1 OVERVIEW
1.2 Data Specification Method
29
1
■Specifying a bit device with nibble specification in the source (s)
When a bit device with nibble specification is specified in the source of an instruction, 0 is stored in the bits, which follow the
bit for which nibble specification is made in the source, in the word device of the destination.
■Specifying a bit device with nibble specification in the destination (d)
When a nibble specification is made in the destination of an instruction, the number of points by the nibble specification is
applicable in the destination.
The bit devices after the number of points specified by nibble remain unchanged.
Handling 32-bit data with word devices/labels
■Word device
Two points of word device can handle 32-bit data.
Note, however, that one point of the following devices can handle 32-bit data.
• Long counter (LC)
• Long index register (LZ)
■Double word type label
One point of double word device can handle 32-bit data.
Ladder example Processing
• 32-bit data instruction
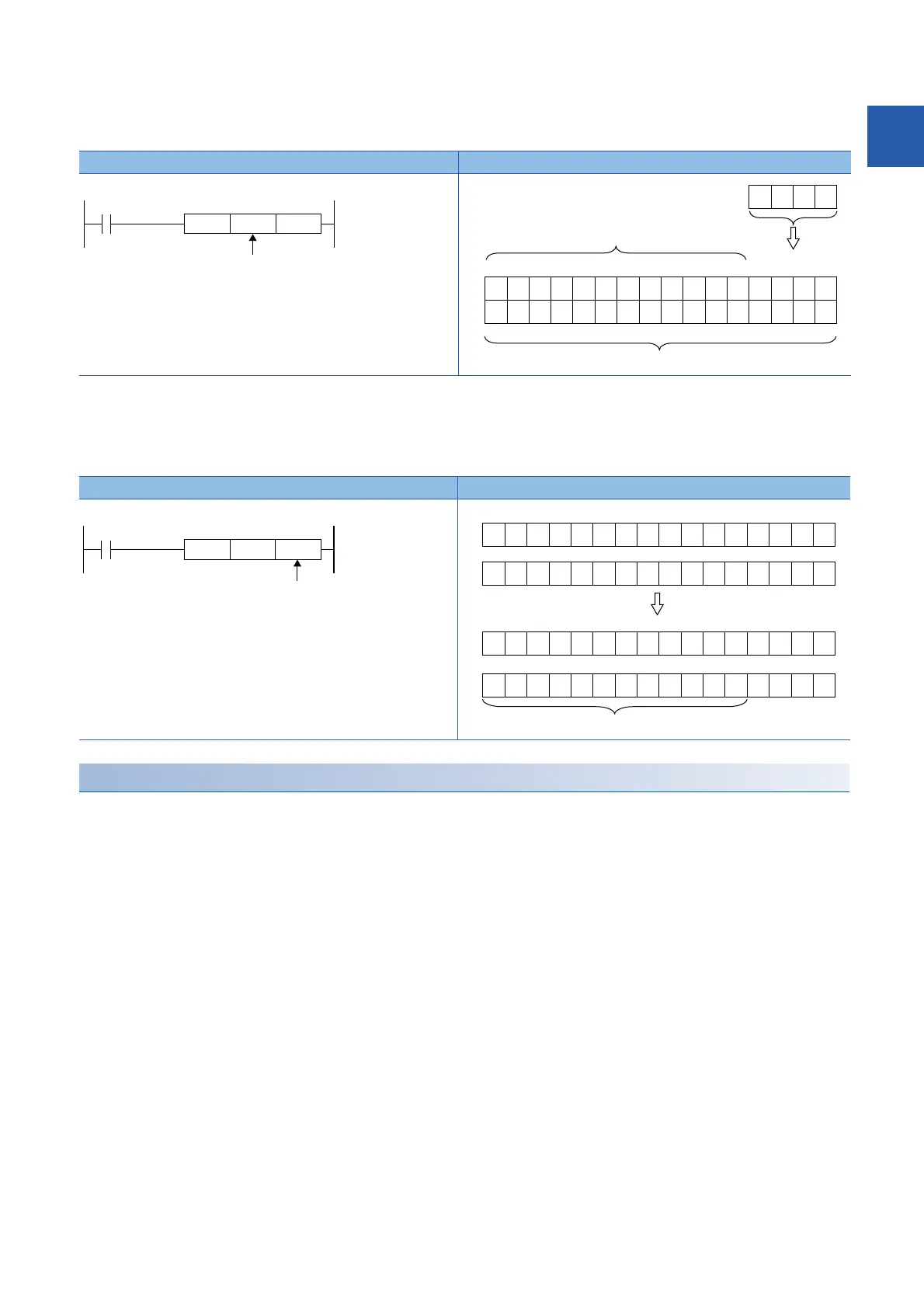
Ladder example Processing
• When the source data is a word device
b0b15
b16b31
∙∙∙
∙∙∙
b3b4 b2 b1
X0
0
00000000 0
0
0X3X2X1
X0X3 X2 X1
K1X0
D0
0
0
00000000 0
0
0000
D1
Filled with 0s.
Filled with 0s.
X10
DMOV D0 K5M10
Destination (d)
M10M25 ∙∙∙ ∙∙∙M17M18
1
0
1
0
11100
1
1
1
0010
M26M41 ∙∙∙ ∙∙∙M29M30
1011
b0b15 ∙∙∙ b7b8 ∙∙∙
1
1
00011010 0
0
1011
D1
b0b15 ∙∙∙ b7b8 ∙∙∙
1
0
10110010 1
0
1110
D0
The data remain the same.

 Loading...
Loading...











