16-4
Software Configuration Guide—Release IOS XE 3.6.0E and IOS 15.2(2)E
OL_28731-01
Chapter 16 Configuring VLANs, VTP, and VMPS
VLANs
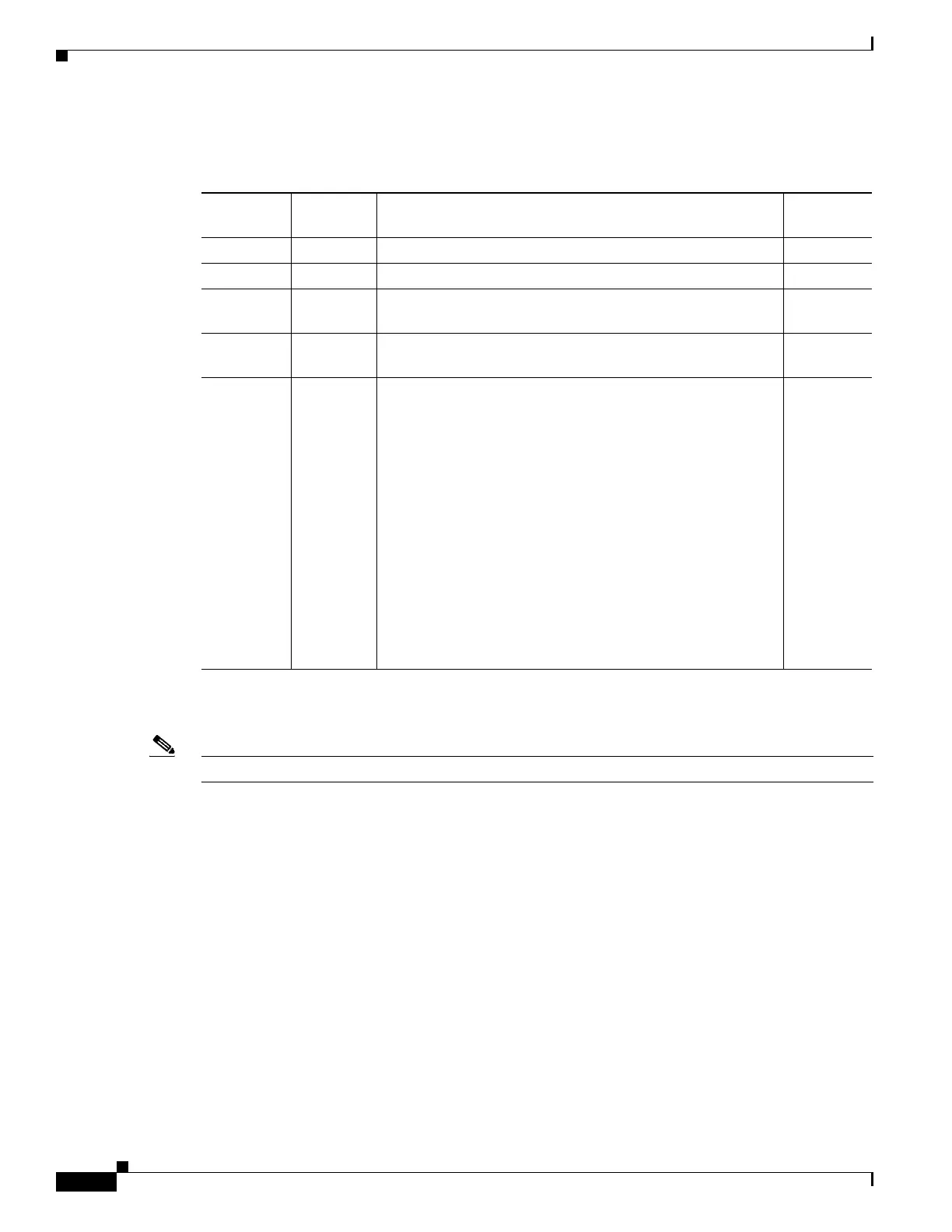
Table 16-1 describes the uses for VLAN ranges.
Configurable Normal-Range VLAN Parameters
Note Ethernet VLANs 1 and 1006 through 4094 use only default values.
You can configure the following parameters for VLANs 2 through 1001:
• VLAN name
• VLAN type
• VLAN state (active or suspended)
• SAID
• STP type for VLANs
VLAN Default Configuration
Table 16-2 shows the default VLAN configuration values.
Table 16-1 VLAN Ranges
VLANs Range Usage
Propagated
by VTP
0, 4095 Reserved For system use only. You cannot see or use these VLANs. —
1 Normal Cisco default. You cannot delete this VLAN. Yes
2–1001 Normal Used for Ethernet VLANs; you can create, use, and delete
these VLANs.
Yes
1002–1005 Normal Cisco defaults for FDDI and Token Ring. You cannot delete
VLANs 1002–1005.
Yes
1006–4094 Extended For Ethernet VLANs only. When configuring extended-range
VLANs, note the following:
• Layer 3 ports and some software features require internal
VLANs. Internal VLANs are allocated from 1006 and
up. You cannot use a VLAN that has been allocated for
such use. To display the VLANs used internally, enter the
show vlan internal usage command.
• Switches running the Catalyst operating system do not
support configuration of VLANs 1006-1024. If you
configure VLANs 1006-1024, ensure that the VLANs do
not extend to any switches running Catalyst operating
system software.
• You must enable the extended system ID to use extended
range VLANs.
No

 Loading...
Loading...




















