Preparation of trenches
OmniTrax Product Guide Page 105
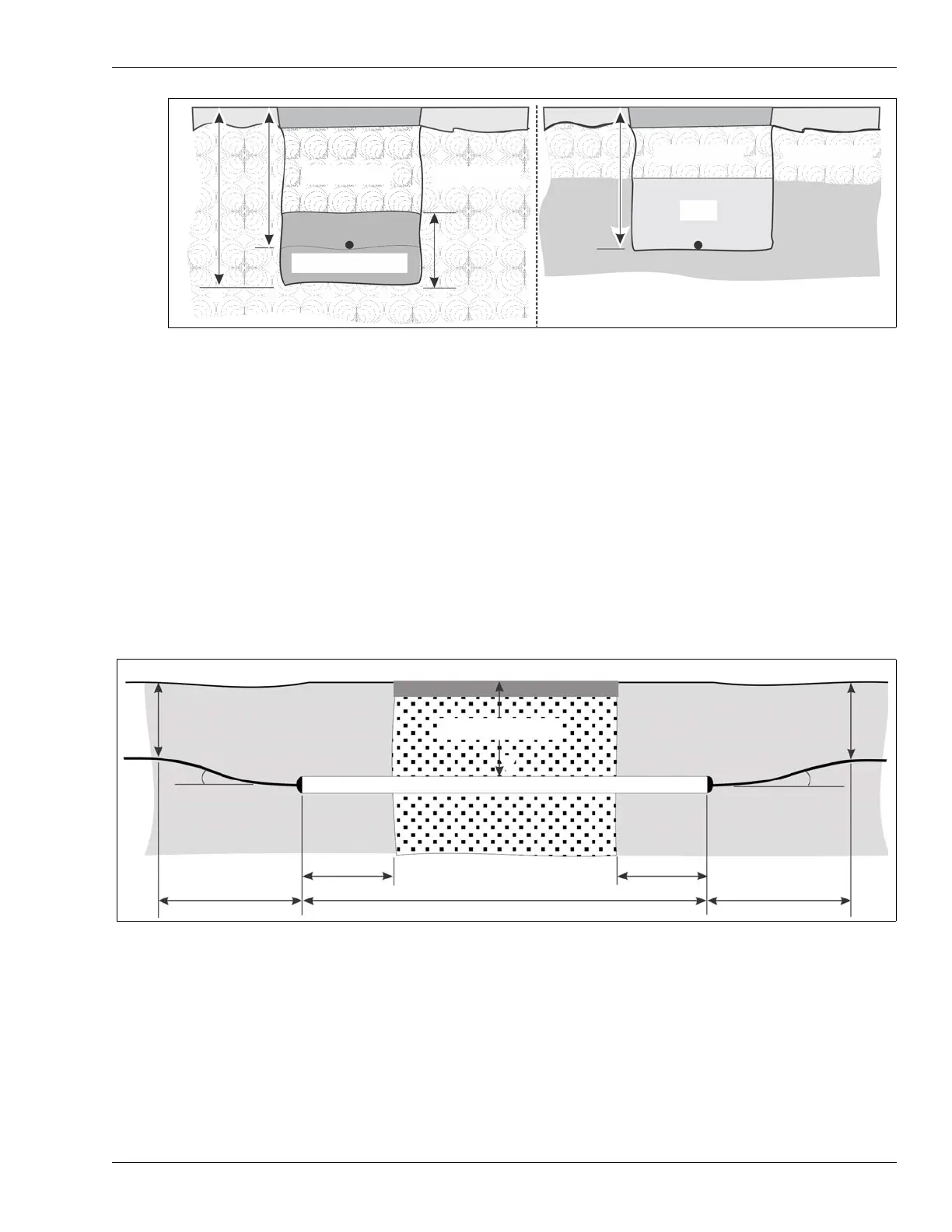
Micro-trenching or boring under a narrow paved strip
If the sensor cable route crosses a narrow section of asphalt or concrete such as a sidewalk or
driveway, Senstar recommends installing the sensor cables below the hard surface in a buried
section of PVC conduit. The conduit requires a 19 mm (3/4 in.) internal diameter and can be a
maximum 7 m (23 ft.) long. You can install the sensor cable under asphalt or non-reinforced
concrete either by micro-trenching, or using a boring technique to cut a path under the concrete.
Before micro-trenching, consider the structural integrity of the asphalt surface given the remaining
thickness after the trenches are dug and the load it must bear.
1. Bore a 2.5 cm (1 in.) hole 30 cm below the surface, through the soil under the hard surface
using pressurized water or compressed air.
2. Feed a PVC conduit through the hole.
3. Pull the sensor cable through the conduit.
4. Continue laying the cable in the trench.
Burial under a large asphalt paved surface
For a large paved asphalt surface, remove a 30 cm wide strip of the hard surface over the sensor
cable’s path, and then dig the trench. After cable installation, the asphalt surface is restored.
Figure 68: Trench dimensions under a thin strip of asphalt
Figure 69: Using conduit under paved surfaces
38 cm
(15 in.)
30 cm
(12 in.)
stone dust or sand
15 cm
(6 in.)
restored asphalt
30 cm
(12 in.)
restored asphalt
crushed stone
crushed stone
soil
crushed stone
crushed stone
soil
soil
soil
23 cm
(9 in.)
sensor cable
seal conduit
at both ends
30° slope (max.)
30° slope (max.)
23 cm (9 in.)
asphalt or concrete surface
0.3 to 1 m
7 m (23 ft.) maximum
30 cm (12 in.)
conduit
1 m (3.3 ft.)
1 m (3.3 ft.)
(1 to 3.3 ft.)
0.3 to 1 m
(1 to 3.3 ft.)

 Loading...
Loading...