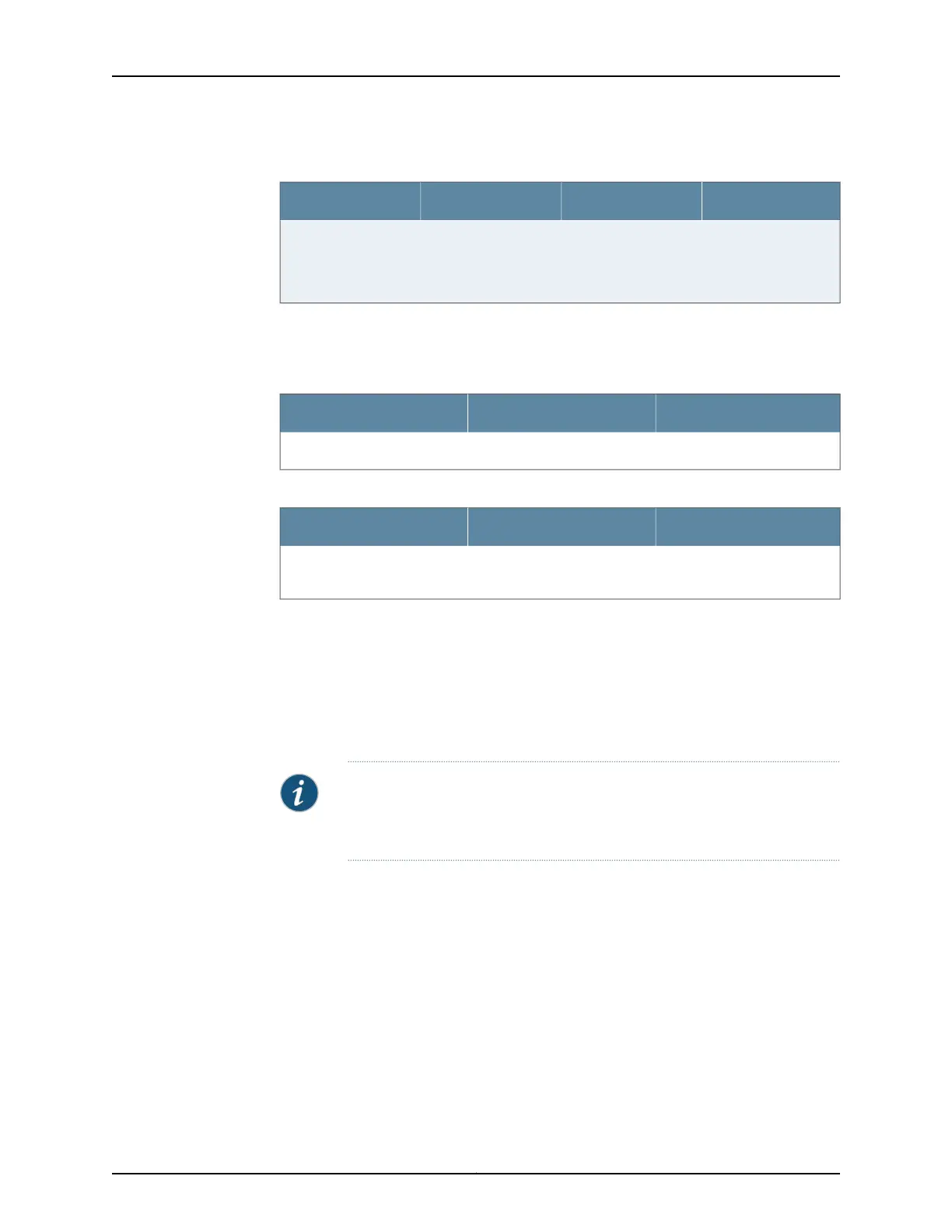
Table 31: Default Interface Configuration for the Services Gateway (continued)
AddressDHCP StateSecurity ZoneInterface
192.168.3.1/24ServerTrustge-0/0/3 (if used)
NOTE: Use this port
as a fabric port.
By default, the security policies and NAT rules in Table 32 on page 119 and
Table 33 on page 119 are created on the SRX Series security policies.
Table 32: Security Policies
Policy ActionDestination ZoneSource Zone
PermitUntrustTrust
Table 33: NAT Rule
NAT ActionDestination ZoneSource Zone
Source NAT to untrust zone
interface
UntrustTrust
For example, a common default firewall configuration includes the followingassumptions:
•
The protected network is connected to the ge-0/0/1 interface and the ge-0/0/2
interface in the trust zone.
•
Connectivity to the Internet is through the ge-0/0/0 interface in the untrust zone.
•
The IP address of the ge-0/0/0 interface is assigned via DHCP.
NOTE: The ge-0/0/1 interfaceand ge-0/0/2 interface are a part of the default
VLAN. The protected hosts can be connected to any one of the ports that
are part of the default VLAN.
You can configure the services gateway using the CLI or J-Web. To use J-Web, connect
a desktop or laptop computer to the ge-0/0/1 interface. The IP address of the desktop
or laptop computer can be statically configured or assigned by the factory default DHCP
server enabled on the VLAN interface.
After you connect your desktop or laptop computer to ge-0/0/1, you can use a Web
browser to visit the address http://192.168.1.1, access the J-Web setup wizard, and
complete the initial setup configuration of the services gateway.
After you perform the initial configuration and commit it by clicking Commit, the configured
services gateway can no longer act as a DHCP server. Therefore, to continue using the
services gateway as a management interface, you should configure the IP address of the
interface as part of the initial configuration.
119Copyright © 2018, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 19: Performing Initial Configuration
 Loading...
Loading...





