9.1
Absolute Position Detection Function
9-3
9.1.2 Reading Absolute Data
Turn ON the MP2300 and the SERVOPACK at the same time or turn ON the SERVOPACK first to
read the absolute data loaded from the absolute encoder to the MP2300.
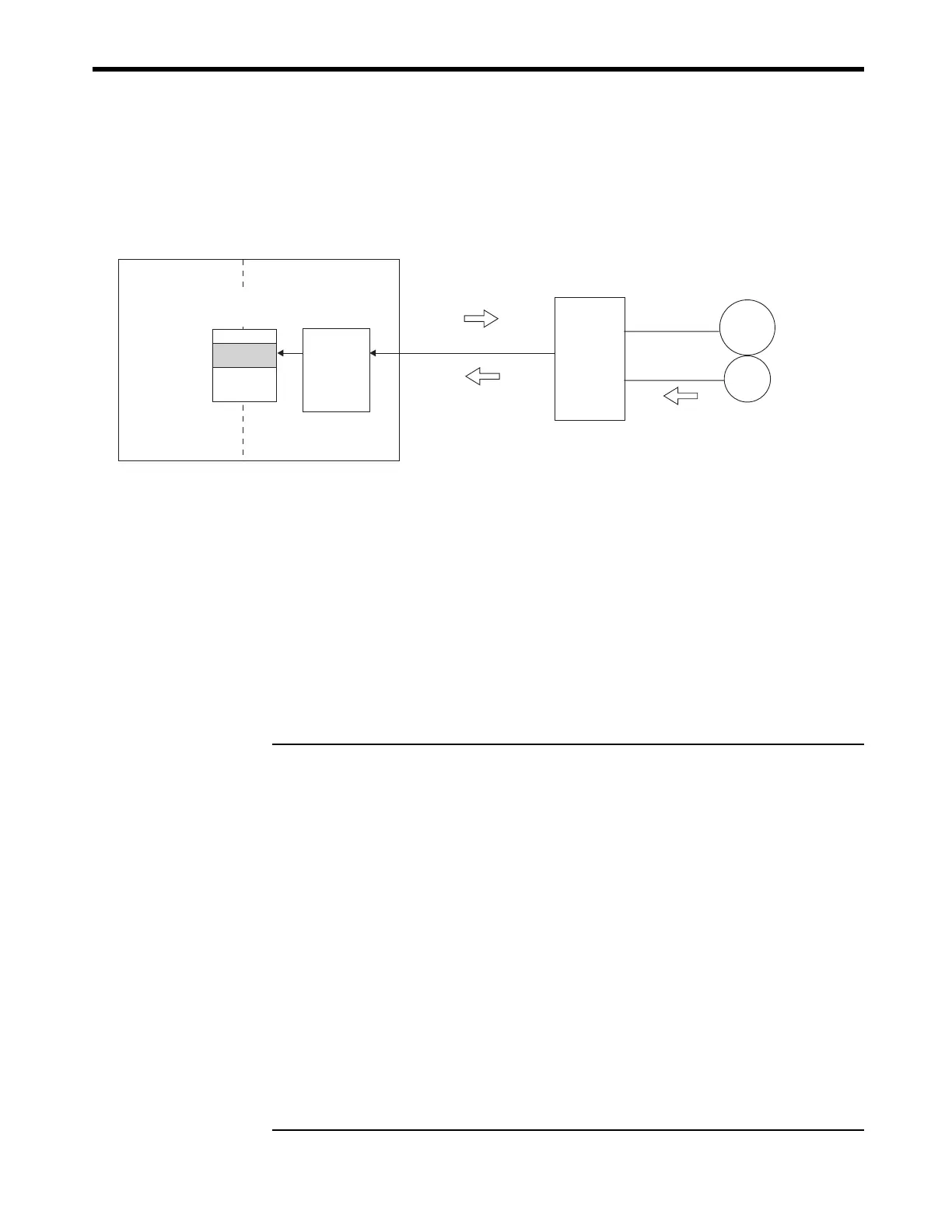
The following diagram shows an overview of the absolute data read operation.
* 1. The execution order of process
①
and
②
may be reserved depending on the
power-ON procedure.
* 2. Refer to 9.3.2 ( 1 ) Calculating the Zero Point of the Machine Coordinate System on page
9-10 for details on how the MP2300 calculates the machine coordinate system.
This way the absolute machine position can be detected and automatic operation can begin
immediately after power is turned ON with an automatic position detection system.
Terminology: Absolute Data
Absolute data that is stored in an absolute encoder has two types of data: the absolute reference position
(initial incremental pulses; PO) and the number of rotations (multi-turn data; N) from the absolute
reference position
The absolute reference position is the phase-C position when the absolute encoder is initialized and is
the reference position for absolute-position detection.
Only the number of rotations (N) can be cleared when the absolute encoder is initialized, and the initial
incremental pulses will not change.
Information: Calculation of Absolute Position
We can determine the absolute position P using the following data.
Data stored in an absolute encoder
• Absolute reference position (initial incremental pulses): PO
• Number of rotations from the absolute reference position (multi-turn data): N
Parameter determined according to the number of bits of servomotor
• Feedback pulses per motor rotation: RP
Equation to calculate the absolute position
• Absolute position (P) = N
×
RP + PO
(1)
*1
The MP2300 sends request to the SERVOPACK for absolute data after MECHATROLINK communications are established.
(2)
*1
The SERVOPACK gets multi-turn data (N) and the initial incremental pulses (PO) from the encoder.
(3) The SERVOPACK sends the multi-turn data (N) and initial incremental pulses (PO) to the MP2300.
(4) The MP2300 calculates the absolute position from the multi-turn data (N) and initial incremental pulses (PO) and then calcu-
lates the electronic gear. The MP2300 then adds the data of Zero Point Offset (OL
48) to the calculation results to auto-
matically set the machine coordinate system
*2
.
Position
monitoring
(IL0E to
IL16)
Motion monitoring
parameters
(4)
Electronic gear
calculation
Machine
coordinate
system
calculation
MP2300
SERVOPACK
MECHATROLINK
Servomotor
Encoder
(3)Send absolute data (N, PO)
(2)
Send absolute data (N, PO)
(1)Request absolute data
㧨Motion Section㧪

 Loading...
Loading...