C H A P T E R 7 – T E S T S A N D T E S T C O N D I T I O N S
AT5600 User Manual 98-119 issue 14 Page 110
Measurement Conditions
To measure capacitance, the tester applies an AC voltage between the windings
to be tested, usually with all taps on each winding shorted together. It then
measures the voltage between the windings, and the resulting current using
harmonic analysis. Dividing the voltage by the current gives the inter-winding
impedance, from which the capacitance may be calculated.
The test voltage can be in the range of 1mV to 5V at a frequency of 20Hz to
3MHz.
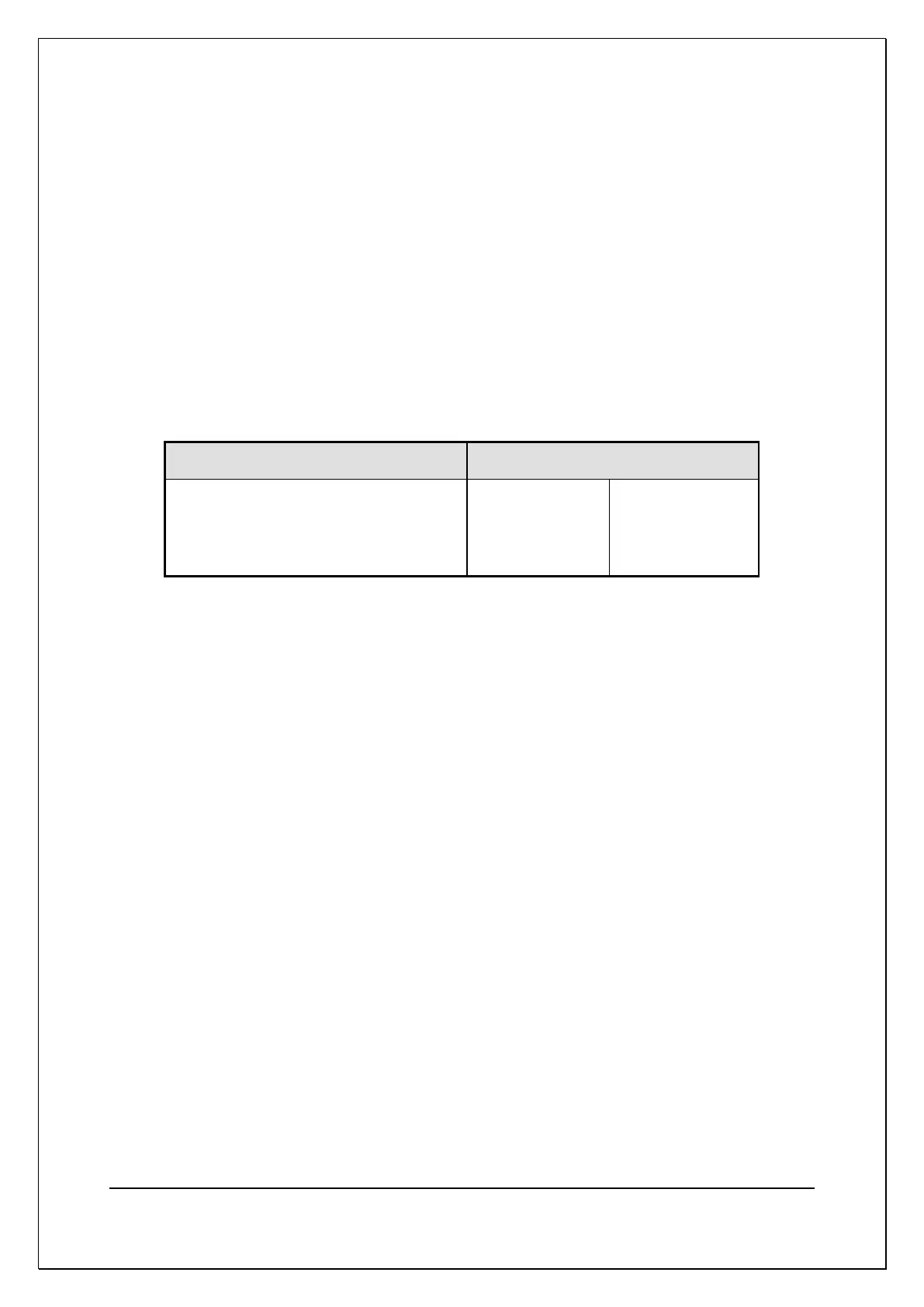
The table below gives the recommended test conditions for different values of
capacitance:
Table 3
The Test Conditions for Capacitance Measurement
When choosing the test conditions, the following potential problems should be
considered:
Current levels
For larger capacitance, particularly at higher frequencies, the current flowing
during the measurement can be very high, and similarly the measured current
could also be very small for small capacitance at lower frequencies and voltages.
Where possible, you should use the recommended test signal levels in the table
above to ensure that the currents which flow can be measured accurately.
Non-linear Capacitance
Normally non-linearity in the stray capacitance of transformers are not a problem,
and therefore capacitance is measured with as large a voltage as possible.
 Loading...
Loading...