2.3
System Startup Using Self-Configuration
2-59
2.3 System Startup Using Self-Configuration
System startup time can be reduced by using self-configuration.
This section describes system startup using self-configuration, in the following three circumstances.
• Starting the system for first time
• Adding an electronic device (e.g., SERVOPACK or Distributed I/O Module)
• Replacing electronic devices
2.3.1 Starting the System for First Time
Use the following procedure to startup a new system.
1.
Wire and Connect Electronic Devices.
Correctly wire and connect all electronic devices to be used.
2.
Make Switch Settings for MECHATROLINK Slaves.
Set the MECHATROLINK communication specifications using the DIP switch and the station
address on the rotary switch on each MECHATROLINK slaves.
Example SERVOPACK Settings (SGDS-
1
)
Refer to each slaves manual for information on the setting details.
3.
Start Up MECHATROLINK Slaves.
Turn ON the power to the MECHATROLINK slaves and check that the electronic devices start
up normally.
If using a new Absolute Encoder, the Absolute Encoder will need to be initialized. Refer to
9.2.2 Initializing the Absolute Encoder on page 9-6 for details.
The servo adjustment can be performed either in this step or after the self-configuration.
4.
Set the Switches on MP2300/Optional Module
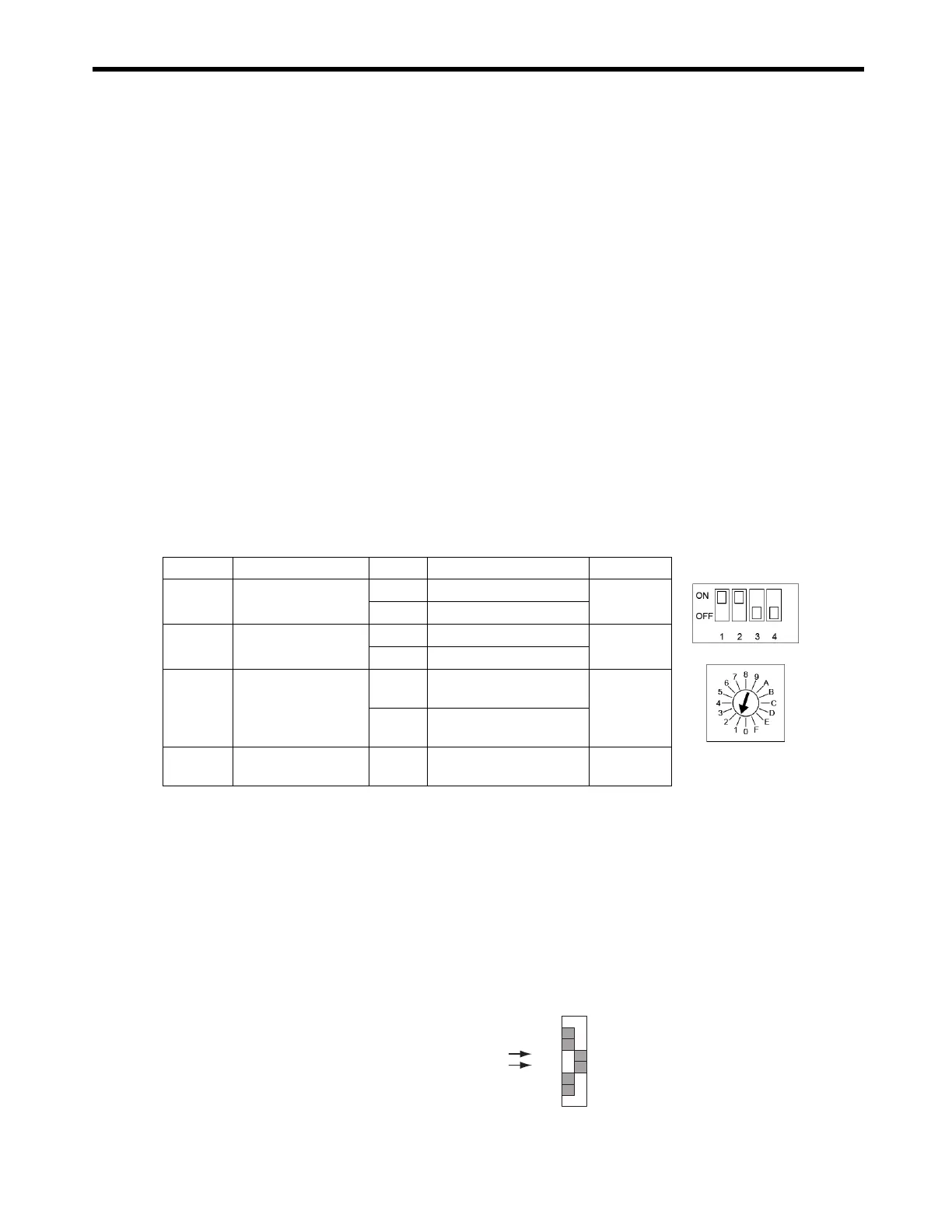
Set the switches of SW1 on MP2300 as shown below.
Make switch settings for communication and station address on each Optional Module
mounted on the MP2300 as required.
SW1 Name Setting Contents Default
Bit 1 Baud rate
OFF 4 Mbps
ON
ON 10 Mbps
Bit 2
No. of transmission
bytes
OFF 17
ON
ON 32
Bit 3 Station address
OFF
Station address =
40H+SW1
OFF
ON
Station address =
50H+SW1
Bit 4
Reserved (Reserved by
the system.)
OFF
-
OFF
SW2 (default setting)
SW1 (default setting)
SW1
OFF
STOP
SUP
INIT
CNFG
MON
TEST
ON

 Loading...
Loading...