Sysmex XP-300 14-21
Technical Information
Revised October 2012
14.6 Functional description
This chapter describes blood cell count detection principle and analysis method used in this
instrument, and flow of individual analysis. Also the hardware elements are explained.
• Detection principle: Principle each of DC detection method and non-cyanide
hemoglobin analysis method is described.
• Flow of analysis: Flow of each analysis parameter on the main unit and analysis
method for particle distribution are described.
Detection principle
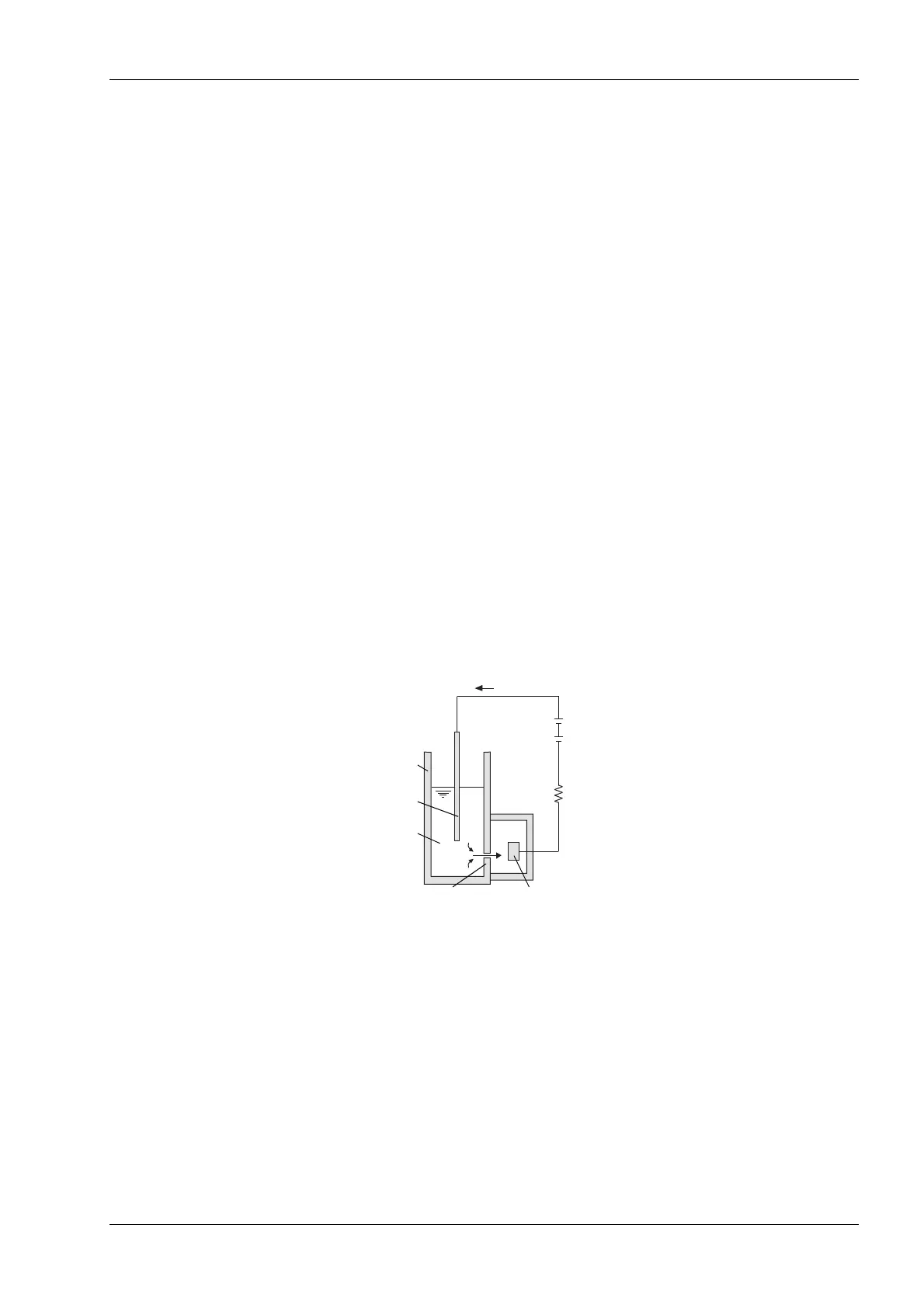
This instrument performs blood cell count by DC detection method.
DC detection method
Blood sample is aspirated, measured to a predetermined volume, diluted at the specified ratio, then
fed into each transducer.
The TD chamber has a minute hole called the aperture. On both sides of the aperture, there are the
electrodes between which flows direct current. Blood cells suspended in the diluted sample pass
through the aperture, causing direct current resistance to change between the electrodes. As direct
current resistance changes, the blood cell size is detected as electric pulses.
Blood cell count is calculated by counting the pulses, and a histogram of blood cell sizes is plotted by
determining the pulse sizes. Also, analyzing a histogram makes it possible to obtain various analysis
data.
TD Chamber
External Electrode +
Blood Cell Suspension
Aperture Internal Electrode -
Resistance
DC Supply
DC
 Loading...
Loading...