5-23 OBSTACLE LANDING DISTANCE
(Max Weight 6690 LB Short Field)
(Refer to the tables on the following pages)
Conditions:
Winds
....................................................................................................Zero
Runway
............................................................................Dry, Level, Paved
Flaps
........................................................................................... 35° (FULL)
• Power for 3° descent to 50 foot obstacle, then gradual reduction to
IDLE at touchdown. BETA range (lever against spring) after touchdown.
Example:
Outside Air Temp
.................................................................................. 20°C
Weight
..................................................................................... 6690 pounds
Pressure Altitude
........................................................................... 2000 feet
Headwind
..............................................................................................Zero
Obstacle Speed (V
): 74 KIAS
Landing Ground Roll: 760 FT
Total Distance Over 50' Obstacle: 1551
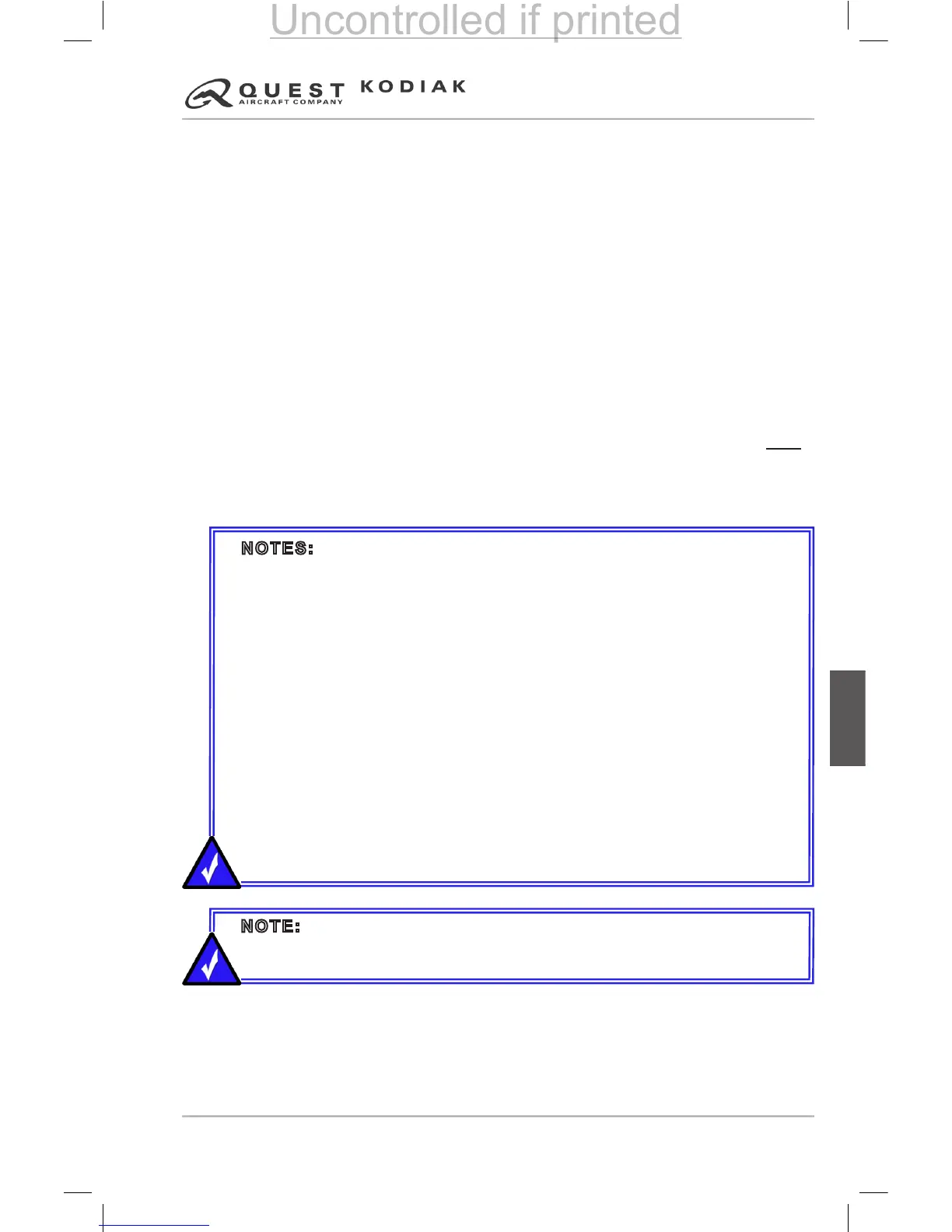
NOTES:
• Short eld technique utilized as outlined in “Section 4” of this manual.
• Decrease distances 10% for each 14 knots headwind.
• For operation in tailwinds up to 10 knots, increase distances 10% for
each 2 knots.
• For operation on a hard, dry, grass runway, increase distances by
20% of the ground roll calculation.
• To land with the aps up, increase approach speed by 22 KIAS and
allow for approximately 55% longer distances.
• Use of maximum reverse thrust after touchdown will reduce ground
roll by approximately 5%.
• For sloped runways (up to 3% slope), increase the distances by 27%
of the ground roll distance for each 1% of downslope. Decrease
distances by 9% of the ground roll distance for each 1% of upslope.
• For operation in air colder than this table provides, use the coldest
data for landing distances.
• Dashed entries indicate atmospheric temperatures beyond the aircraft
operating limits.
NOTE: Red shaded areas represent data at temperatures greater than
the maximum approved operating OAT, but may be used for the purpose of
interpolating.
 Loading...
Loading...