Equation 1 is a heuristic that describes total jitter as a function of bit error rate (BER) and is
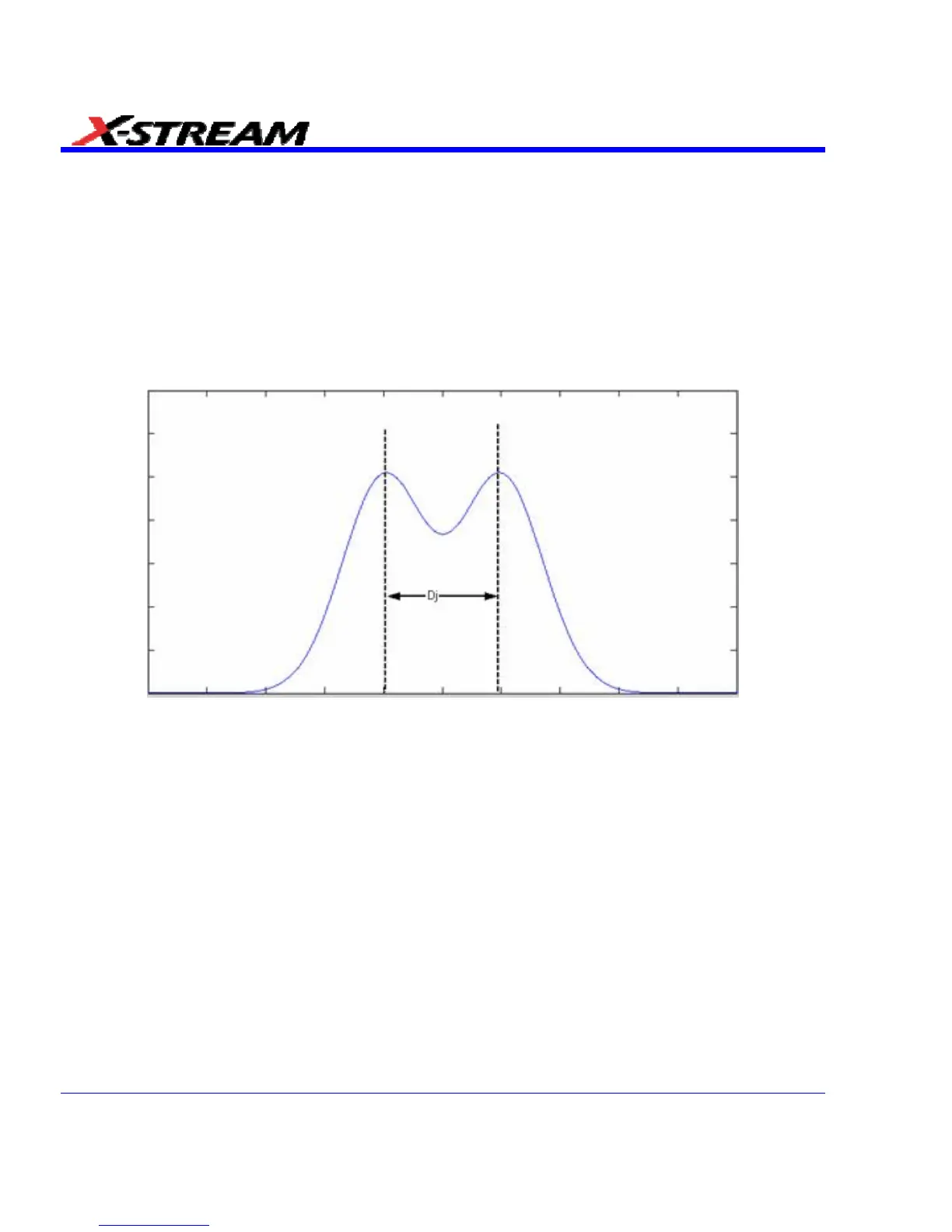
related to a distribution consisting of a Gaussian convolved with a pair of impulses as shown in
Figure 7. The constants Rj and Dj represent all of the components of random and deterministic
jitter. The Greek letter Psi is a function of BER and represents the total peak-to-peak jitter of a
unit normal distribution (i.e., a Gaussian with zero mean and a standard deviation of 1 at the
specified bit error rate. The process of determining Rj and Dj involves finding the “best fit” values
that solve equation 1. There are many possible ways to fit Rj and Dj to (1) and since it is a
simplification, no single set of solutions can completely describe the behavior of actual jitter
completely. It is for this reason that the SDA uses two separate methods to measure Rj and Dj,
effective and direct, and presents these to the user.
Figure 7. Jitter PDF model corresponding to the heuristic in equation 1. The random jitter is modeled
by a Gaussian and the deterministic jitter by a pair of impulses separated by the value of the
parameter Dj. The curve shown is the convolution of Rj and Dj.
374 SDA-OM-E Rev H
 Loading...
Loading...