Cortex-M4 Peripherals
ARM DUI 0553A Copyright © 2010 ARM. All rights reserved. 4-7
ID121610 Non-Confidential
4.2.6 Interrupt Active Bit Registers
The NVIC_IABR0-NVIC_IABR7 registers indicate which interrupts are active. See the register
summary in Table 4-2 on page 4-3 for the register attributes.
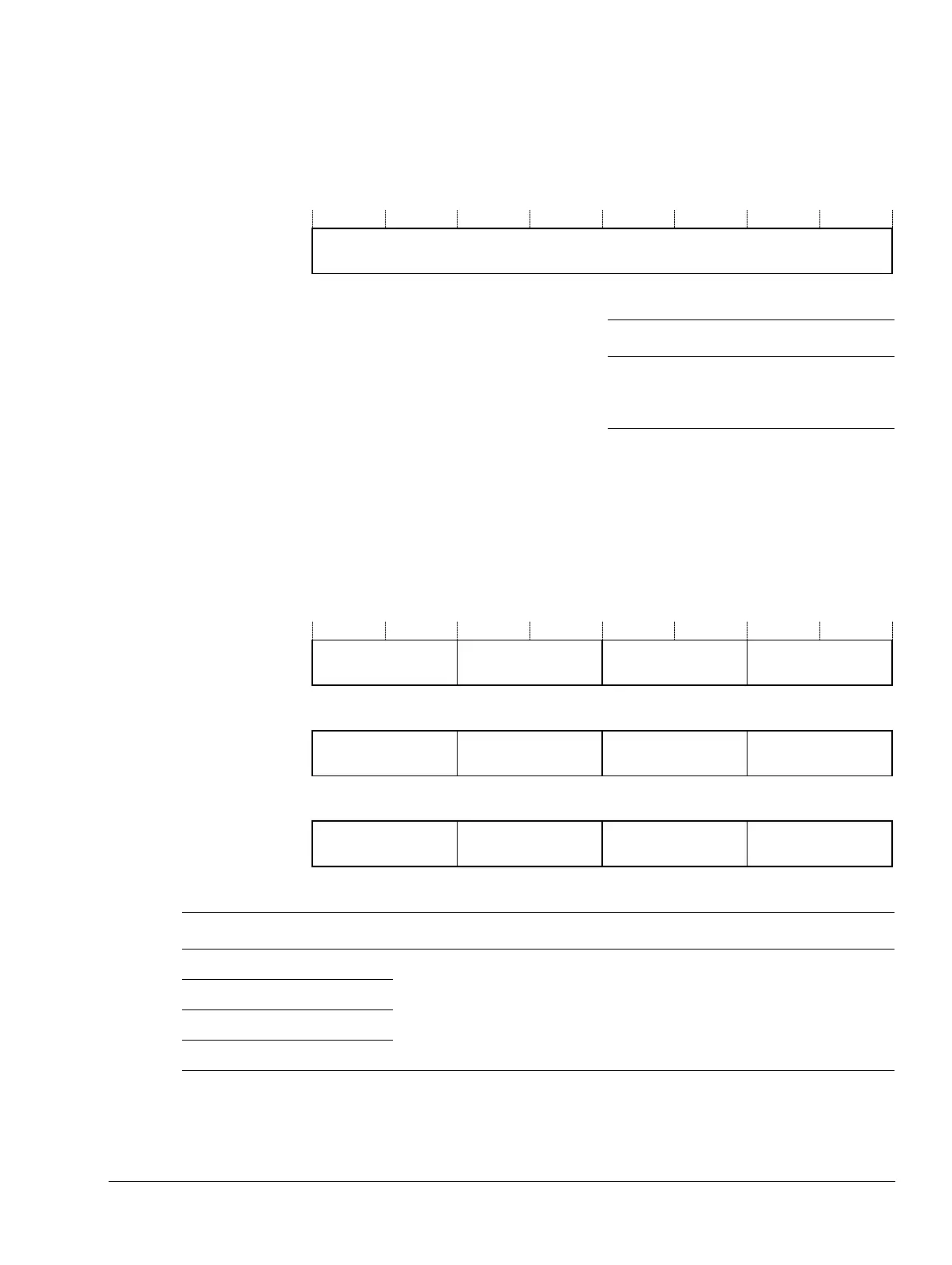
The bit assignments are:
A bit reads as one if the status of the corresponding interrupt is active or active and pending.
4.2.7 Interrupt Priority Registers
The NVIC_IPR0-NVIC_IPR59 registers provide an 8-bit priority field for each interrupt and
each register holds four priority fields. These registers are byte-accessible. See the register
summary in Table 4-2 on page 4-3 for their attributes. Each register holds four priority fields as
shown:
See Accessing the Cortex-M4 NVIC registers using CMSIS on page 4-4 for more information
about the access to the interrupt priority array, which provides the software view of the interrupt
priorities.
Table 4-8 IABR bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:0] ACTIVE Interrupt active flags:
0 = interrupt not active
1 = interrupt active.
Table 4-9 IPR bit assignments
Bits Name Function
[31:24] Priority, byte offset 3 Each implementation-defined priority field can hold a priority value, 0-255. The
lower the value, the greater the priority of the corresponding interrupt. Register
priority value fields are eight bits wide, and non-implemented low-order bits read as
zero and ignore writes.
[23:16] Priority, byte offset 2
[15:8] Priority, byte offset 1
[7:0] Priority, byte offset 0
PRI_239
31 24 23 16 15 8 7 0
PRI_238 PRI_237 PRI_236
IPR59
PRI_4n+3 PRI_4n+2 PRI_4n+1 PRI_4n
IPRn
PRI_3 PRI_2 PRI_1 PRI_0
IPR0
. . . . . .
. . . . . .

 Loading...
Loading...