Setting up a virtual network reduces the cost of a fixed connection between two or more LANs and ensures se-
cure data transfer over the non-secure Internet. Using a tunneling protocol sets up a secure connection called a
VPN tunnel.
In the connection scenarios described in 9.3 and 9.4, a client can only access the router’s serial interfaces (for a
description of serial interfaces, see Serial Interfaces). This does not allow for access to the LAN interface via
the Internet. Using a VPN connection however, it is possible to reach or access subscribers connected to the
LAN interface, such as panel PCs.
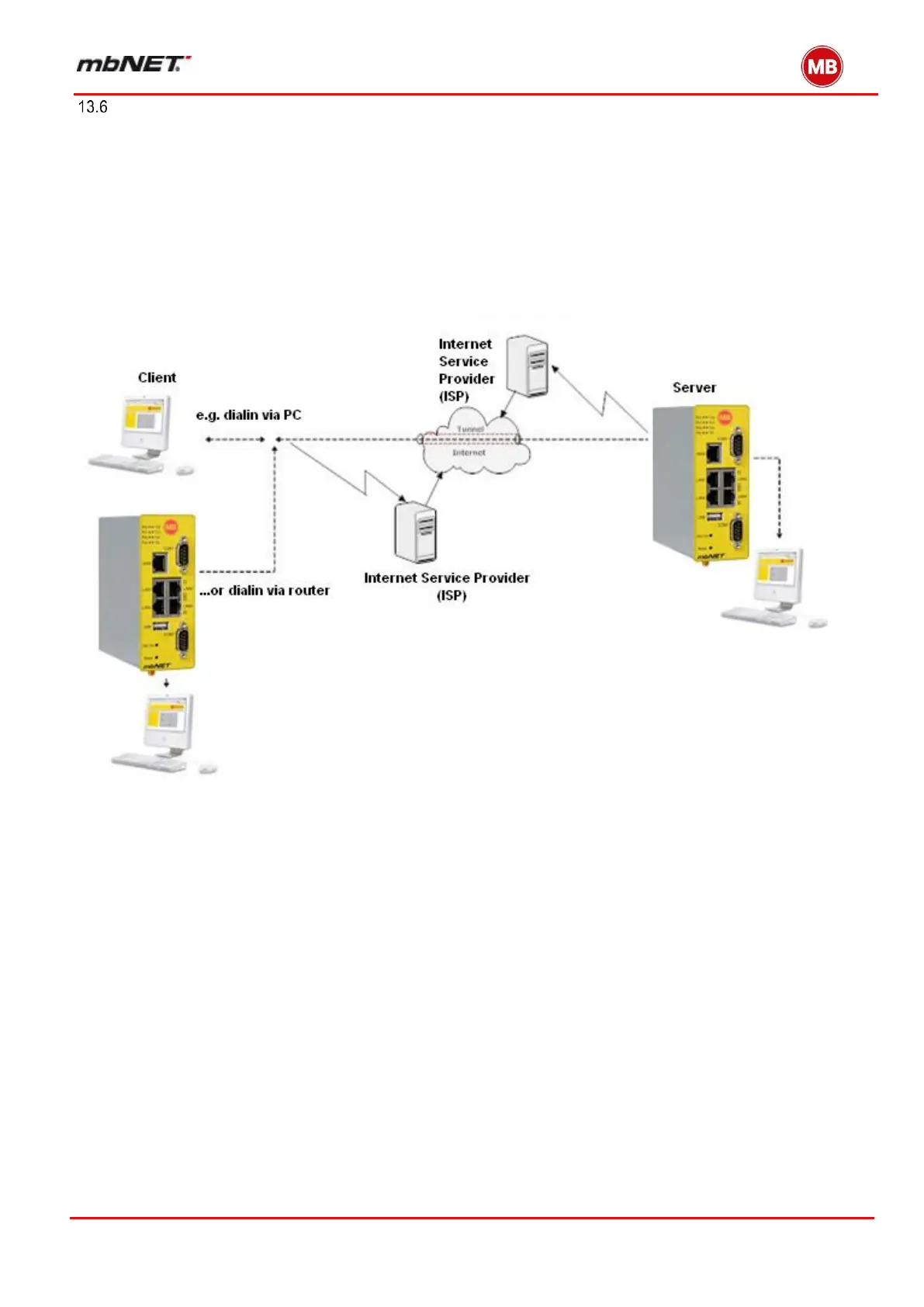
The diagram below represents a VPN connection. The client can be e.g. a PC or another industrial router, pre-
configured for Internet access.

 Loading...
Loading...


