I/O Controller Hub 2
R
174 Intel
®
Pentium
®
4 Processor / Intel
®
850 Chipset Family Platform Design Guide
9.9.3.5 Critical Dimensions
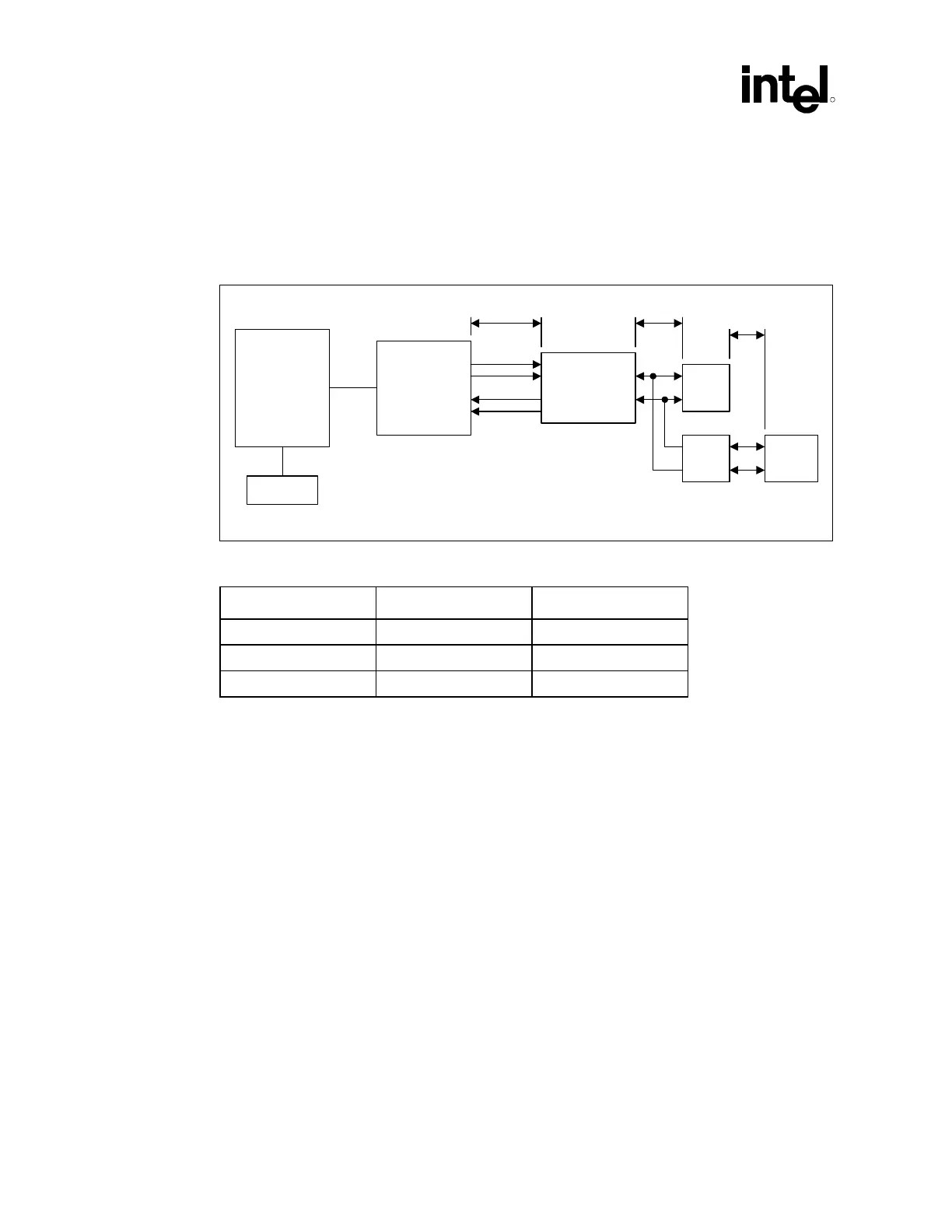
There are three dimensions to consider during layout. Distance ‘B’ from the line RJ11 connector
to the magnetics module, distance ‘C’ from the phone RJ11 to the LPF (if implemented), and
distance ‘A’ from 82562EH to the magnetics module (See Figure 124).
Figure 124. Critical Dimensions for Component Placement
LAN_crit_dim_comp_place
ICH2 82562EH
Magnetics
module
Line
RJ11
B
A
EEPROM
LPF
Phone
RJ11
C
Table 40. Critical Dimension Values
Distance Priority Guideline
B 1 < 1 inch
A 2 < 1 inch
C 3 < 1 inch
9.9.3.5.1 Distance from Magnetics Module to Line RJ11
This distance ‘B’ should be given highest priority and should be less then 1 inch. In regards to
trace symmetry, route differential pairs with consistent separation and with exactly the same
lengths and physical dimensions.
Asymmetrical and unequal length in the differential pairs contribute to common mode noise and
this can degrade the receive circuit performance and contribute to radiated emissions from the
transmit side.
9.9.3.5.2 Distance from Intel
®
82562EH to Magnetics Module
Due to the high-speed of signals present, distance ‘A’ between the 82562EH and the magnetics
should also be less than 1 inch, but should be second priority relative to distance form connects to
the magnetics module.
And in general, any section of trace that is intended for use with high-speed signals should observe
proper termination practices. Proper signal termination can reduce reflections caused by
impedance mismatches between device and traces route. The reflections of a signal may have a
high-frequency component that may contribute more EMI than the original signal itself.

 Loading...
Loading...











