Operation
Theory of Operation
MagneMover LITE User Manual 327
Rockwell Automation Publication MMI-UM002F-EN-P - October 2022
Power-Related Faults
Fluctuations in the voltage that is seen at the motor power terminals are due to voltage drops
when the MM LITE motors consume power while moving vehicles. These fluctuations can
lead to the motor issuing faults and can cause motor shutdown as shown in Table 6-1.
Propulsion Power Not Ready Fault
On initial power-up, when the internal propulsion bus in the motor is below +32V DC, the
motor reports a propulsion power not ready fault to the HLC. The HLC reports this fault to the
host controller as a propulsion power not ready fault (see either the Host Controller TCP/IP
Communication Protocol User Manual, MMI-UM003, or the Host Controller EtherNet/IP
Communication Protocol User Manual, MMI-UM004) and the motor does not allow vehicle
motion to occur. Once +32V DC is reached, the motor supports vehicle motion and the pro-
pulsion power fault message self-clears.
If the internal propulsion bus voltage drops below +27V DC during operation, the motor
reports a propulsion power not ready fault through the HLC to the host controller. When this
fault is reported, all inverters within the motor are disabled, and any vehicles in motion over
the motor are no longer under active control and as such their motion is undefined. Normal
operation resumes once the internal propulsion bus rises back up to +32V DC.
Undervoltage Fault
On initial power-up, when the internal propulsion bus in the motor is below +27V DC, the
motor reports an undervoltage fault to the HLC. Once this fault clears, it only reappears if the
internal propulsion bus voltage drops below +27V DC. The HLC reports this fault to the host
controller as an undervoltage fault (see either the Host Controller TCP/IP Communication
Protocol User Manual, MMI-UM003, or the Host Controller EtherNet/IP Communication
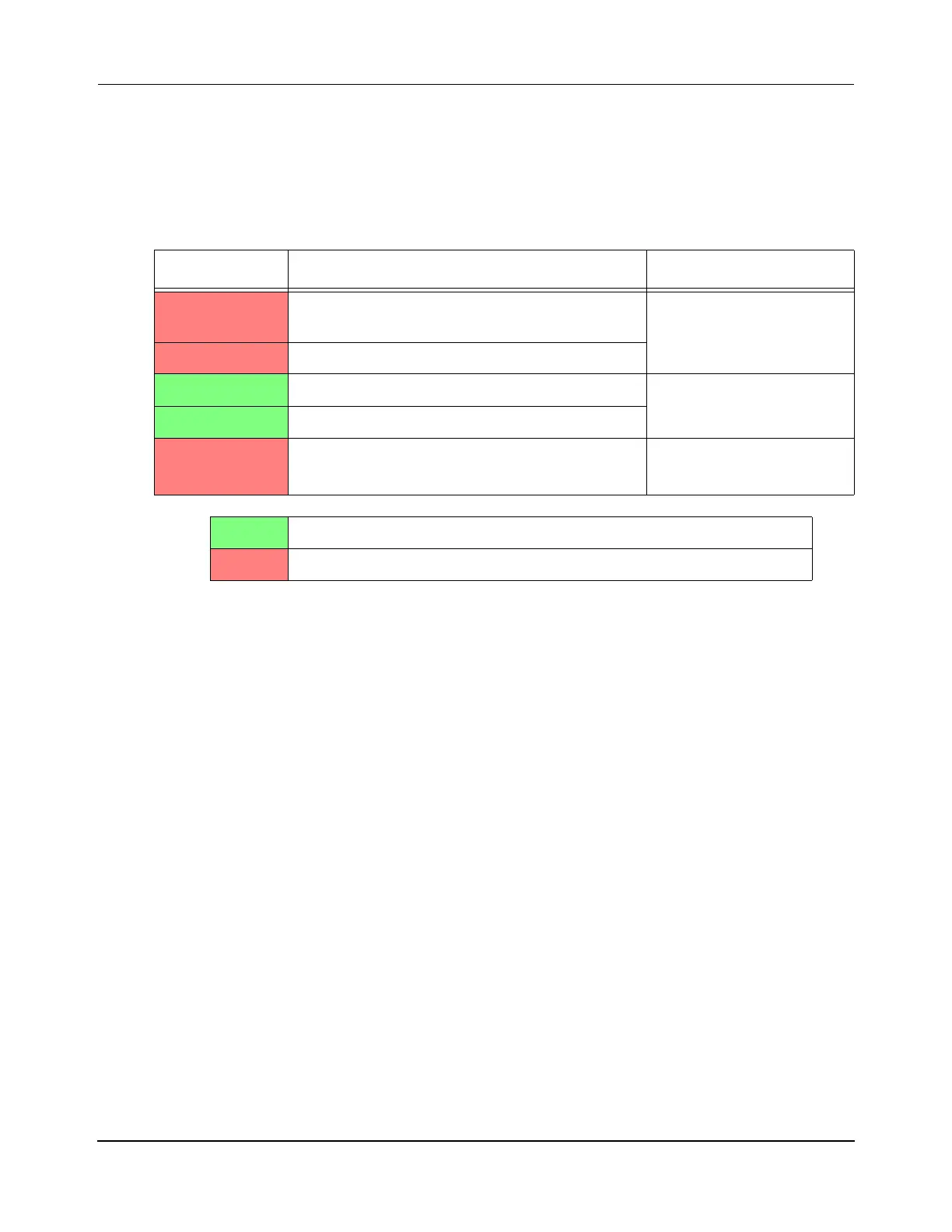
Table 6-1: Propulsion Voltage Range
Voltage (VDC) Event Status
27 Propulsion Power Not Ready fault triggered (Soft
Start not enabled).
Voltage too low.
Motor operation suspended.
27 Undervoltage fault triggered.
28 Minimum recommended operating voltage.
Operating Range.
38 Maximum recommended operating voltage.
42 Overvoltage fault triggered.
Voltage too high.
Motor operation suspended.
Motor in normal operating condition.
Motor in fault condition – does not control vehicles (motion is undefined).

 Loading...
Loading...