10 Monitoring SpO2
178
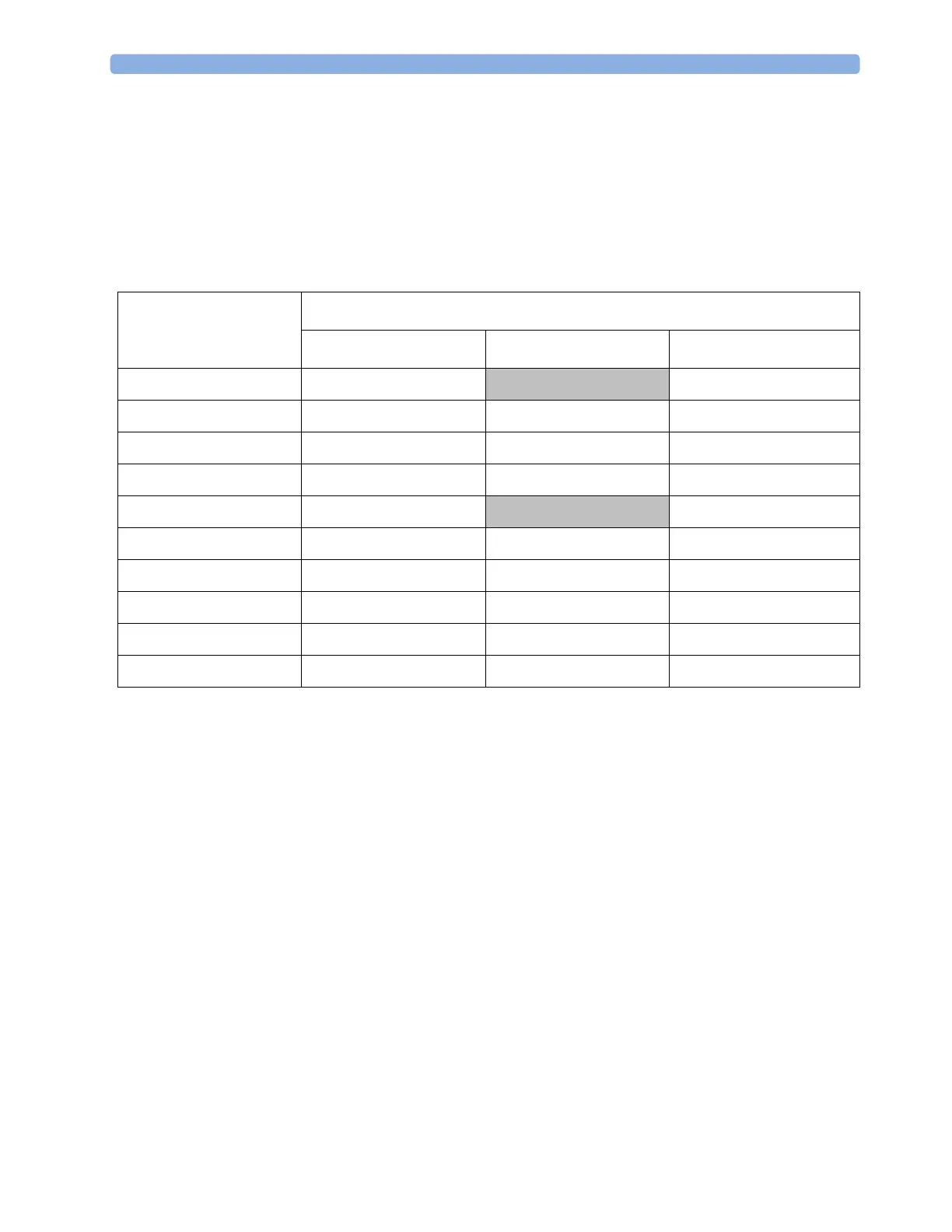
Clinical Example
You are monitoring a patient with a low SpO
2
limit of 90%. Then, while sleeping, your patient drops
to 89% for 20 seconds, and then recovers.
The Smart Alarm Delay would tolerate this limit violation up to 50 seconds (upper shaded cell in the
table) before issuing an SpO
2
low alarm. So in this case there would be no alarm notification.
If the SpO
2
drops further (e.g. to 85%), the tolerance time is much lower (10 seconds, see lower
shaded cell).
Table with Detailed Delays for Specific Limit Violations
In the clinical example above, the Medium delay mode has been selected. For less stable or more robust
patients, the tolerance time can be adjusted using
Short or Long mode.
Actual deviation from
violated alarm limit
Resulting alarm notification delay according to selected mode
Short Medium Long
1% 25 sec (maximum delay)
50 sec (maximum delay) 100 sec (maximum delay)
2% 12 sec 25 sec 50 sec
3% 10 sec (minimum delay) 16 sec 33 sec
4% 10 sec 12 sec 25 sec
5% 10 sec
10 sec (minimum delay) 20 sec
6% 10 sec 10 sec 16 sec
7% 10 sec 10 sec 14 sec
8% 10 sec 10 sec 12 sec
9% 10 sec 10 sec 11 sec
>9% 10 sec 10 sec 10 sec (minimum delay)
 Loading...
Loading...











