198 • SMP Gateway User Manual
Note: IRIG-B signals come in two flavors: demodulated and modulated. Demodulated
IRIG-B signals cannot be carried over long distances while the modulated IRIG-B
can be carried over distances larger than 350 meters (1000 feet) without
degrading.
NTP stands for Network Time Protocol, and is a standard Internet protocol used to synchronize
the clocks of computers to a time reference. NTP was originally developed by Professor David L.
Mills of the University of Delaware. As a full implementation of the NTP protocol seemed too
complicated for many systems, a simplified version of the protocol was defined: SNTP (Simple
Network Time Protocol). SNTP is basically NTP minus certain internal algorithms that are not
required by all types of servers.
21.3.2 Configuring the SMP 16 GPS Clock Option
The SMP 16 GPS Clock uses the time information provided by the GPS system to provide a
highly accurate time source for the substation.
Setting up the GPS clock option is explained in detail in the SMP 16 GPS Clock Option
installation guide, GUI-316-47 which is included on the SMP Gateway Software & Tools CD-
ROM.
Some software configuration is required, using SMP Config:
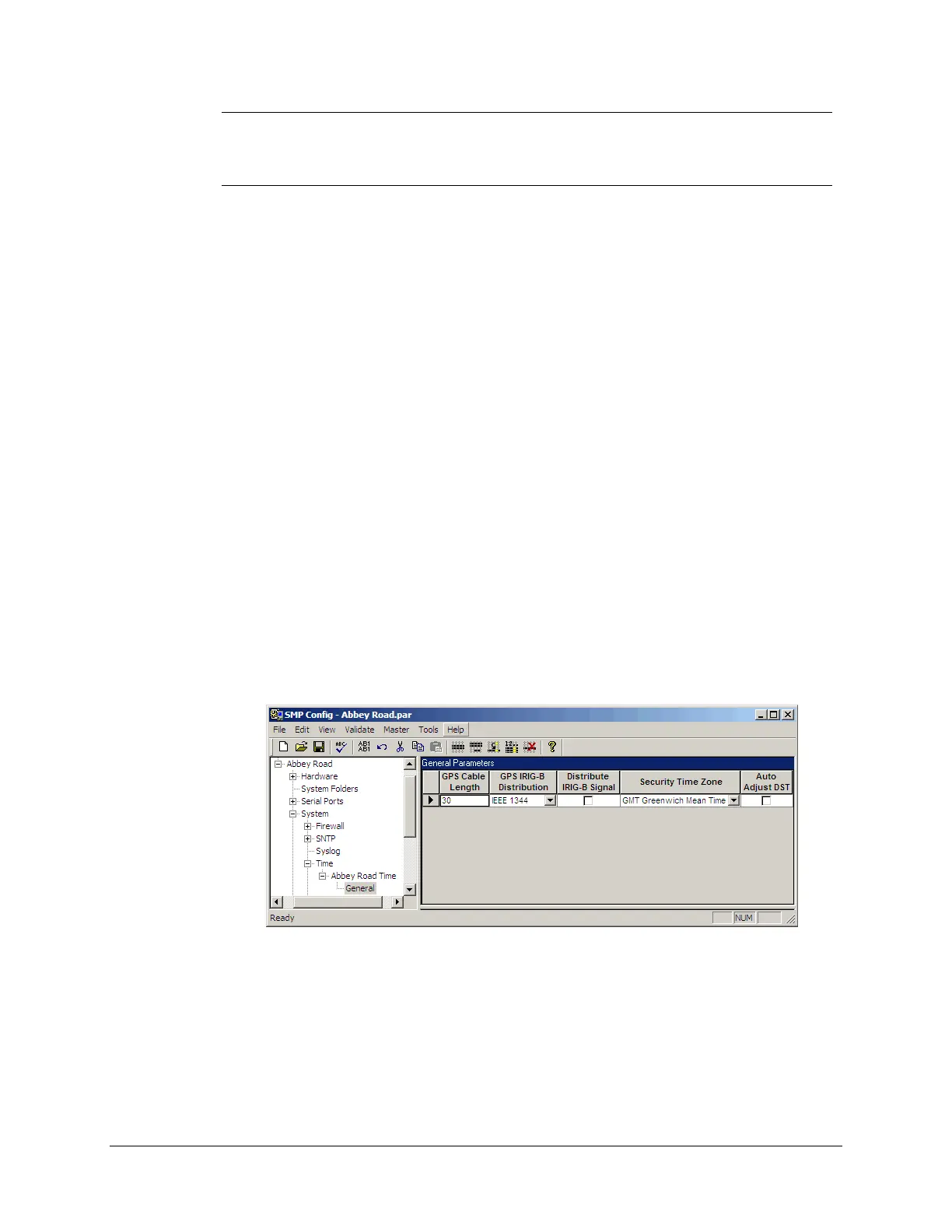
Under the System branch, select Time. If the Time instance has not been created yet, type a
name in the blank Name text box, and then click again the Time branch.
Under the Time instance branch, select the General branch.
Under GPS Cable Length, type the total length, in meters, of the cable that links the
SMP Gateway to the GPS antenna.
21.3.3 Using IRIG-B for Internal Clock’s Adjustment
If your SMP Gateway supports IRIG-B and is not equipped with a GPS clock, the preferred time
adjustment solution is to use an external IRIG-B time source.
Setting up IRIG-B is described in the installation guide of your SMP Gateway, which is included
on the SMP Gateway Software & Tools CD-ROM.

 Loading...
Loading...