOL
s Input Input variable ANY_BIT
n Number of shift bits Input variable ANY_BIT
ENO Output status (TRUE: Normal, FALSE: Abnormal) Output variable BOOL
d Output Output variable ANY_BIT
When the data type of (s) is WORD When the data type of (s) is DWORD
A value in (n) is within 0 to 15.
The lower 4-bit data of the value in (n) is used.
[Example]
When the input value is 6: 6
When the input value is 22: 6
A value in (n) is within 0 to 31.
The lower 5-bit data of the value in (n) is used.
[Example]
When the input value is 6: 6
When the input value is 22: 22
IN (WORD)
270FH 27H
WORD
0100100011100111
270FH
0 1110 10000000000
27H
These bits become "0".

 Loading...
Loading...











