Planning the cable path
Page 46 OmniTrax Product Guide
Mid-cable obstacles (cable bypasses)
If there is an obstacle in the cable path along the length of the active cable, you can splice in a
section of non-detecting cable to bypass the obstacle. PVC conduit should be used to protect the
non-detecting cables, if they pass through the obstacle. Some obstacles that may be encountered
include roadways, trees, fences, storage buildings, culverts, streams, ponds, etc.
If it is not possible to go through an obstacle, it may be possible to go around the obstacle. If you
go around the obstacle, be sure to follow the recommended separation distances from obstacles.
Otherwise, cut and terminate the cables 7 m away from the obstacle.
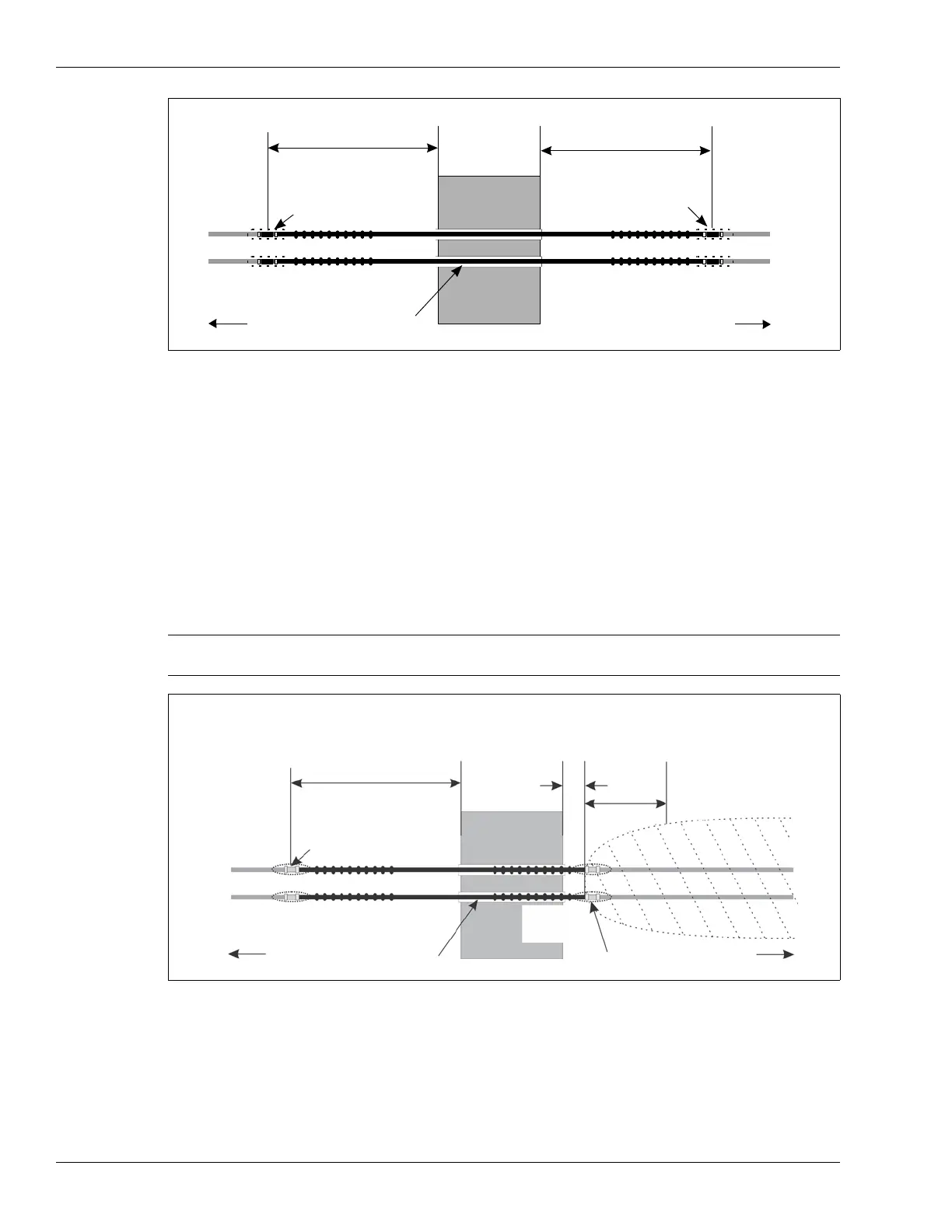
Figure 20: Obstacle bypass at the end of two OC2 cable sets
Note The full length of an OmniTrax cable bypass must be defined as a cable
segment and set to Zone 0 via the UCM software.
Figure 21: Mid-cable obstacle bypass (OC2 example)
7 m (23 ft.)
7 m (23 ft.)
required section of lead-out cable = 7 m + 7 m + width of obstacle (non-detecting cable shown in black)
decouplers indicate the
end of detecting cable
decouplers
ferrite beads
detecting cable
to
processor
obstacle
lead out
cable
conduit through obstacle
to
processor
detecting cable
7 m (23 ft.)
(12 in.)
4 m (13 ft.)
conduit through obstacle
bypass end
bypass start
detecting cable
non-detecting cable
ferrite
beads
to
processor
required section of non-detecting cable = 7 m + width of obstacle + 30 cm
required section of detecting cable removed = 7 m + width of obstacle + 30 cm
required software bypass = 7 m + width of obstacle + 30 cm + 4 m
30 cm
detection field
to build up to full
strength
requires 4 m (13 ft.)
to
decouplers
 Loading...
Loading...