A - 8
FORE Systems ES-2810 Ethernet Switch User’s Manual
Concepts in Switching
A.3 Half- and Full-duplex
A.3.1 Half-duplex and Full-duplex Concepts
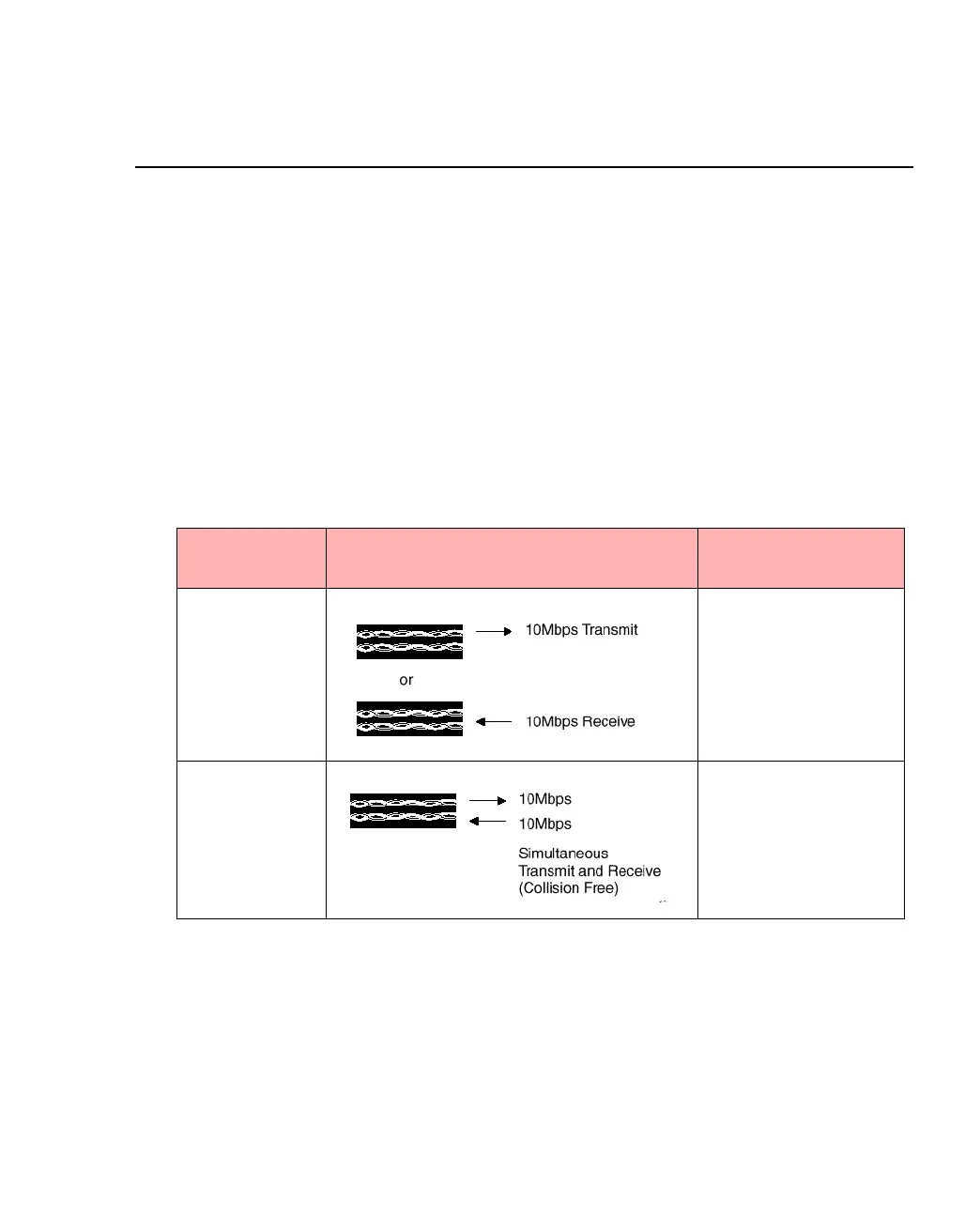
Half-duplex works optimally only if one device is transmitting and all the other devices are
receiving—otherwise, collisions occur. When the collisions are detected, the devices causing
the collision wait for a random time before retransmitting. This means that at half duplex,
Ethernet throughput is limited by the need to retransmit data when collisions occur. Half-
duplex is the most common transmission method and is adequate for normal workstation and
PC connections.
Full-duplex provides dual communication on a point-to-point connection and allows each
device to simultaneously transmit and receive on a connection. Full-duplex mode is typically
used to connect to other switches or to connect fast access devices such as workgroup servers.
Table A.3 -
Half-duplex and Full-duplex
Transmission
mode
Capacity
Half-duplex Less than 10Mbps
when communicating
Full-duplex 20 Mbps
 Loading...
Loading...