Device Overview
MFR4310 Reference Manual, Rev. 2
Freescale Semiconductor 53
Figure 2-9 shows how to connect the CC to an HCS12 MCU with EBI paged mode support.
Figure 2-10 shows how to connect he CC to an HCS12 MCU with EBI unpaged mode support.
• The HCS12 interface supports the paged and the unpaged modes of the HCS12 External Bus
Interface connected to it.
• The HCS12 interface is implemented as an synchronous HCS12 External Bus slave module, thus
enabling the fast data exchange between them.
• The HCS12 interface decodes the addresses of read/write transactions to its internal registers, and
generates its internal chip select signal, CS, using the address/data lines PA[0:7], PB[0:7],
ACS[0:2], and XADDR[14:19]:
— The address and data lines PA[0:7], PB[0:7] are multiplexed. They are denoted ADR[0:15]
when referring to the address, and DATA[0:15] when referring to the data. The FlexRay CC is
selected only when the address ADR[13:15] matches ACS[0:2] (ADR13 matches ACS0,
ADR12 matches ACS1, etc.) and the address XADDR[14:19] matches 0.
• The HCS12 interface accepts only aligned 16-bit read and 8-bit or 16-bit write transactions. The
HCS12 interface does not support 8-bit read accesses.
— The internal chip select, CS, the low byte strobe, LSTRB, the least significant bit of the address,
ADR0, and the read/write select, RW_CC#, are used to determine the type of access, as shown
in Table 2-10.
• RW_CC# indicates the direction of data transfer for a transaction.
• INT_CC# is an interrupt line that can be used for requesting, by means of the internal interrupt
controller, a service routine from the HCS12 device.
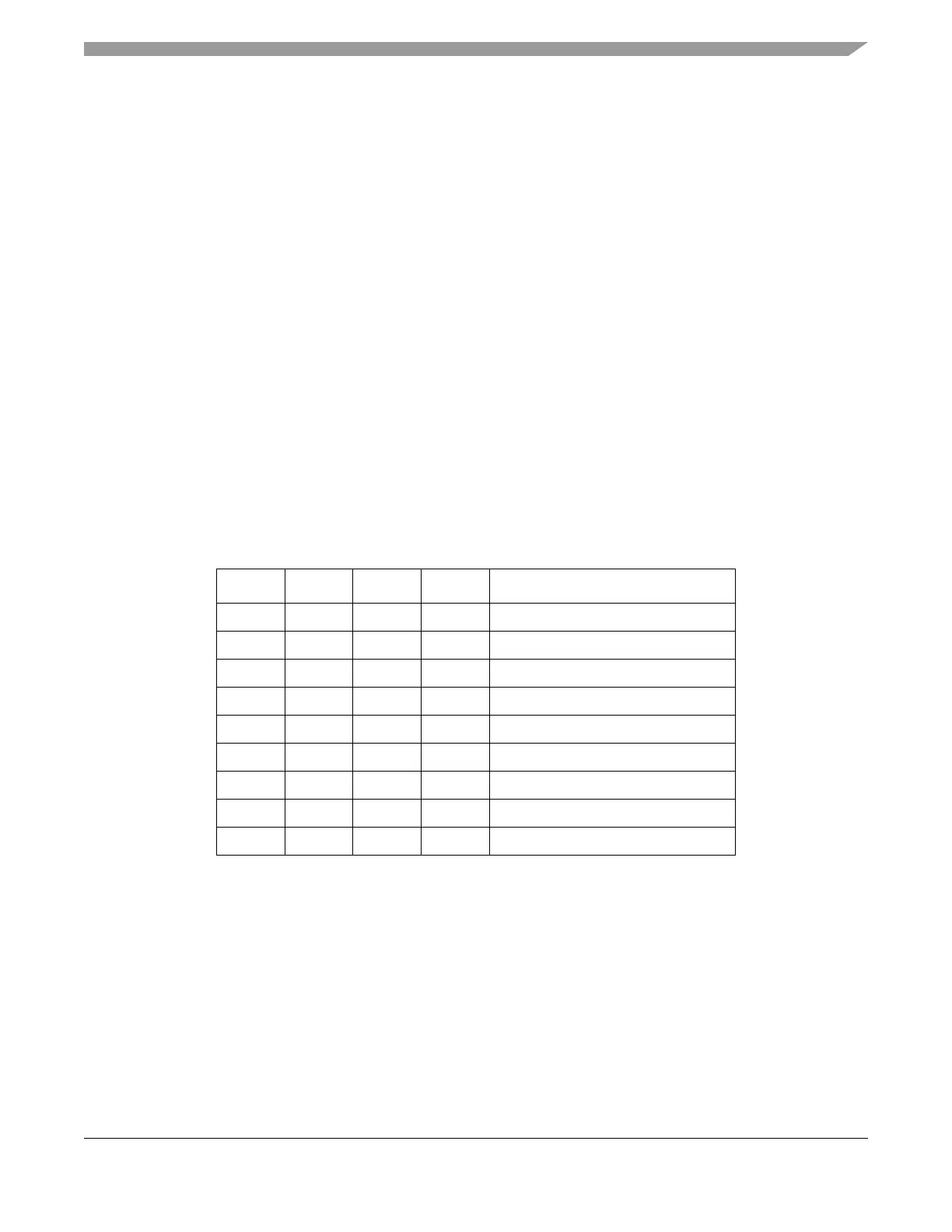
Table 2-10. HCS12 Access Types
CS RW_CC# LSTRB ADR0 Type of Access
0 X X X No access
1 0 0 0 16-bit write to word address
1
1
Write data from PA to even byte address and from PB to odd byte address.
1 0 0 1 8-bit write to an odd address
2
2
Write data from PB.
1 0 1 0 8-bit write to an even address
2
1011Not supported
1 1 0 0 16-bit read from an even address
3
3
Read data from even byte address at PA and from odd byte address at PB.
1101Not supported
1110Not supported
1111Not supported
 Loading...
Loading...