5
Outline of Motion Control Systems
5.3.2
Data Types and Register Specifications
5-24
5.3.2 Data Types and Register Specifications
There are five kinds of data: Bit, integer, double-length integer, real number, and address data. Each
is used differently depending on the application. Address data, however, is used only inside functions
when specifying pointers. The following table shows the types of data.
Type Data types Numeric Value Range Remarks
B Bit
0
,
1
Used by relay circuits.
W Integer
−
32768 to +32767
(8000H)
(7FFFH)
Used for numeric value operations. The values in
parentheses ( ) indicate use with logical operations.
L
Double-length
integer
−
2147483648 to +2147483647
(80000000H)
(7FFFFFFFH)
Used for numeric value operations. The values in
parentheses ( ) are for use with logical operations.
F Real number
±
(1.175E-38 to 3.402E+38), 0
Used for numeric value operations.
A Address 0 to 32767 Used only when specifying pointers.
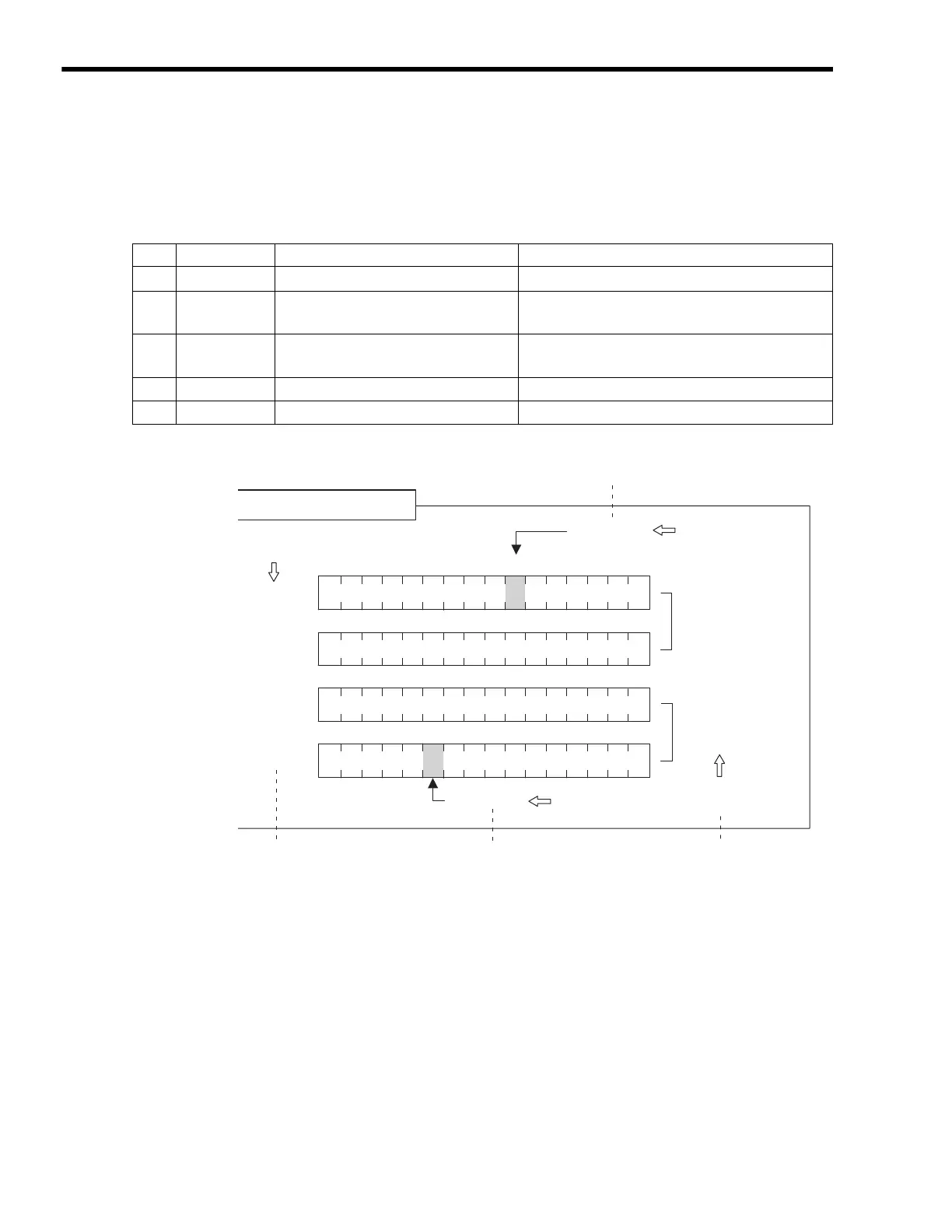
0123456789ABCDEF
[ MW00101 ]
[ MW00102 ]
[ MW00103 ]
[ MW00100 ]
[ MB001006 ]
[ MF00102 ]
[ ML00102 ]
[ MF00100 ]
[ ML00100 ]
[ MB00103A ]
ta Types and Register
ecifications
A digit to indicate the bit (A) is added to
the register number (00103).
The words for the given register nu
(00102) and the next number (001
included. Therefore, every second
is used.
Bit type
Bit type
Double-length and real
number type
Integer type
Each register number
is one word.
A digit to indicate the bit (6) is added to
the register number (00100).

 Loading...
Loading...