Common Analysis and Display Functions
R&S
®
FSVA3000/ R&S
®
FSV3000
487User Manual 1178.8520.02 ─ 01
The detector activated for the specific trace is indicated in the corresponding trace
information by an abbreviation.
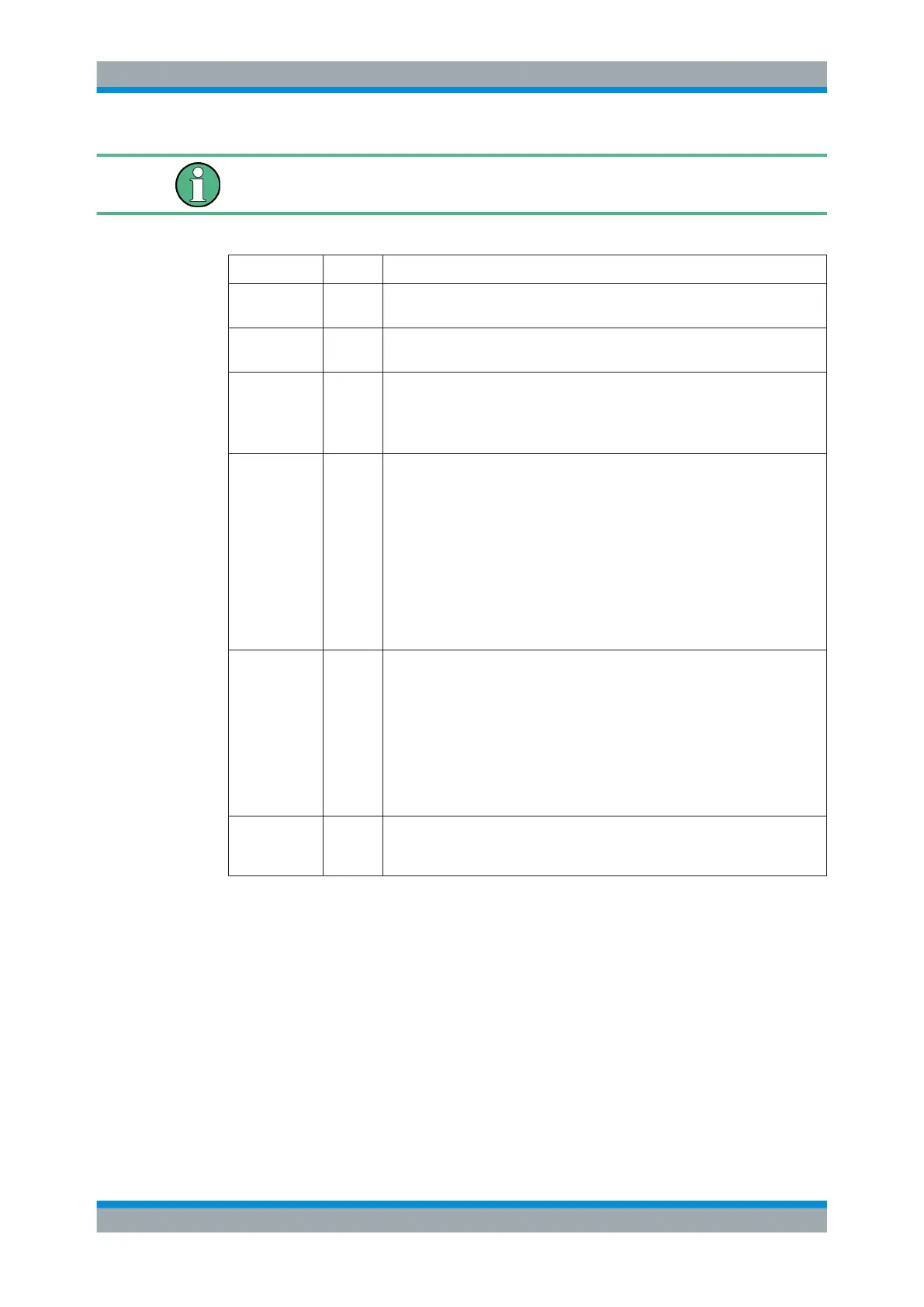
Table 9-3: Detector types
Detector Abbrev. Description
Positive Peak Pk Determines the largest of all positive peak values of the levels measured at the
individual frequencies which are displayed in one sample point
Negative Peak Mi Determines the smallest of all negative peak values of the levels measured at
the individual frequencies which are displayed in one sample point
Auto Peak Ap Combines the peak detectors; determines the maximum and the minimum
value of the levels measured at the individual frequencies which are displayed
in one sample point
(not available for SEM)
RMS Rm Calculates the root mean square of all samples contained in a sweep point.
To do so, R&S FSV/A uses the linear voltage after envelope detection. The
sampled linear values are squared, summed and the sum is divided by the
number of samples (= root mean square). For logarithmic display, the loga-
rithm is formed from the square sum. For linear display, the root mean square
value is displayed. Each sweep point thus corresponds to the power of the
measured values summed up in the sweep point.
The RMS detector supplies the power of the signal irrespective of the wave-
form (CW carrier, modulated carrier, white noise or impulsive signal). Correc-
tion factors as needed for other detectors to measure the power of the different
signal classes are not required.
Average Av Calculates the linear average of all samples contained in a sweep point.
To this effect, R&S FSV/A uses the linear voltage after envelope detection. The
sampled linear values are summed up and the sum is divided by the number of
samples (= linear average value). For logarithmic display, the logarithm is
formed from the average value. For linear display, the average value is dis-
played. Each sweep point thus corresponds to the average of the measured
values summed up in the sweep point.
The average detector supplies the average value of the signal irrespective of
the waveform (CW carrier, modulated carrier, white noise or impulsive signal).
Sample Sa Selects the last measured value of the levels measured at the individual fre-
quencies which are displayed in one sample point; all other measured values
for the frequency range are ignored
The result obtained from the selected detector for a sweep point is displayed as the
value at this frequency point in the trace.
Trace Configuration

 Loading...
Loading...