D-8 824 Reference Manual 11/3/00
the table below.
Standard
: ANSI S12.19
Far Field
There are two types of far fields: the
acousti
c far field and
the
geometric
far field.
Acoustic Far Field
: The distance from a source of sound is
greater than an acoustic wavelength. In the far field, the
effect of the type of sound source is negligible. Since the
wavelength varies with frequency (See the definition of
Wavelength), the distance will vary with frequency. To be in
the far field for all frequencies measured, the lowest fre-
quency should be chosen for determining the distance. For
example, if the lowest frequency is 20 Hz, the wavelength at
normal temperatures is near 56 ft. (17 m); at 1000 Hz, the
wavelength is near 1.1 ft. (1/3 m). See the definition of
Acoustic Near Field for the advantages of in the acoustic far
field.
Geometric Far Field
: The distance from a source of sound is
greater than the largest dimension of the sound source. In the
far field, the effect of source geometry is negligible. Sound
sources often have a variety of specific sources within them,
such as exhaust and intake noise. When in the far field, the
sources have all merged into one, so that measurements
made even further away will be no different. See the defini-
tion of Geometric Near Field for the advantages of being in
the geometric far field.
Free Field
A sound field that is
free
of reflections. This does not mean
that the sound is all coming from one direction as is often
assumed, since the source of sound may be spatially exten-
sive. See the definitions of near and far fields for more
detail. This definition is often used in conjunction with
reverberant field.
Frequency (Hz, rad/sec)
The rate at which an oscillating signal completes a complete
cycle by returning to the original value. It can be expressed
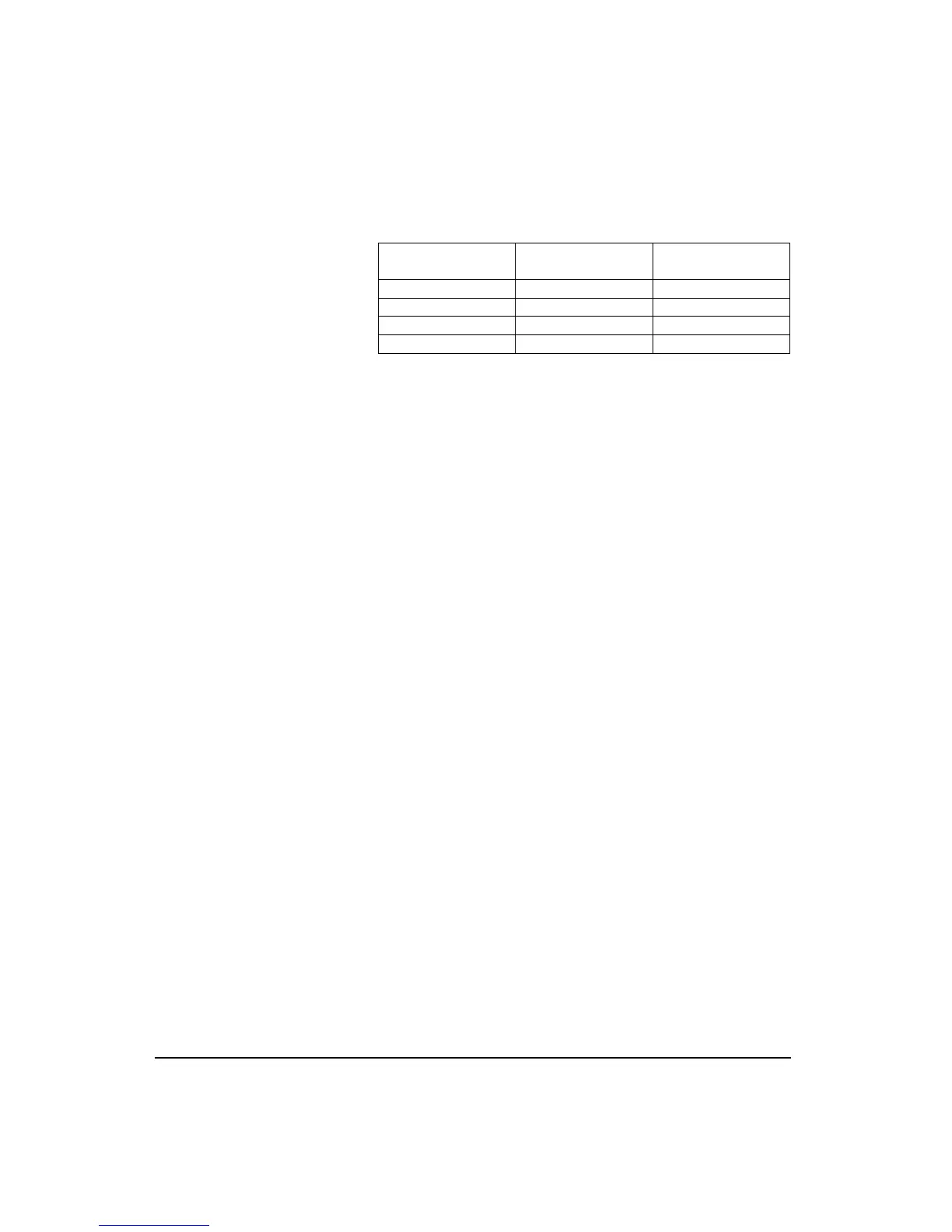
Exchange Rate, Q Exchange Rate
Factor, q
Exposure Factor, k
3.01 10 1
4 13.333 .75
5 16.667 .60
6.02 20 .50
 Loading...
Loading...