CDM-570A/570AL Satellite Modem with Optional Packet Processor
Revision 5
DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier Option G–8 MN-CDM570A
G.4.1 DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier Cancellation Process
The state-of-the-art signal processing technology employed via DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier
continually estimates and tracks all parametric differences between the local uplink signal and its
image within the downlink. Through advanced adaptive filtering and phase locked loop
implementations, it dynamically compensates for these differences by appropriately adjusting the
delay, frequency, phase and amplitude of the sampled uplink signal, resulting in excellent
cancellation performance.
When a full duplex satellite connection is established between two sites, separate satellite
channels are allocated for each direction. If both directions transmitted on the same channel,
each side would normally find it impossible to extract the desired signal from the aggregate due to
interference originating from its local modulator. However since this interference is produced
locally, it is possible to estimate and remove its influence prior to demodulation of the data
transmitted from the remote location.
For the DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier cancellation, it is necessary to provide each demodulator
with a copy of its local modulator’s output.
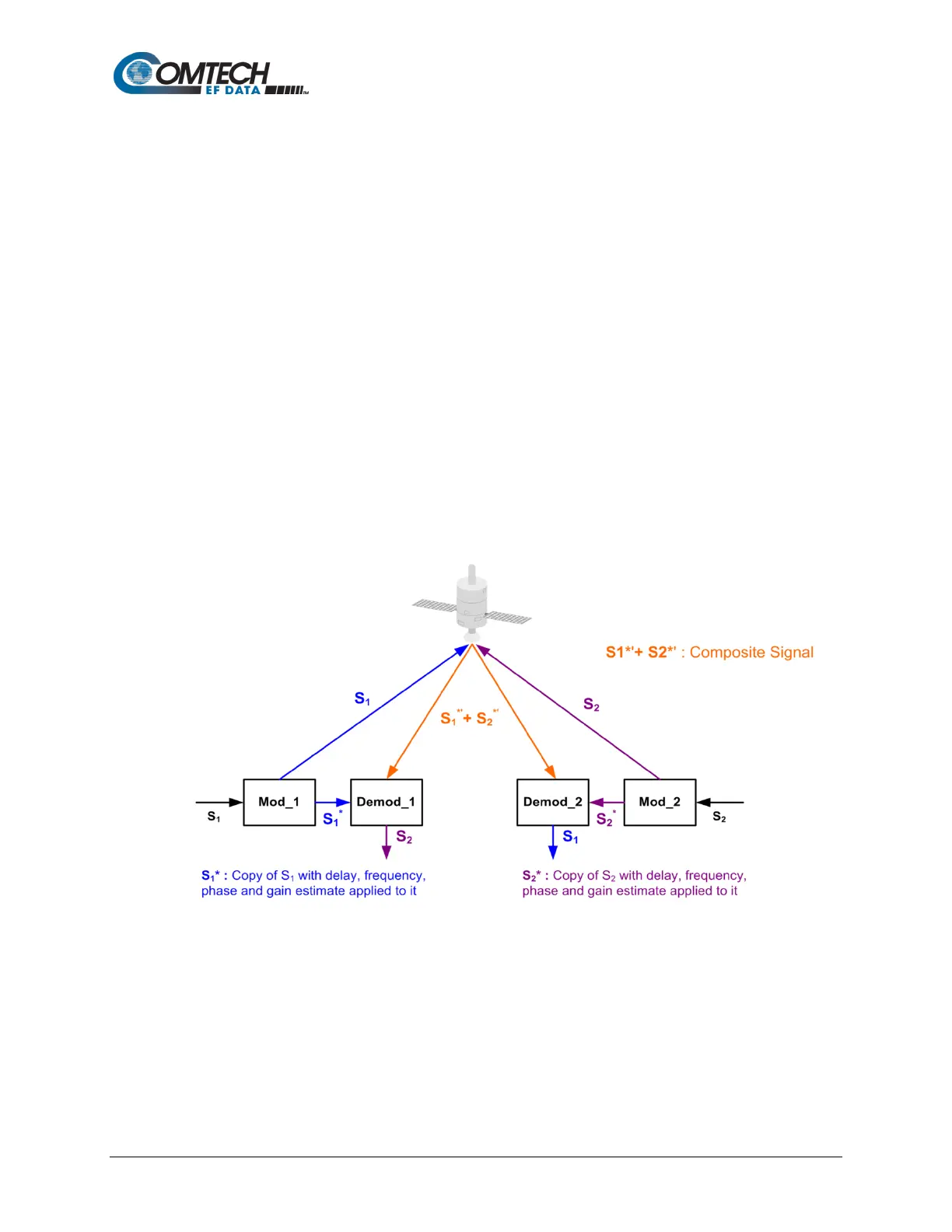
Refer to Figure G-5: Modem 1 and Modem 2 transmit signals S1 and S2 respectively. The
satellite receives, translates, and retransmits the composite signal. The downlink signals S1* and
S2*, received at Modem 1 and Modem 2 differ from the transmit signals primarily in terms of
phase, frequency, and delay offsets.
Figure G-5. DoubleTalk Carrier-in-Carrier Signals
Refer to Figure G-6: For round trip delay estimation, a search algorithm is utilized that correlates
the received satellite signal to a stored copy of the local modulator’s transmitted signal. The
interference cancellation algorithm uses the composite signal and the local copy of S1 to estimate
the necessary parameters of scaling (complex gain/phase), delay offset and frequency offset. The
algorithm continuously tracks changes in these parameters as they are generally time-varying in
a satellite link.
 Loading...
Loading...