3.1.8.3.9.6 Torque loop input shaping filter
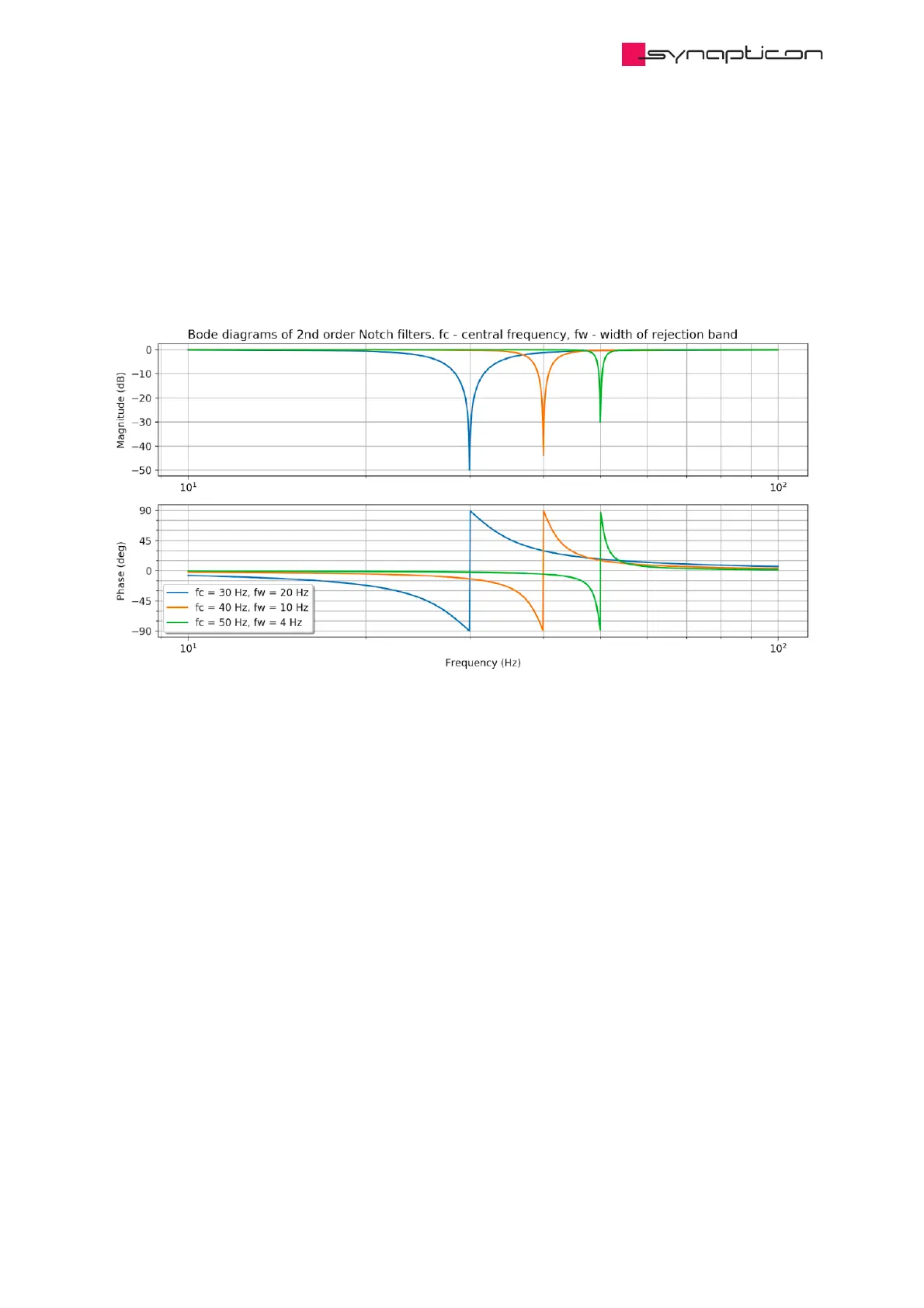
If the mechanical system has a resonance (for example a natural frequency) or if the system contains another
source of distortion at a known frequency, exciting this particular frequency with the output of the torque
controller may result in unwanted oscillations. This filter can be used to remove a specified frequency band
around the resonance.
In practice, there is a certain challenge in usage of notch filters. If the resonance frequency is too low,
introducing a notch filter will impair the control signal by adding a phase delay. It is therefore recommended
to use notch filters only for high frequency resonances. *
* The frequency depends on both the central frequency and the rejection width. Generally, it should be higher
than 50 Hz.
A practical guide to notch filter design:
1. Find resonances of the system. This can be done by observing a frequency response during the system
identification procedure: Check the velocity reaction to a specific torque input frequency.
2. Decide which resonance should be compensated and identify the width of excitation frequencies.
3. Record the reference behavior of the system before applying the notch filter.
4. Configure the filter with the obtained parameters.
5. Check the resulting performance of the setup and optimize the filter parameters.
 Loading...
Loading...