25-11
Software Configuration Guide—Release IOS XE 3.6.0E and IOS 15.2(2)E
OL_28731-01
Chapter 25 Configuring Optional STP Features
About UplinkFast
Switch#
About UplinkFast
Note UplinkFast is most useful in wiring-closet switches. This feature might not be useful for other types of
applications.
Spanning Tree UplinkFast provides fast convergence after a direct link failure and uses uplink groups to
achieve load balancing between redundant Layer 2 links. Convergence is the speed and ability of a group
of internetworking devices running a specific routing protocol to agree on the topology of an
internetwork after a change in that topology. An uplink group is a set of Layer 2 interfaces (per VLAN),
only one of which is forwarding at any given time. Specifically, an uplink group consists of the root port
(which is forwarding) and a set of blocked ports, except for self-looping ports. The uplink group provides
an alternate path in case the currently forwarding link fails.
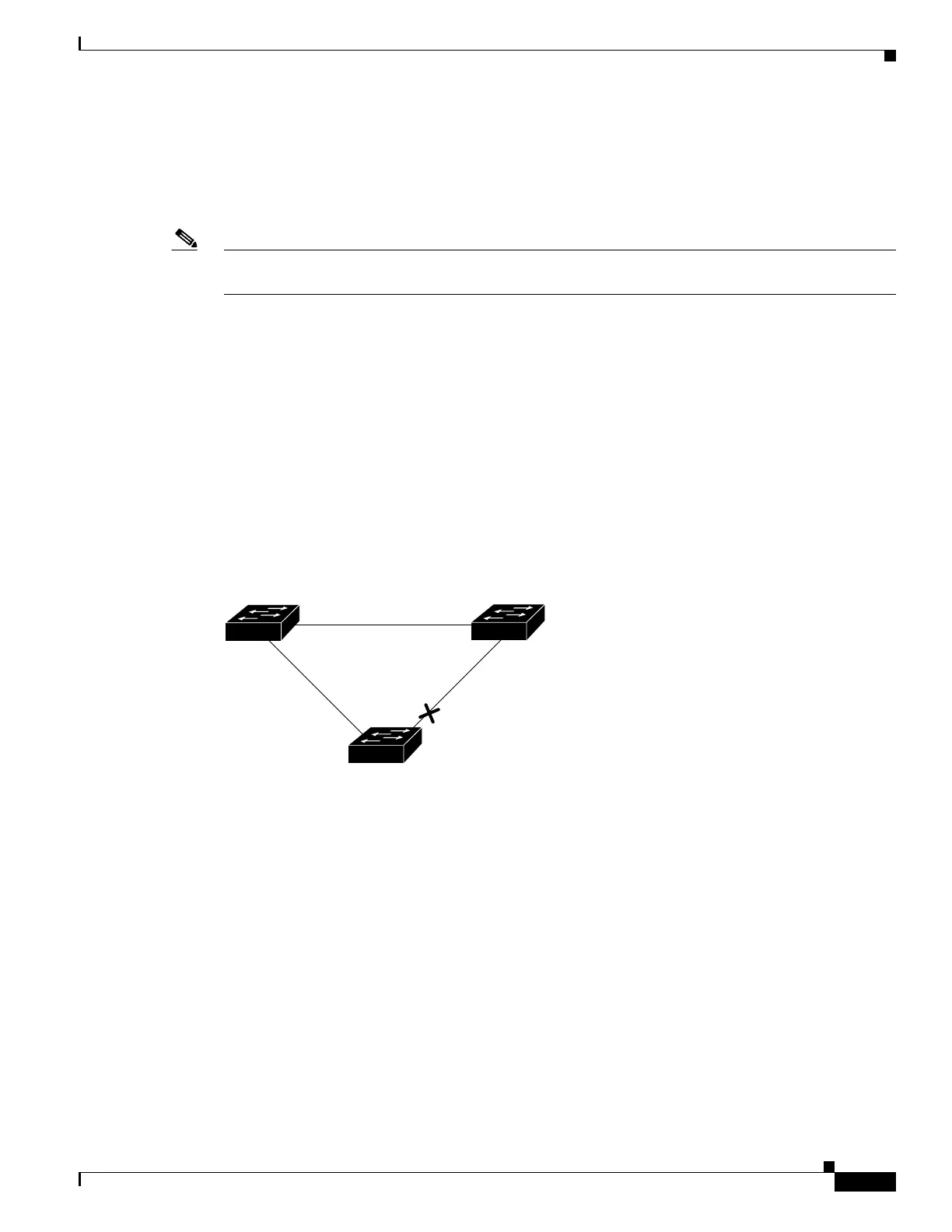
Figure 25-2 shows an example of a topology with no link failures. Switch A, the root switch, is
connected directly to Switch B over link L1 and to Switch C over link L2. The Layer 2 interface on
Switch C that is connected directly to Switch B is in the blocking state.
Figure 25-2 UplinkFast Before Direct Link Failure
If Switch C detects a link failure on the currently active link L2 on the root port (a direct link failure),
UplinkFast unblocks the blocked port on Switch C and transitions it to the forwarding state without
going through the listening and learning states, as shown in Figure 25-3. This switchover takes
approximately one to five seconds.
L1
L2 L3
Switch C
Switch A
(Root)
Switch B
Blocked port
11241

 Loading...
Loading...




















