54-20
Software Configuration Guide—Release IOS XE 3.6.0E and IOS 15.2(2)E
OL_28731-01
Chapter 54 Configuring Network Security with ACLs
Configuring VLAN Maps
Creating and Deleting VLAN Maps
Each VLAN map consists of an ordered series of entries. To create, add to, or delete a VLAN map entry,
perform this task:
You can use the no vlan access-map name global configuration command to delete a map. You can use
the no vlan access-map name number global configuration command to delete a single sequence entry
from within the map. You can use the no action access-map configuration command to enforce the
default action, which is to forward.
VLAN maps do not use the specific permit or deny keywords. To deny a packet by using VLAN maps,
create an ACL that would match the packet, and then set the action to drop. A permit in the ACL is the
same as a match. A deny in the ACL means no match.
Examples of ACLs and VLAN Maps
These examples show how to create ACLs and VLAN maps for specific purposes.
Example 1
This example shows how to create an ACL and a VLAN map to deny a packet. In the first map, any
packets that match the ip1 ACL (TCP packets) would be dropped. You first create the ip1 ACL to permit
any TCP packet and no other packets. Because there is a match clause for IP packets in the VLAN map,
the default action is to drop any IP packet that does not match any of the match clauses.
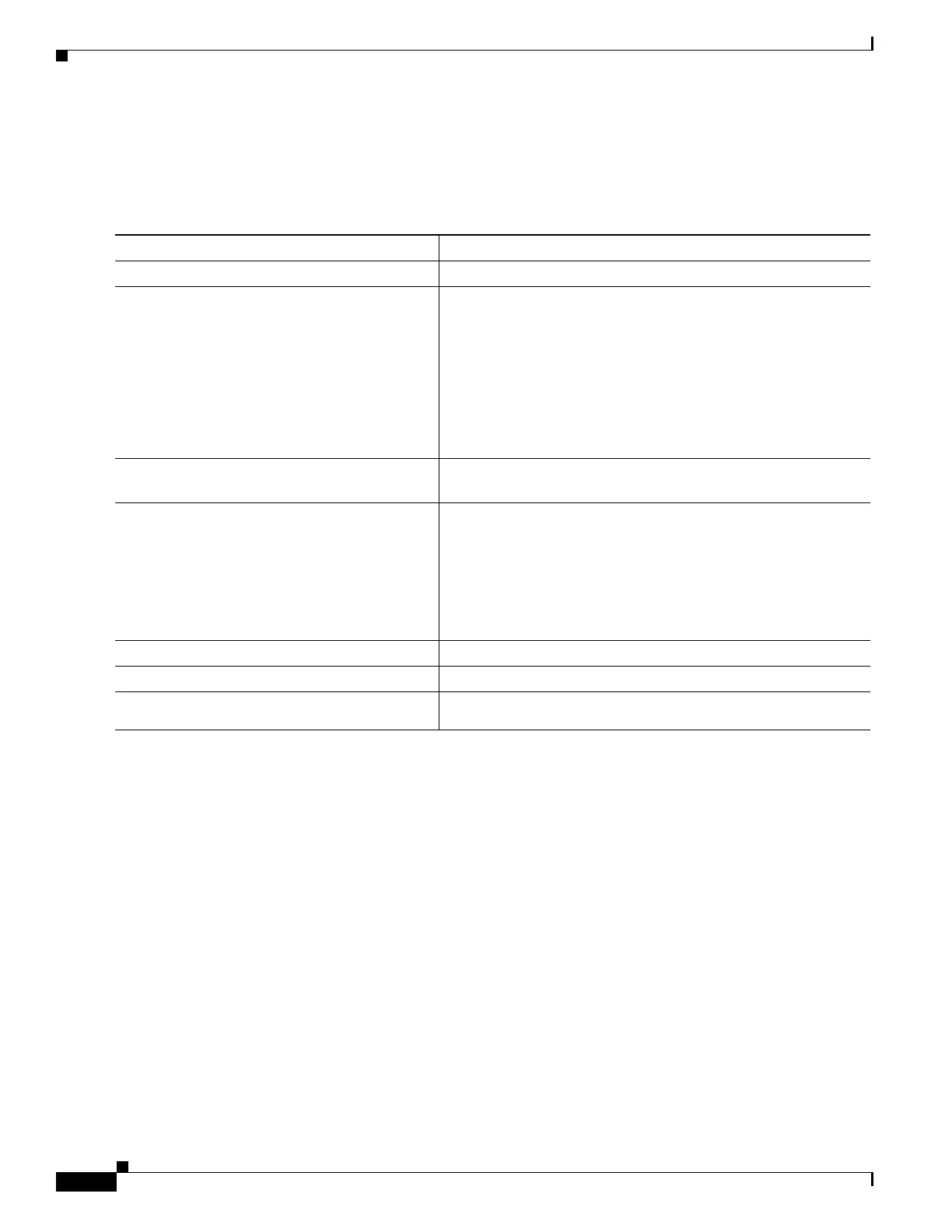
Command Purpose
Step 1
Switch# configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 2
Switch(config)# vlan access-map name
[number]
Creates a VLAN map, and give it a name and (optionally) a
number. The number is the sequence number of the entry within
the map.
When you create VLAN maps with the same name, numbers are
assigned sequentially in increments of 10. When modifying or
deleting maps, you can enter the number of the map entry that
you want to modify or delete.
This command enables access-map configuration mode.
Step 3
Switch(config-access-map)# action {drop |
forward}
(Optional) Sets the action for the map entry. The default is to
forward.
Step 4
Switch(config-access-map)# match {ip |
ipv6 | mac} address {name | number} [name
| number]
Matches the packet (using either the IP, IPv6, or MAC address)
against one or more standard or extended access lists. Note that
packets are matched only against access lists of the correct
protocol type. IP packets are compared with standard or extended
IP access lists. Non-IP packets are only compared with named
MAC extended access lists. If a match clause is not specified, the
action is taken on all packets.
Step 5
Switch(config-access-map)# end
Returns to global configuration mode.
Step 6
Switch(config)# show running-config
Displays the access list configuration.
Step 7
Switch(config)# copy running-config
startup-config
(Optional) Saves your entries in the configuration file.

 Loading...
Loading...




















