1-2
DHCP Address Allocation
Allocation Mechanisms
DHCP supports three mechanisms for IP address allocation.
z Manual allocation: The network administrator assigns an IP address to a client like a WWW server,
and DHCP conveys the assigned address to the client.
z Automatic allocation: DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a client.
z Dynamic allocation: DHCP assigns an IP address to a client for a limited period of time, which is
called a lease. Most DHCP clients obtain their addresses in this way.
Dynamic IP Address Allocation Process
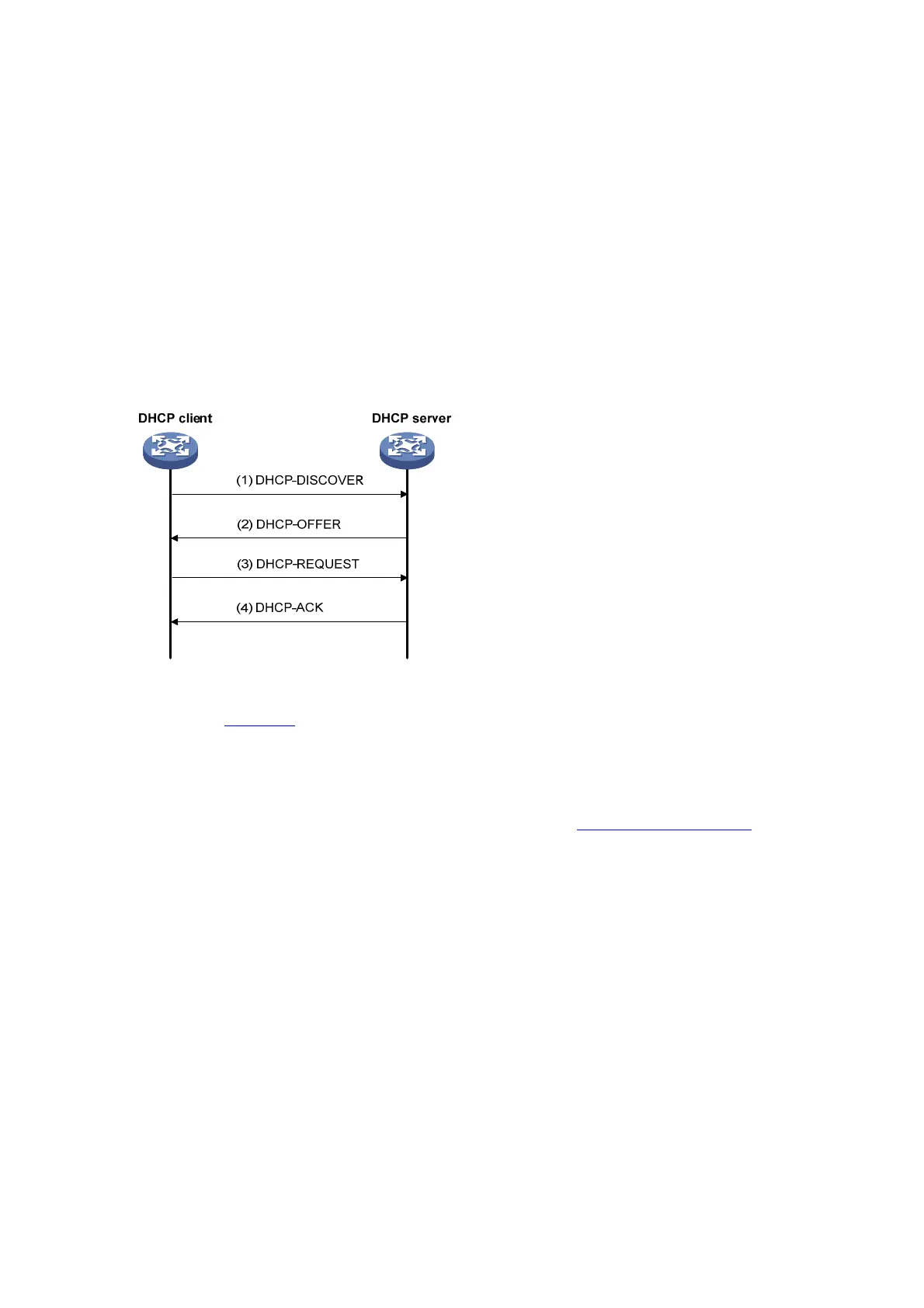
Figure 1-2 Dynamic IP address allocation process
As shown in
Figure 1-2, a DHCP client obtains an IP address from a DHCP server via four steps:
1) The client broadcasts a DHCP-DISCOVER message to locate a DHCP server.
2) A DHCP server offers configuration parameters including an IP address to the client in a
DHCP-OFFER message. The sending mode of the DHCP-OFFER message is determined by the
flag field in the DHCP-DISCOVER message. Refer to
DHCP Message Format for related
information.
3) If several DHCP servers send offers to the client, the client accepts the first received offer, and
broadcasts it in a DHCP-REQUEST message to formally request the IP address.
4) All DHCP servers receive the DHCP-REQUEST message, but only the server from which the client
accepts the offered IP address responds. The server returns a DHCP-ACK message to the client,
confirming that the IP address has been allocated to the client, or a DHCP-NAK unicast message,
denying the IP address allocation.

 Loading...
Loading...


















