User's Manual 464 Document #: LTRT-10466
Mediant 500L MSBR
The table below shows an example of designating ERLs to physical areas (floors) in a
building and associating each ERL with a unique ELIN.
Table 29-4: Designating ERLs and Assigning to ELINs
ERL Number Physical Area IP Address ELIN
1 Floor 1 10.13.124.xxx 503 972-4410
2 Floor 2 10.15.xxx.xxx 503 972-4411
3 Floor 3 10.18.xxx.xxx 503 972-4412
In the table above, a unique IP subnet is associated per ERL. This is useful if you
implement different subnets between floors. Therefore, IP phones, for example, on a
specific floor are in the same subnet and therefore, use the same ELIN when dialing 9-1-1.
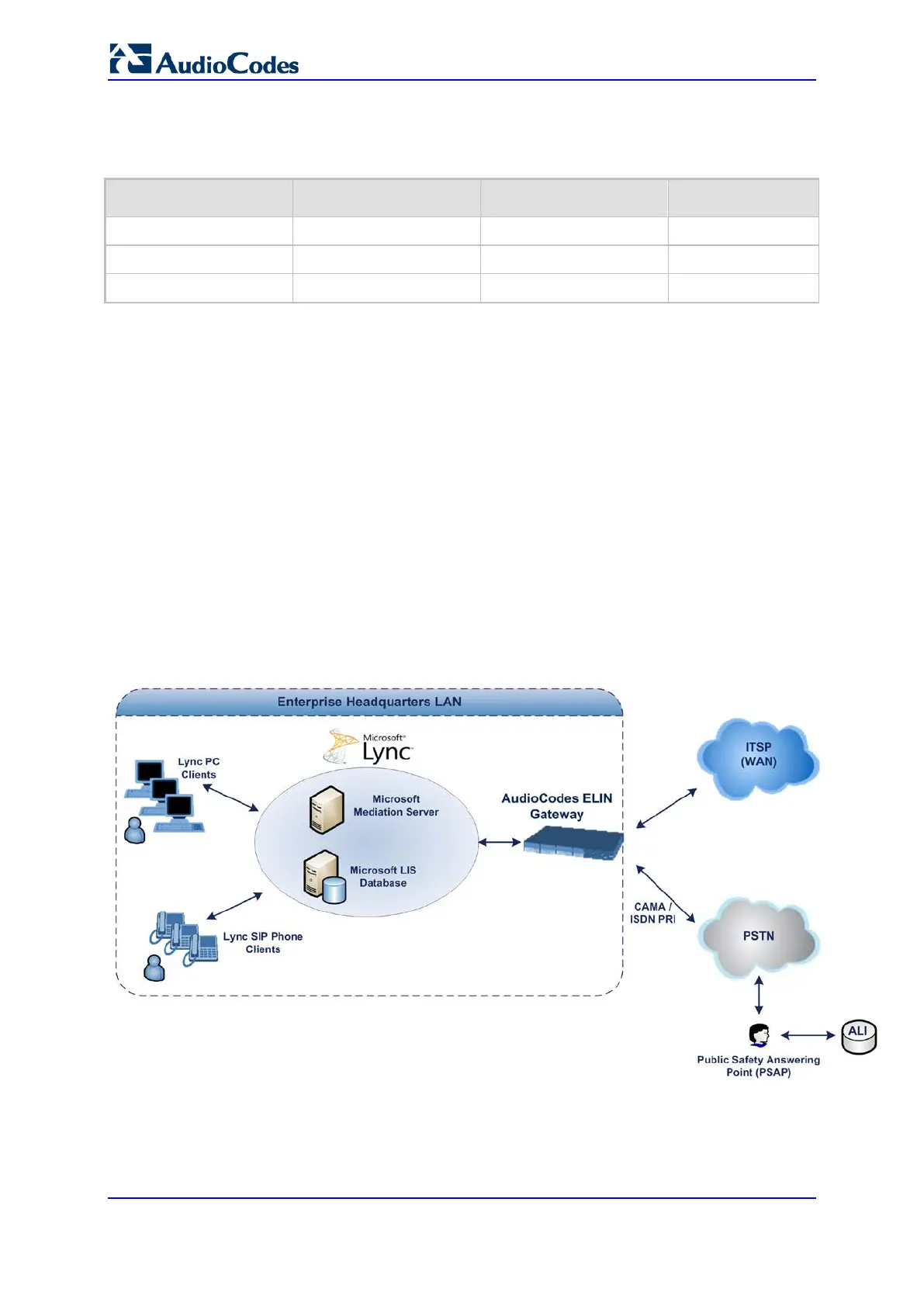
29.11.4.3 AudioCodes ELIN Gateway for Lync Server 2010 E9-1-1 Calls to
PSTN
The Microsoft Mediation Server sends the location information of the E9-1-1 caller in the
XML-based PIDF-LO body contained in the SIP INVITE message. However, this content
cannot be sent on the PSTN network using ISDN PRI due to protocol limitations. To solve
this issue, Lync Server 2010 requires a PSTN Gateway (ELIN Gateway) to send the E9-1-1
call to the PSTN. When Lync Server 2010 sends the PIDF-LO to the PSTN Gateway, it
parses the content and translates the calling number to an appropriate ELIN. This ensures
that the call is routed to an appropriate PSAP, based on ELIN-address match lookup in the
Emergency Services provider's ALI database.
The figure below illustrates an AudioCodes ELIN Gateway deployed in the Lync Server
2010 environment for handling E9-1-1 calls between the Enterprise and the PSTN.
Figure 29-8: AudioCodes ELIN Gateway for E9-1-1 in Lync Server 2010 Environment

 Loading...
Loading...



