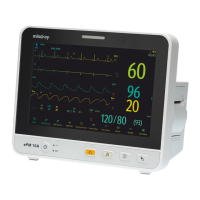
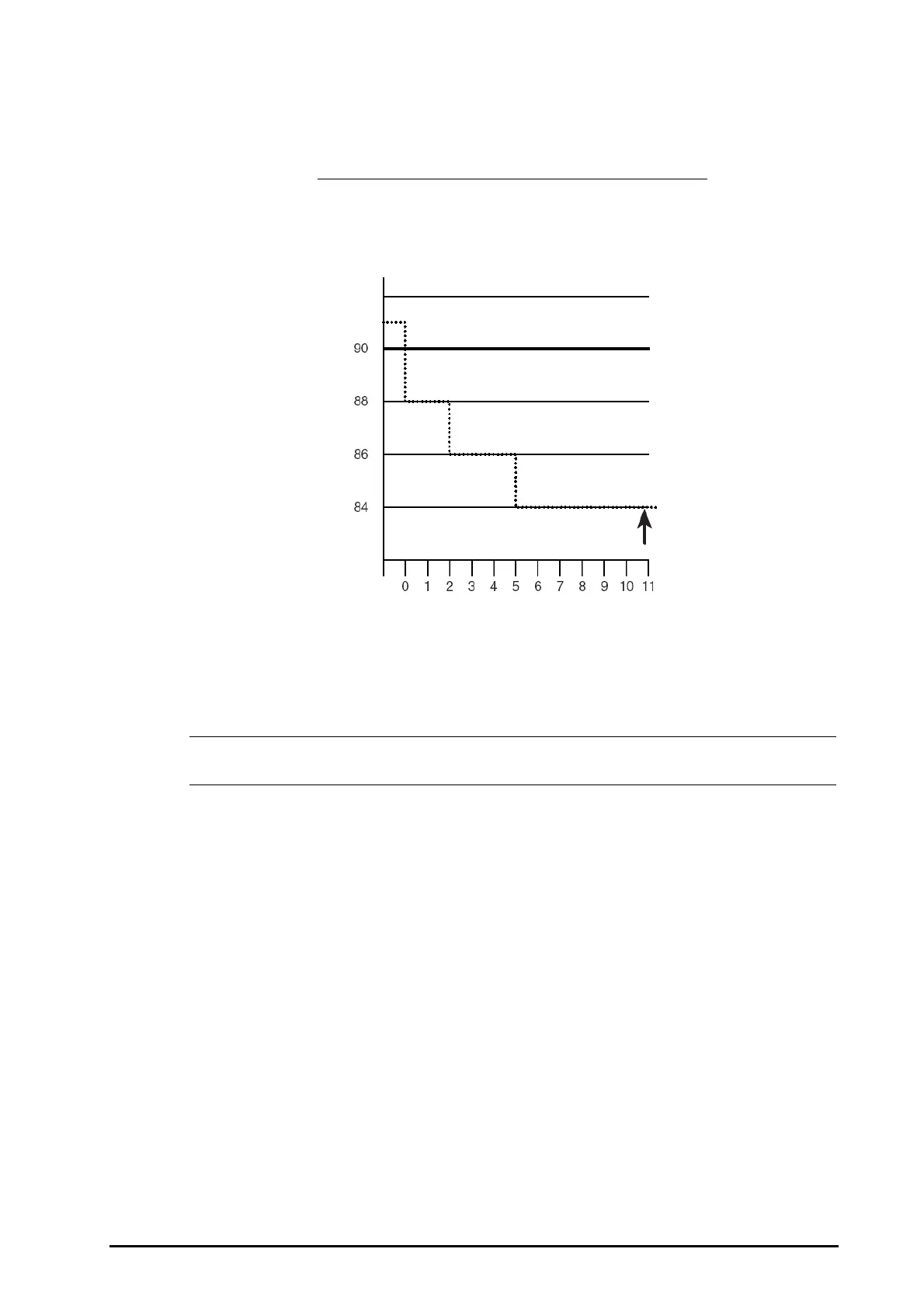
13 - 5
After approximately 10.9 seconds, a Sat-Second alarm would sound, because the limit of 50 Sat-Seconds would
have been exceeded.
Saturation levels may fluctuate rather than remaining steady for a period of several seconds. Often, the patient
SpO
2
may fluctuate above and below an alarm limit, re-entering the non-alarm range several times. During such
fluctuation, the monitor integrates the number of SpO
2
points, both positive and negative, until either the Sat-
Seconds limit is reached, or the patient SpO
2
re-enters the non-alarm range and remains there.
• The SpO
2
Too Low or SpO
2
Too High alarm is presented in the case that SpO
2
value violates the alarm
limits for 3 times within one minute even if the setting of Sat-Seconds is not reached.
13.6.3 Setting the Nellcor SpO
2
Sat-Seconds
To set the Sat-Seconds, follow this procedure:
1. Select the SpO
2
numeric area or waveform area to enter the SpO2 menu.
2. Select the Alarm tab.
3. Set Sat-Seconds.
13.6.4 Setting SpO
2
Sensitivity (for Masimo SpO
2
)
For Masimo SpO
2
, selects the Sensitivity as per signal quality and patient motion.
Normal sensitivity is the recommended for patients who are experiencing some compromise in blood flow or
perfusion. It is advisable for care areas where patients are observed frequently, such as the intensive care unit
(ICU).
Adaptive Probe Off Detection (APOD) sensitivity is the recommended sensitivity mode where there is a high
probability of the sensor becoming detached. It is also the suggested mode for care areas where patients are not
visually monitored continuously. This mode delivers enhanced protection against erroneous pulse rate and
arterial oxygen saturation readings when a sensor becomes inadvertently detached from a patient due to
excessive movement.
% SpO
2
Seconds Sat-Seconds
2× 2= 4
4× 3= 12
6× 6= 36
Total Sat-Seconds= 52

 Loading...
Loading...