26-17
Software Configuration Guide—Release IOS XE 3.6.0E and IOS 15.2(2)E
OL_28731-01
Chapter 26 Configuring EtherChannel and Link State Tracking
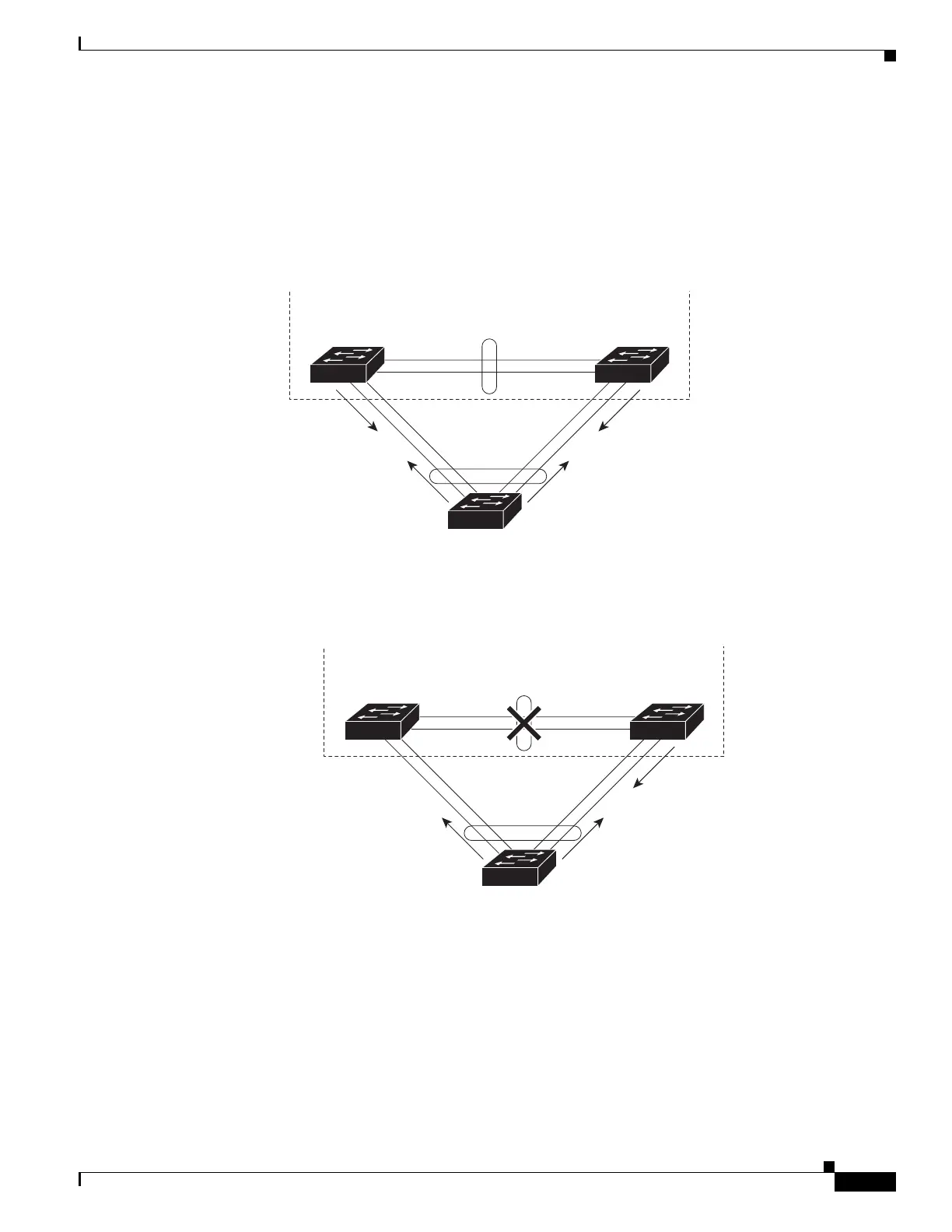
Displaying EtherChannel to a Virtual Switch System
(the VSS client) connected to both VSS components by using EtherChannel links, compares every
received active ID with its stored active ID. If they match, the remote switch sends TLVs containing its
stored active ID back to the VSS in its regularly scheduled PAgP messages. If they do not match, the
remote switch stores the new active ID and immediately transmits asynchronous PAgP messages with
TLVs containing the new active ID. Upon receiving the new active ID from the remote switch, the
original active virtual switch detects the dual-active scenario and takes appropriate actions.
Figure 26-1 Enhanced PAgP in VSS Normal Operation
Figure 26-2 Enhanced PAgP in VSS Dual-active Scenario
As a remote switch, the Catalyst 4500 series switch supports stateful VSS client. In particular, the ID of
the current active virtual switch is synchronized from the active supervisor engine to the redundant
supervisor engine of the Catalyst 4500 series switch. This ensures that dual-active detection is not
disrupted even when the active supervisor engine switches over to the redundant supervisor engine.
Virtual
Switch A
(active)
Virtual
Switch B
(standby)
Remote switch
(Catalyst 4500 series switch)
Active_ID = A’s MAC
Virtual switch TLV
Active_ID = A’s MAC
Virtual switch TLV
Active_ID = A’s MAC
Remote switch TLV
Active_ID = A’s MAC
Remote switch TLV
Active_ID = A’s MAC
VSL
EtherChannel
204283
Remote switch
(Catalyst 4500 series switch)
Active_ID = B’s MAC
Virtual switch TLV
Active_ID = B’s MAC
Remote switch TLV
Active_ID = B’s MAC
Dual-active detected by A
Remote switch TLV
Active_ID = B’s MAC
VSL
204284
Virtual
Switch A
(active)
Virtual
Switch B
(standby)
EtherChannel

 Loading...
Loading...




















