ABL90 FLEX reference manual 5. Sensors and optical system
5-33
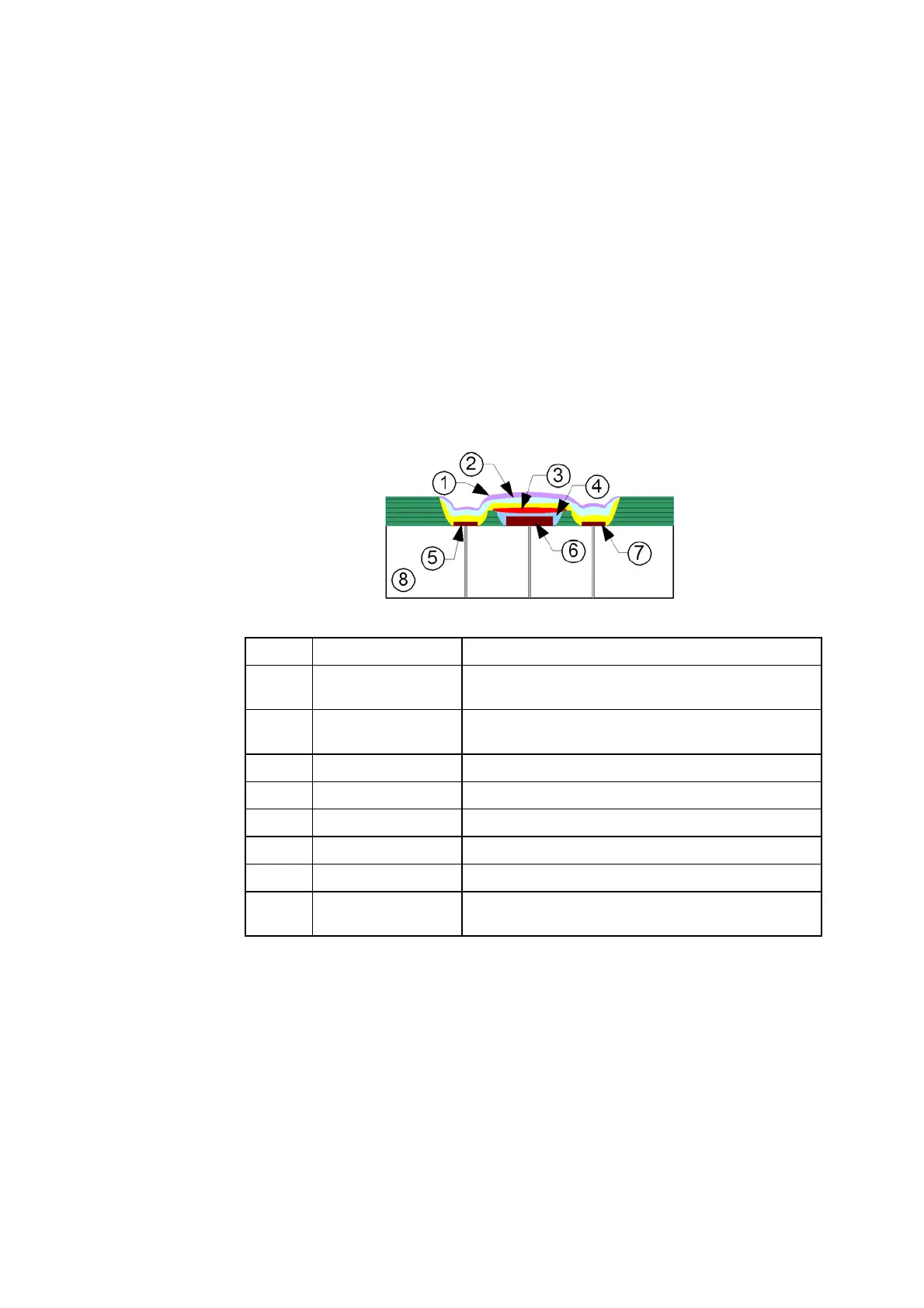
Construction of the metabolite sensors
The cGlu and cLac sensors are three-electrode sensors consisting of an internal
silver/silver chloride reference electrode, a platinum auxiliary electrode, and a
platinum anode. The sensors are covered by a multi-layer membrane bound to
the sensor board.
The membrane consists of four layers:
The biocompatible layer
The outer membrane – permeable to
cGlu/cLac
The enzyme layer
The inner membrane – permeable to H
2
O
2
Item Part Description
1 Biocompatible
layer
Biocompatible layer
2 Outer membrane Outer membrane permeable to glucose –
diffusion control
3 Enzyme layer Contains glucose/lactate oxidase.
4 Inner membrane Cellulose acetate.
5 Reference Ag/AgCl electrode.
6 Anode Platinum electrode.
7 Cathode Platinum electrode.
8 Electrode base The structural platform on which the sensor is
formed.
The zero current is a small background current measured at the electrode when
no
cGlu/cLac is present in a solution. As CAL 1 contains no cGlu/cLac, a baseline
representing the zero current, I
0
as a function of time (I
0
= f(t)), is obtained
from continuous measurements on CAL 1.
This I
0
baseline is obtained as follows:
At the end of a rinse, with CAL 1 in the measuring chamber, the zero
current of the metabolite electrodes is measured periodically
The previous N (N = 8) measurements on the CAL 1 – before a calibration
or a sample measurement starts – are used to obtain a baseline
representing the time function of I
0
Basic
description
Diagram
Parts and
description
Zero current

 Loading...
Loading...