Call routing
265
System functions and features as of R3.0
syd-0367/1.3 – R3.0 – 03.2013
6. 9 Testing overflow routing in the PISN
When a connection is setup the system checks the availability of the selected path.
If it is not available due to overloading or due to a defect, an attempt will be made
to set up the connection via an alternative route, depending on the configuration.
There are two types of overflow routing:
• Overflow routing within the private leased-line network:
Both the initial and the alternative connection path run via dedicated lines of
the private leased-line network.
• Overflow routing via the public network:
The initial connection path runs via dedicated lines of the private leased-line
network while the alternative connection path runs via the public network.
Transmission of the CLIP number depends on the CLIP settings. See also the over-
flow situations illustrated in the example onpage 98.
• Direct dialling plan 1 (relevant only if a suitable DD number is found)
• Call Distribution Element Not relevant to this case
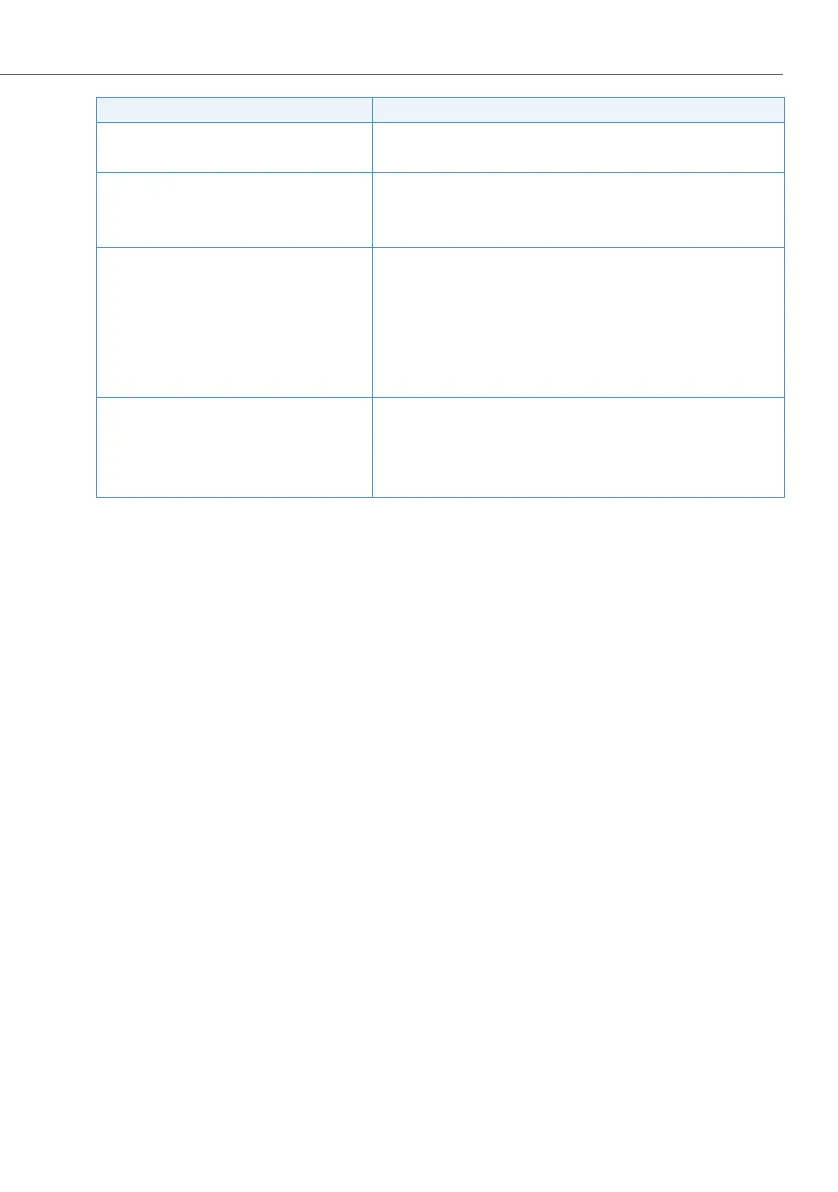
User configuration PISN-BN 330:
• Route 2 (route reference number)
• Number Phone number to be dialled without exchange access prefix
Route 2:
• Trunk group 2 2 (reference number of one or more trunk group(s))
• Digit barring Use or do not use digit barring
• Outgoing connections Number of connections allowed simultaneously
• Numbering plan identifier NPI PNP
• Type of number TON Unknown
Trunk group 2:
• Network interfaces Network interfaces of this trunk group
• Network type Private
• Protocol QSIG or QSIG / PSS1 ISO
Parameter Parameter value

 Loading...
Loading...