A - 6
FORE Systems ES-2810 Ethernet Switch User’s Manual
Concepts in Switching
A.2 Flow Control
A.2.1 Flow Control Concept
The switch can become overloaded if incoming frames arrive faster than the switch can pro-
cess them, and this results in the frames being discarded until the overload condition passes.
The flow control mechanism overcomes this problem and eliminates the risk of lost frames.
If a potential overload situation occurs, the switch simply generates a “pseudo collision”
which forces all transmitting stations to immediately stop transmitting and wait a random
amount of time before trying to retransmit. Followi7ng a simulated collision, any buffered
frames are sent to their destination—clearing the switch’s buffers and allowing it to receive
future frames.
A.2.2 When to Use Flow Control
The flow control mechanism is ideal for situations where only one station is attached to one
switch port—do not use flow control on a port connected to a hub. However, consider the case
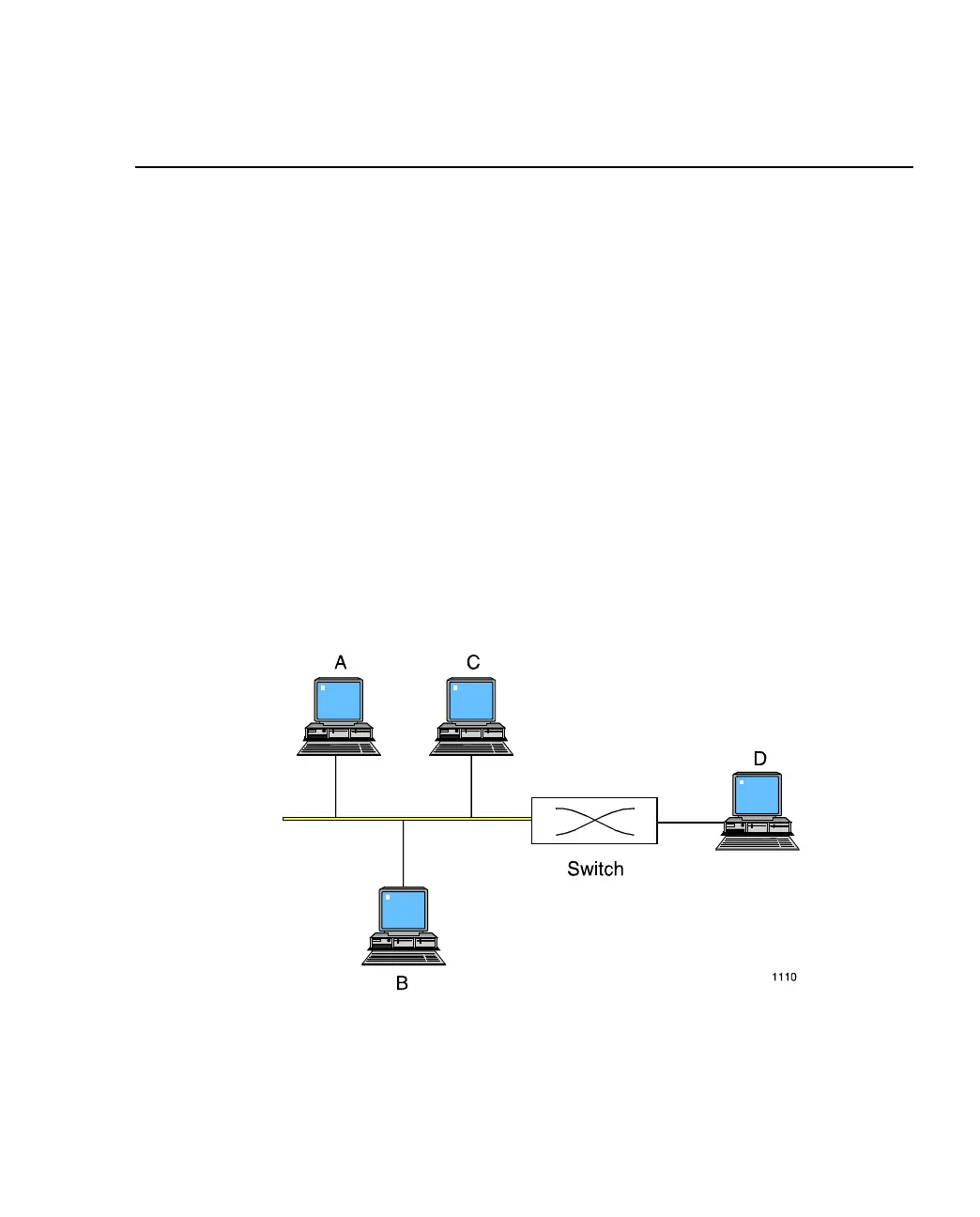
where there is more than one station attached to a port as shown below:
Figure A.1 -
Flow Control
 Loading...
Loading...