300
6 BASIC INSTRUCTIONS
6.6 Data Transfer Instructions
Digit move
SMOV(P)
These instructions distribute and compose data in units of nibble (4 bits).
■Descriptions, ranges, and data types
*1 Set so that m2m1, m2n.
■Applicable devices
These instructions distribute and compose data in units of nibble (4 bits). The contents of the transfer source (s) and transfer
destination (d) are converted into 4-digit BCD (0000 to 9999). (m2) nibbles starting from the (m1)th nibble are transferred to
the transfer destination (d) starting from the (n)th nibble, converted into binary, and then stored to the transfer destination (d).
■Extension function
When SM8168 is set to ON first and then SMOV instruction is executed, conversion from binary to BCD is not executed. Data
is moved in units of 4 bits.
Ladder diagram Structured text
ENO:=SMOV(EN,s,m1,m2,n,d);
ENO:=SMOVP(EN,s,m1,m2,n,d);
Operand Description Range Data type Data type (label)
(s) Word device number storing data whose nibbles will be
moved
16-bit signed binary ANY16
(m1)
*1
Head nibble position to be moved 1 to 4 16-bit unsigned binary ANY16_U
(m2)
*1
Number of nibbles to be moved 1 to 4 16-bit unsigned binary ANY16_U
(d) Word device number storing data whose nibbles are
moved
16-bit signed binary ANY16
(n)
*1
Head digit position of movement destination 1 to 4 16-bit unsigned binary ANY16_U
Operand Bit Word Double word Indirect
specification
Constant Others
X, Y, M, L,
SM, F, B, SB
U\G T, ST,
C, LC
T, ST, C, D,
W, SD, SW, R
U\G Z LC LZ K, H E $
(s)
(m1)
(m2)
(d)
(n)
• While the command input is OFF, the transfer destination (d) does not change.
• When the command input turns ON, only the specified digits in the transfer destination (d) are changed. The transfer source (s) and unspecified digits in the
transfer destination (d) do not change.
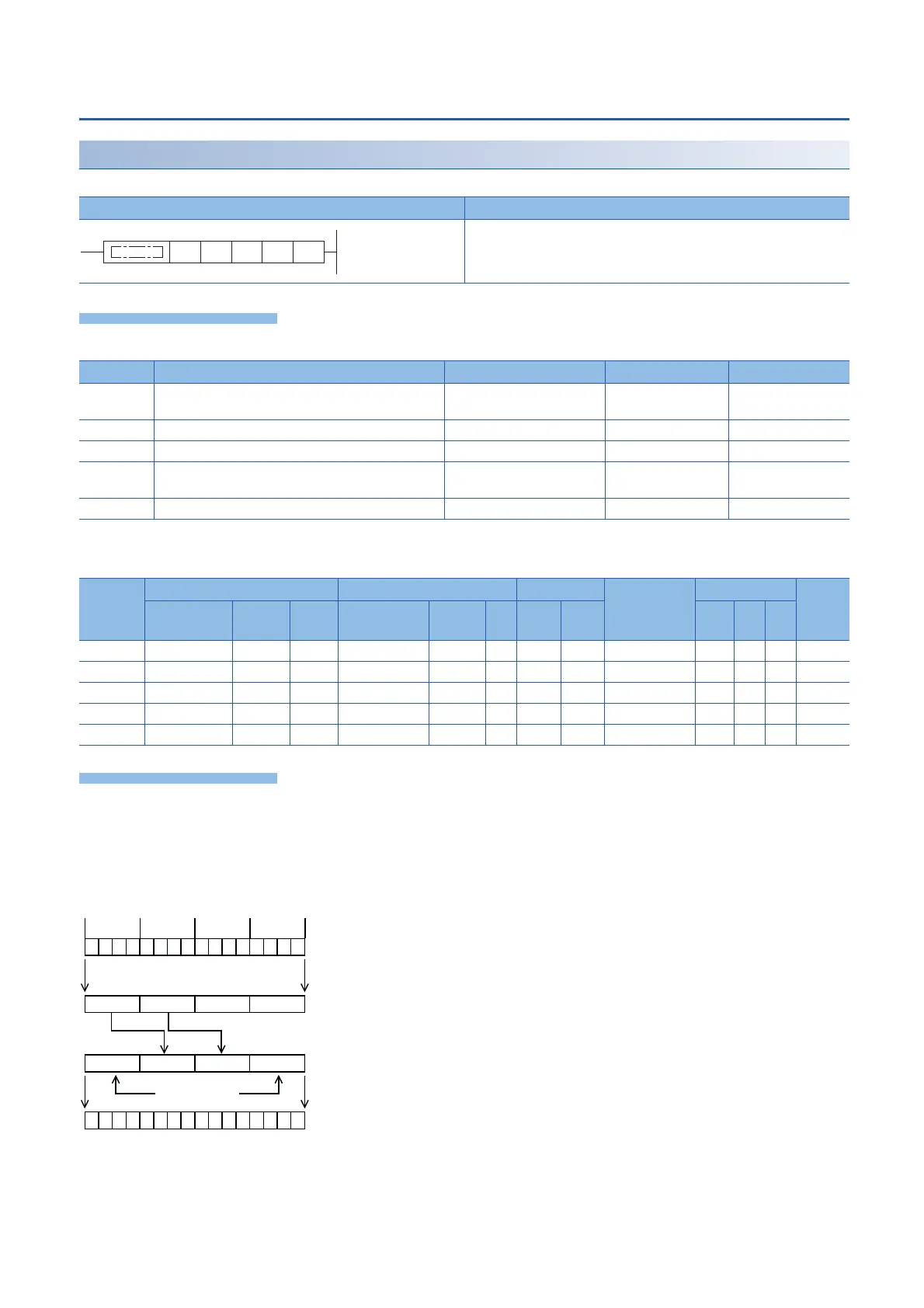
(1): (s) is converted from binary to BCD data.
(2): (m2) digits starting from the (m1)th digit are transferred (combined) to
(d)' starting from the (n)th digit. The first and fourth digits of (d)' are not
affected even if data is transferred from (s)'.
(3): The combined data (BCD) is converted into binary, and stored to (d).
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
10
0
10
1
10
2
10
3
(s)
(s)'
(d)'
(d)
4th nibble 1st nibble2nd nibble3rd nibble
Do not change.
(16-bit binary data)
(4-digit BCD data)
Nibbles are moved(2)
(4-digit BCD data)
(16-bit binary data)
In the case of "m1 = 4, m2 = 2, n = 3".
When command input turns ON
Data is automatically
converted(1)
Data is automatically
converted(3)

 Loading...
Loading...











