272
6 BASIC INSTRUCTIONS
6.5 Data Conversion Instructions
Converting decimal ASCII to 32-bit binary data
DDABIN(P)(_U)
These instructions convert the decimal ASCII data in the device numbers specified by (s) and later to 32-bit binary data, and
store the converted data in the device specified by (d).
■Descriptions, ranges, and data types
■Applicable devices
*1 T, ST, C cannot be used.
• These instructions convert the decimal ASCII data in the device numbers specified by (s) and later to 32-bit binary data,
and store the converted data in the device specified by (d).
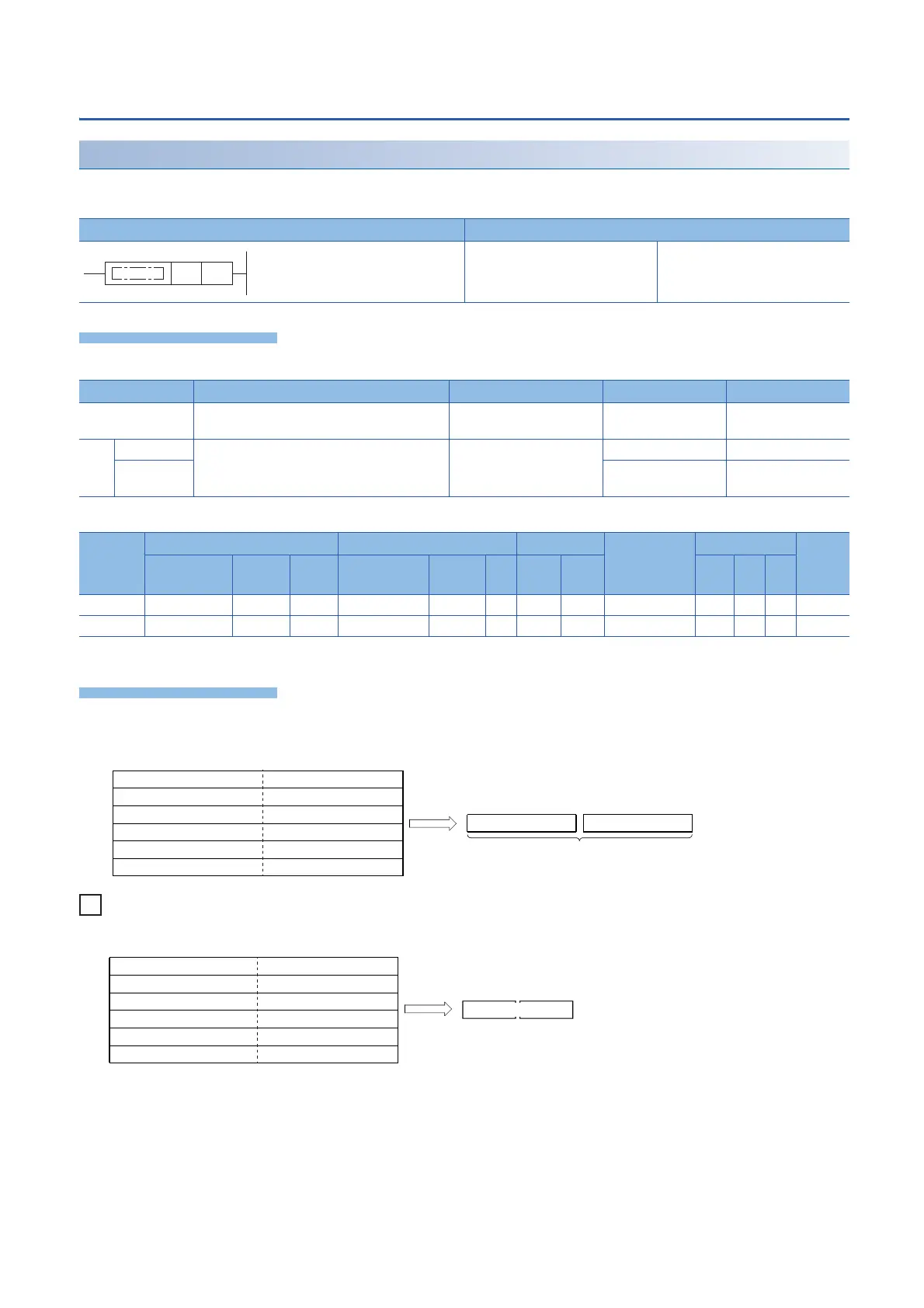
When the ASCII data, -1234543210 (signed), is specified by (s)
• The ASCII data that can be specified by (s) to (s)+5 is -2147483648 to +2147483647 for signed data, and 0 to 429496729
for unsigned data. The data stored in the high-order byte of (s)+5 is ignored.
• As signed data, "20H" is stored if the ASCII data is positive, and "2DH" is stored if the data is negative. (If a value other than
"20H" and "2DH" is set, the data will be processed as positive data.) (DABIN(P))
• A value "30H" to "39H" can be set in the each place of the ASCII code.
• If a value "20H" or "00H" is set, the value will be processed as "30H".
Ladder diagram Structured text
ENO:=DDABIN(EN,s,d);
ENO:=DDABINP(EN,s,d);
ENO:=DDABIN_U(EN,s,d);
ENO:=DDABINP_U(EN,s,d);
Operand Description Range Data type Data type (label)
(s) ASCII data or the head device where the ASCII
data is stored
Character string ANYSTRING_SINGLE
(d) DDABIN(P) Head device for storing the converted data 32-bit signed binary ANY32_S
DDABIN(P)_
U
32-bit unsigned binary ANY32_U
Operand Bit Word Double word Indirect
specification
Constant Others
X, Y, M, L,
SM, F, B, SB
U\G T, ST,
C, LC
T, ST, C, D,
W, SD, SW, R
U\G Z LC LZ K, H E $
(s)
(d)
*1
(s)
(s)+1
(s)+2
(s)+3
(s)+4
(s)+5
b15 b0··· ···b7b8
b0··· ···b31 b16 b15
(d)+1 (d)
ASCII code for the billions place
ASCII code for the ten-millions place
ASCII code for the hundred-thousands place
ASCII code for sign
ASCII code for billions place
ASCII code for the millions place
ASCII code for the thousands place
ASCII code for the tens place
(Ignore.)
ASCII code for the ten-thousands place
ASCII code for the hundreds place
ASCII code for ones place
32-bit binary data
Upper 16 bits Lower 16 bits
(s)
(s)+1
(s)+2
(s)+3
(s)+4
(s)+5
b15 b0··· ···b7b8
(d)+1 (d)
31H (1)
33H (3)
35H (5)
2DH (-)
32H (2)
34H (4)
33H (3)
31H (1)
34H (4)
32H (2)
30H (0)
1234 3 2 10
54-

 Loading...
Loading...











