8 Monitoring Respiration Rate (Resp)
162
Cardiac Overlay
Cardiac activity that affects the Resp waveform is called cardiac overlay. It happens when the Resp
electrodes pick up impedance changes caused by the rhythmic blood flow. Correct electrode
placement can help to reduce cardiac overlay: avoid the liver area and the ventricles of the heart in the
line between the respiratory electrodes. This is particularly important for neonates.
Lateral Chest Expansion
Some patients, especially neonates, expand their chests laterally. In these cases it is best to place the
two respiratory electrodes in the right midaxillary and left lateral chest areas at the patient's maximum
point of breathing movement to optimize the respiratory wave.
Abdominal Breathing
Some patients with restricted chest movement breathe mainly abdominally. In these cases, you may
need to place the left leg electrode on the left abdomen at the point of maximum abdominal expansion
to optimize the respiratory wave.
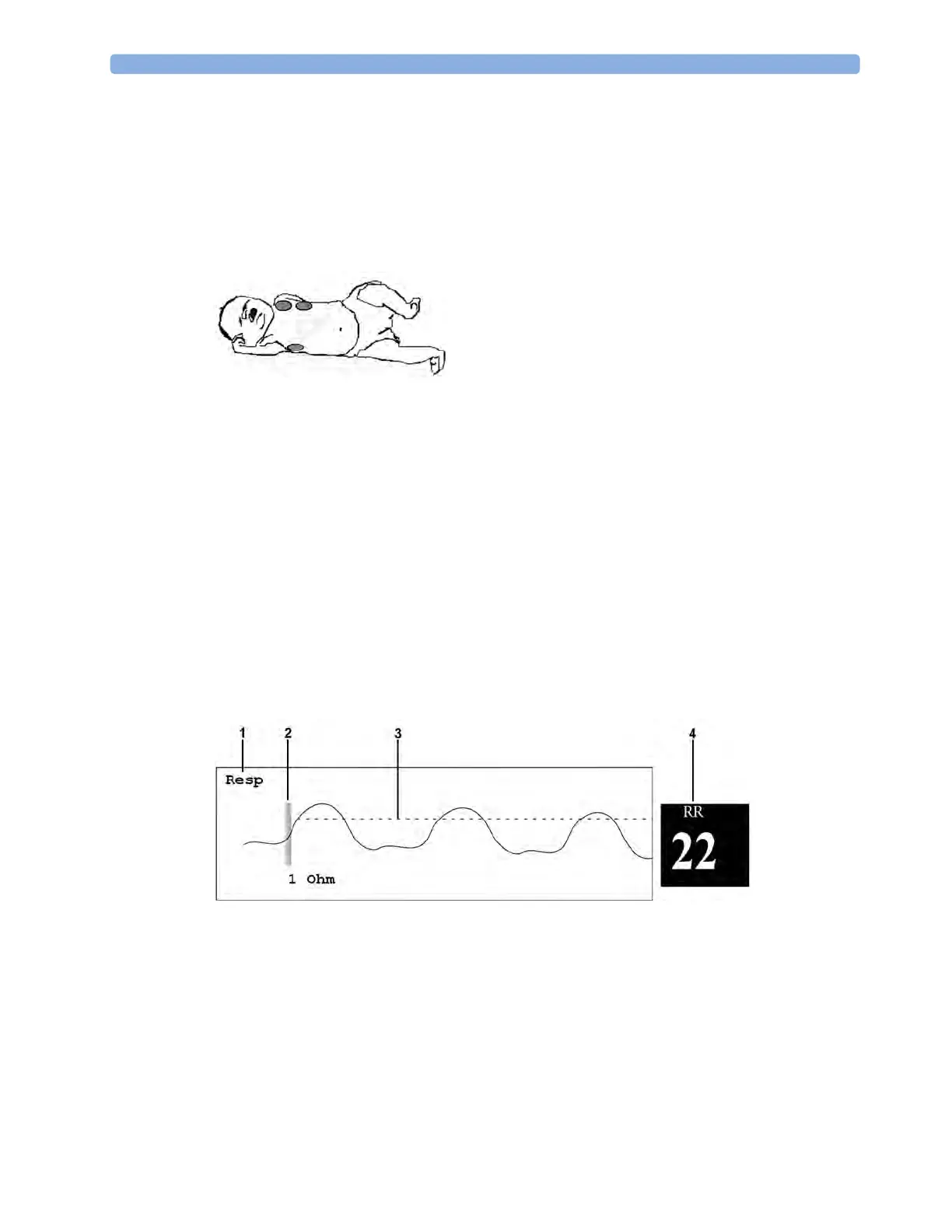
Understanding the Resp Display
The Resp measurement is displayed on the monitor as a continuous wave and a numeric respiration
rate. If the detected respiration rate is close to the heart rate, this is indicated by the text
HR = RR next
to the respiration wave if you are in manual monitoring mode. Your monitor screen may look slightly
different from the illustration.
1 Resp wave label
2 One Ohm calibration bar
3 Manually-set Resp detection level
4 Resp numeric and label

 Loading...
Loading...











