RTC
®
5 PC Interface Board
Rev. 1.9 e
7 Basic Functions for Scan Head and Laser Control
94
Mark Commands
The RTC
®
5 automatically turns on the “laser active”
laser control signals at the beginning of a mark
command. During a mark command (mark_abs or
mark_rel
(1)
), the laser focus moves along the spec-
ified vector with a constant marking speed,
producing a straight mark on the workpiece.
If another mark (or arc) command follows immedi-
ately afterward, the RTC
®
5 leaves the “laser active”
laser control signals on. Therefore, a sequence of
individual mark (and arc) commands creates a
continuous marking (polyline mark). Turn-off of the
“laser active” laser control signals occurs at the
beginning of the jump (or generally: non-mark/non-
arc) command that follows the final mark (or arc)
command of a polygonal traversal (also see
"Edgelevel", page 104).
The commands set_mark_speed and
set_mark_speed_ctrl (see page 448) define the
marking speed. The marking speed can be changed
anywhere in a list or via the corresponding control
command if no list is currently being processed.
Arc Commands
The arc commands arc_abs and arc_rel can be used
for marking circular arcs
(2)
. These commands require
parameters for the X and Y coordinates of the arc
center and the arc angle. The circular arc starts at the
current output position, with angles counted posi-
tively and clockwise (in contrast to mathematical
convention).
At the beginning of an arc command, the RTC
®
5 also
automatically turns on the “laser active” laser control
signals. During an arc command, the laser focus
moves with the defined marking speed along the
specified arc. The “laser active” laser control signals
are turned off at the beginning of the subsequent
jump (or generally: non-mark, non-arc or non-ellipse)
command, provided no further arc commands (or a
series of arc, mark or ellipse commands) follow.
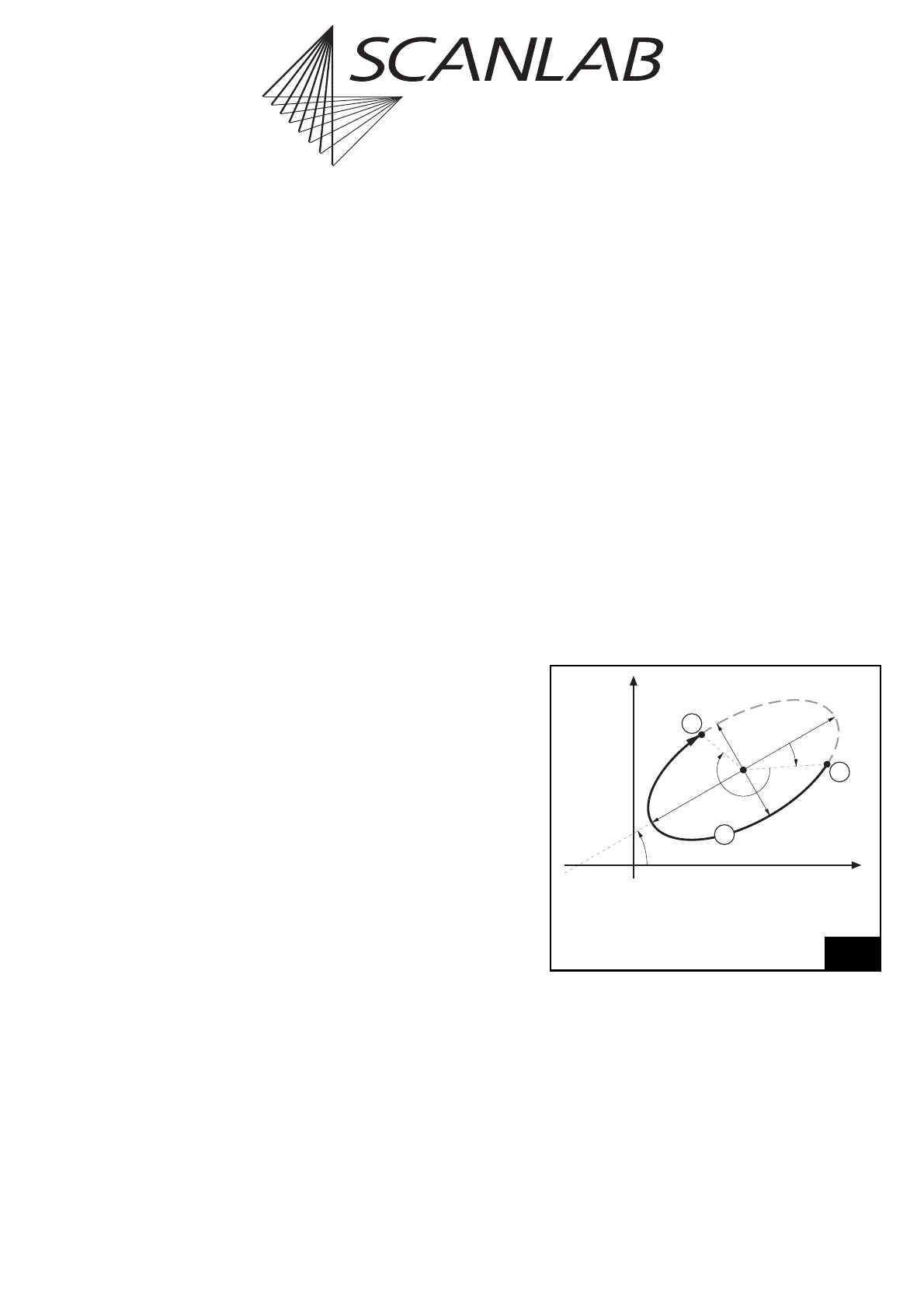
Ellipse Commands
The RTC
®
5 software driver also provides commands
for marking elliptical arcs. Here (unlike marking of
vectors or circular arcs), you’ll generally need two
commands per arc: set_ellipse and the arc command
mark_ellipse_abs or mark_ellipse_rel
(3)
.
The set_ellipse command is used for specifying the
arc’s shape in the following manner (see figure 28):
•Lengths
a
and
b
of the ellipse’s half-axes
• The beginning phase angle
Phi0
(and thereby the
arc starting point’s position relative to the end
point of half-axis
a
)
• The arc angle
Phi
(and thereby the length of the
to-be-marked ellipse section)
The arc commands mark_ellipse_abs or
mark_ellipse_rel specify the to-be-executed arc’s
position and orientation in the following manner
(siehe figure 28):
• The coordinates
(X,Y)
of the ellipse’s midpoint
•The angle
Alpha
between the ellipse’s half-axis
a
and the X axis.
Notes
•Via
a
, you can specify either the short or long half-
axis (then use
b
for the other axis).
Phi0
,
Phi
and
Alpha
are always relative to axis
a
.
•
Phi0
and
Phi
are counted positively clockwise (in
contrast to mathematical convention). In
contrast,
Alpha
is counterclockwise (in accor-
dance with mathematical convention).
(1) For using abs and rel commands see “AbsCalls” page 77.
Additionally, the RTC
®
5 provides timed vector commands (see
page 198), para vector commands (see page 147) and – if the
3D option is enabled – 3D vector commands (see page 172).
(2) For using abs and rel commands see “AbsCalls” page 77.
Additionally, the RTC
®
5 provides timed arc commands (see
page 198). (3) For using abs and rel commands see “AbsCalls” page 77.
28
Marking ellipse-shaped arcs
Legend
1 Starting point
2 Marked arc
3 End point

 Loading...
Loading...