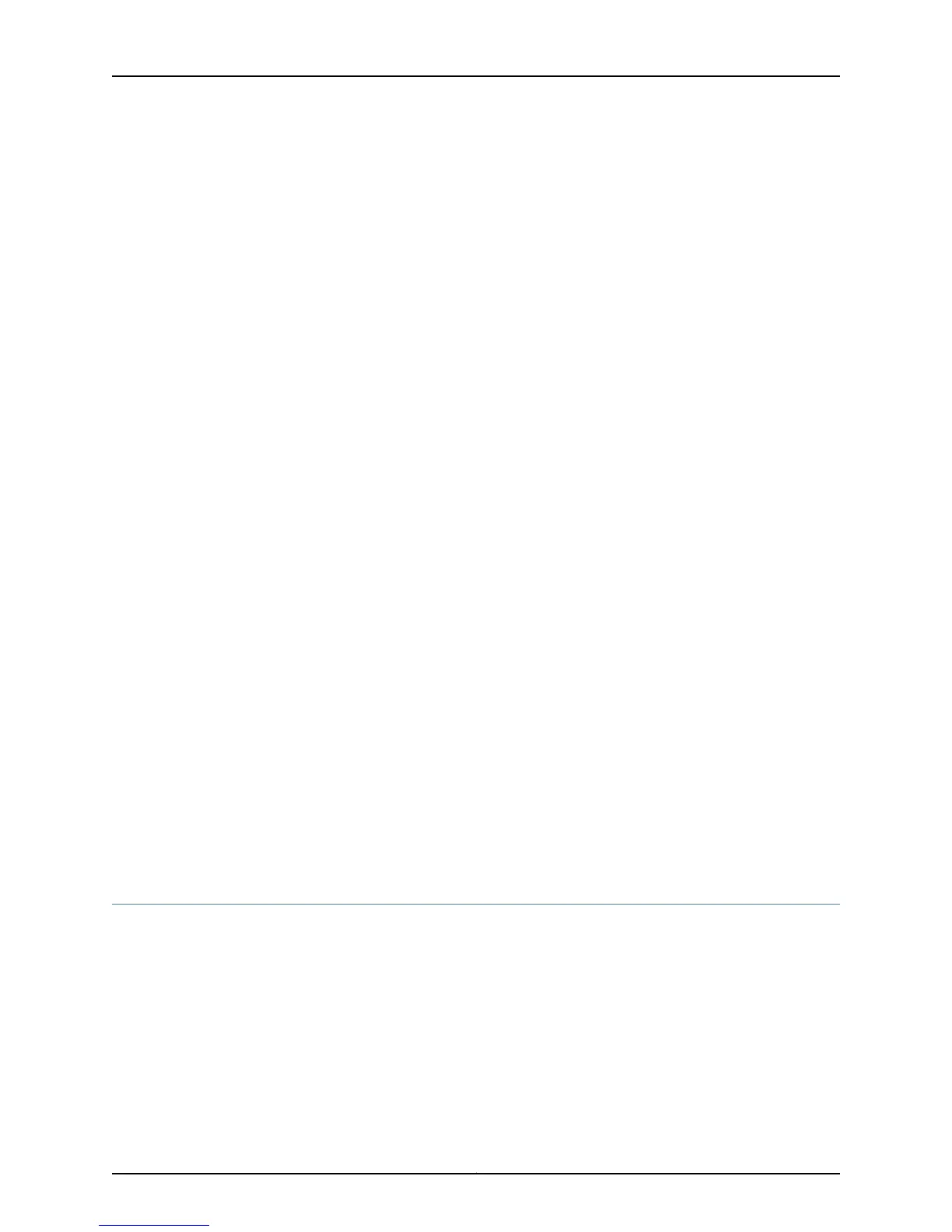Input bytes : 0
Output bytes : 0
Input packets: 0
Output packets: 0
Transit statistics:
Input bytes : 0 0 bps
Output bytes : 0 0 bps
Input packets: 0 0 pps
Output packets: 0 0 pps
IPv6 transit statistics:
Input bytes : 0
Output bytes : 0
Input packets: 0
Output packets: 0
Protocol inet, Generation: 144, Route table: 0
Flags: uRPF
Addresses, Flags: Is-Preferred Is-Primary
Meaning The show interfaces ge-1/0/10 extensive command (and the show interfaces ge-1/0/10
detail command) displays in-depth information about the interface. The Flags: output
field near the bottom of the display reports the unicast RPF status. If unicast RPF has
not been enabled, the uRPF flag is not displayed.
On EX3200, EX4200, and EX4300 switches, unicast RPF is implicitly enabled on all
switch interfaces, including aggregated Ethernet interfaces (also referred to as link
aggregation groups or LAGs), integrated routing and bridging (IRB) interfaces, and routed
VLAN interfaces (RVIs) when you enable unicast RPF on a single interface. However, the
unicast RPF status is shown as enabled only on interfaces for which you have explicitly
configured unicast RPF. Thus, the uRPF flag is not displayed on interfaces for which you
have not explicitly configured unicast RPF even though unicast RPF is implicitly enabled
on all interfaces on EX3200 and EX4200 switches.
Related
Documentation
show interfaces xe- on page 307•
• Example: Configuring Unicast RPF on an EX Series Switch
• Configuring Unicast RPF (CLI Procedure) on page 97
• Disabling Unicast RPF (CLI Procedure) on page 99
• Troubleshooting Unicast RPF on page 331
Verifying IP Directed Broadcast Status
Purpose Verify that IP directed broadcast is enabled and is working on the subnet.
Action Use the show vlans extensive command to verify that IP directed broadcast is enabled
and working on the subnet as shown in Example: Configuring IP Directed Broadcast on an
EX Series Switch.
Related
Documentation
• Configuring IP Directed Broadcast (CLI Procedure)
• Configuring IP Directed Broadcast (CLI Procedure) on page 100
241Copyright © 2015, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 4: Routine Monitoring
 Loading...
Loading...