3.1.3.5 Commutation Offset Detection
3.1.3.5.1 Overview
Controlling a motor with Field Oriented Control requires precise measurement of the motor’s electrical angle.
With phase order and commutation angle offset detection (hereinafter referred to as “Offset Detection”), the
relationship between the motor electrical angle and the motor mechanical angle (position sensor feedback) is
identified, afterwards the motor position sensor feedback is used to determine the motor’s electrical angle for
motion control.
Note
This feature is needed for every motor control setup. The application will not work properly before the
Offset Detection routine is successfully executed.
If an incremental encoder without index is used for commutation, the offset detection has to be done on
every power on. Otherwise, the routine only needs to be done once during the first commissioning and
after mechanical changes of the motor or of the commutation encoder.
3.1.3.5.2 Basic Principles
The Offset Detection routines identify two parameters for the relationship between the motor electrical angle
(rotor magnetic field angle) and the motor position sensor feedback:
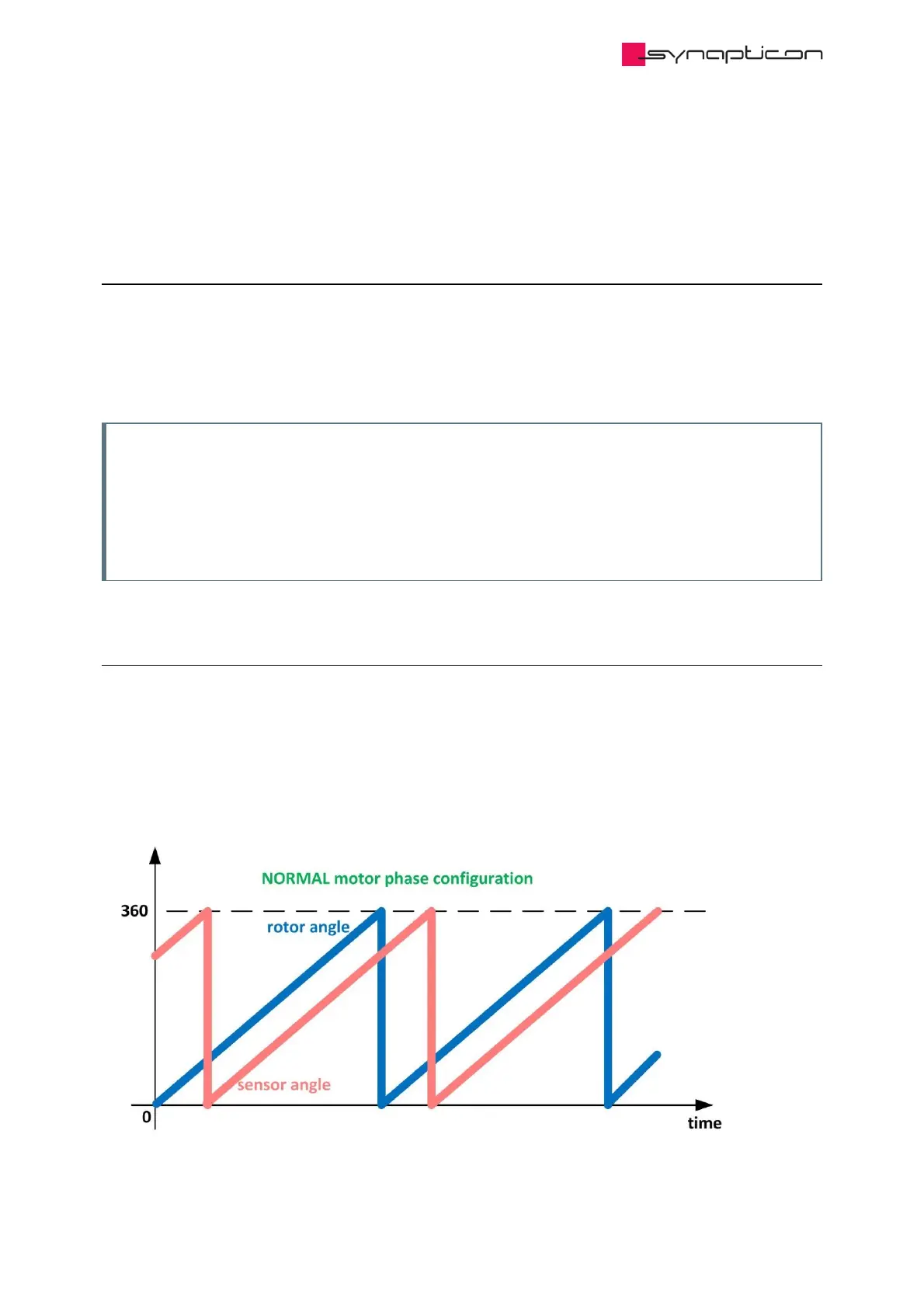
1. The motor phase configuration (NORMAL or INVERTED) (0x2003:5)
Normally, both rotor angle and sensor angle should increase/decrease at the same time. This situation is
called “NORMAL motor phase configuration” and is shown in Fig. 1.
 Loading...
Loading...