466
7 APPLICATION INSTRUCTION
7.9 Index register operation instruction
7.9 Index register operation instruction
Saving all data of the index register
ZPUSH(P)
These instructions save the contents of index registers and long index registers in the devices specified by (d) and later.
■Descriptions, ranges, and data types
■Applicable devices
• These instructions save the contents of index registers and long index registers in the devices specified by (d) and later.
• When the contents of index registers are saved, "1" is added to (d).
• These instructions save the contents of index registers and long index registers for 24 words regardless of the assignment
of the number of the registers. Thus, when the number of index registers is 0, the contents of long index registers are saved
for 12 points.
• The ZPOP(P) instructions are used to return the data. The ZPUSH(P) and ZPOP(P) instructions are used in pairs, and by
using the same device in (d) a nesting structure can be adopted. (
Page 468 Returning all data of the index register)
• When a nesting structure is adopted, the areas to be used are added to (d) and later every time the ZPUSH(P) instructions
are used. Check the number of index registers and long index registers by SD300 and SD302, and secure the areas for the
number of instructions to be used in advance.
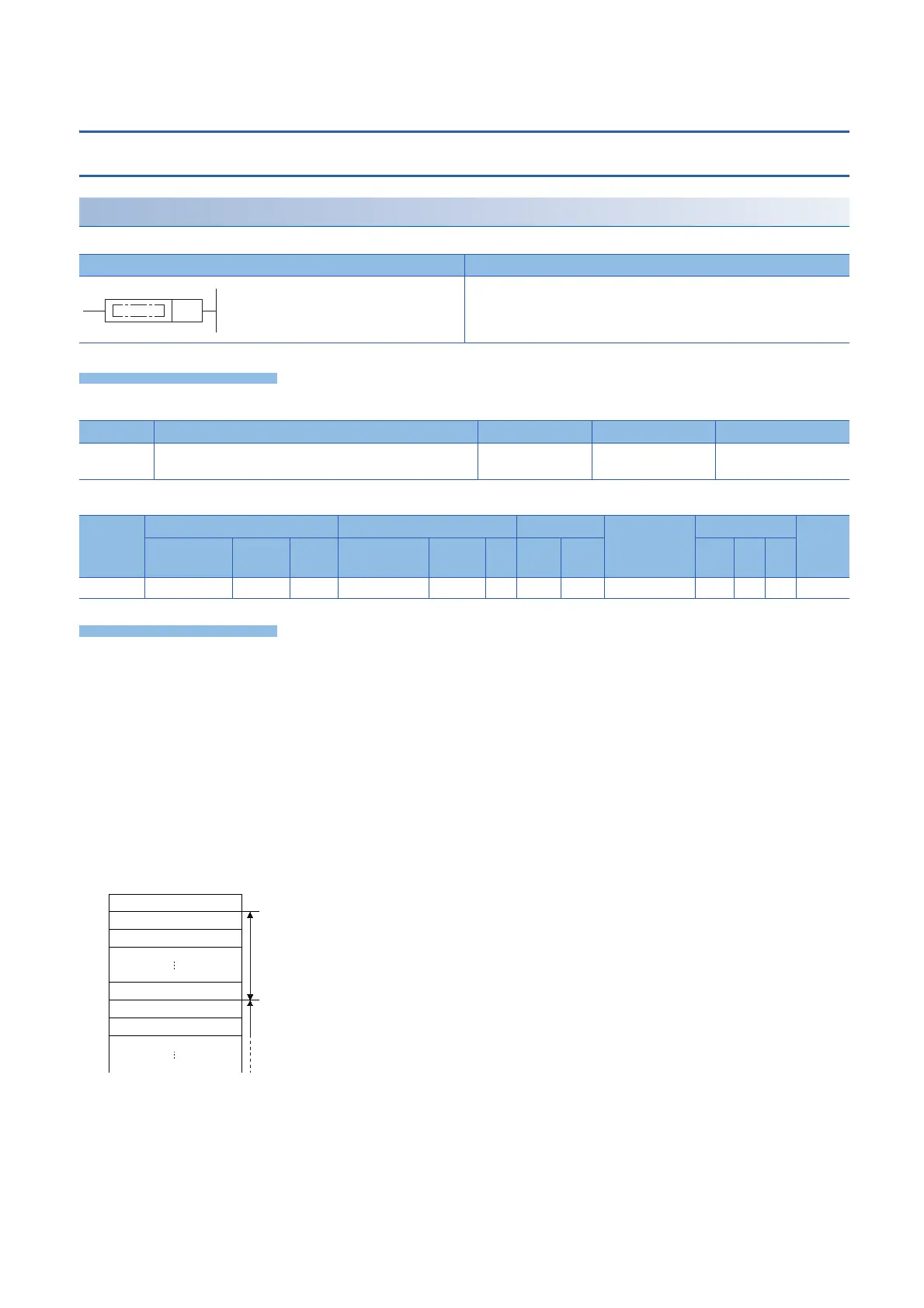
• The following shows the areas of (d) and later to be used.
Ladder diagram Structured text
ENO:=ZPUSH(EN,d);
ENO:=ZPUSHP(EN,d);
Operand Description Range Data type Data type (label)
(d) Head device number for saving the data of index registers and
long index registers
16-bit signed binary ANY16
Operand Bit Word Double word Indirect
specification
Constant Others
X, Y, M, L,
SM, F, B, SB
U\G T, ST,
C, LC
T, ST, C, D,
W, SD, SW, R
U\G Z LC LZ K, H E $
(d)
(d)+0
+1
+2
+24
+25
+26
Z0
Z1
Z0
Z1
Z23
Number of times of batch-storage
1st nesting (24 words for one nesting)
2nd nesting

 Loading...
Loading...











