Appendix – Quality control ABL90 FLEX reference manual
I-12
Westgard rules
The Westgard rules are a set of statistical rules that, when applied to the quality
control results, can aid the following:
Increase the probability of detecting an error on the analyzer by analyzing
the quality control measurements
Help detecting a shift or trend in your quality control results by comparing
current measurement values of a control solution to previous values, thus
further enabling you to determine the quality and validity of your blood
sample results
Westgard rules are based on the calculation of the mean and standard deviation
(SD) of quality control measurement values for a particular parameter and a
specific device, through modification of control ranges. They are best expressed
in the form of plots.
Westgard rules are divided into two types:
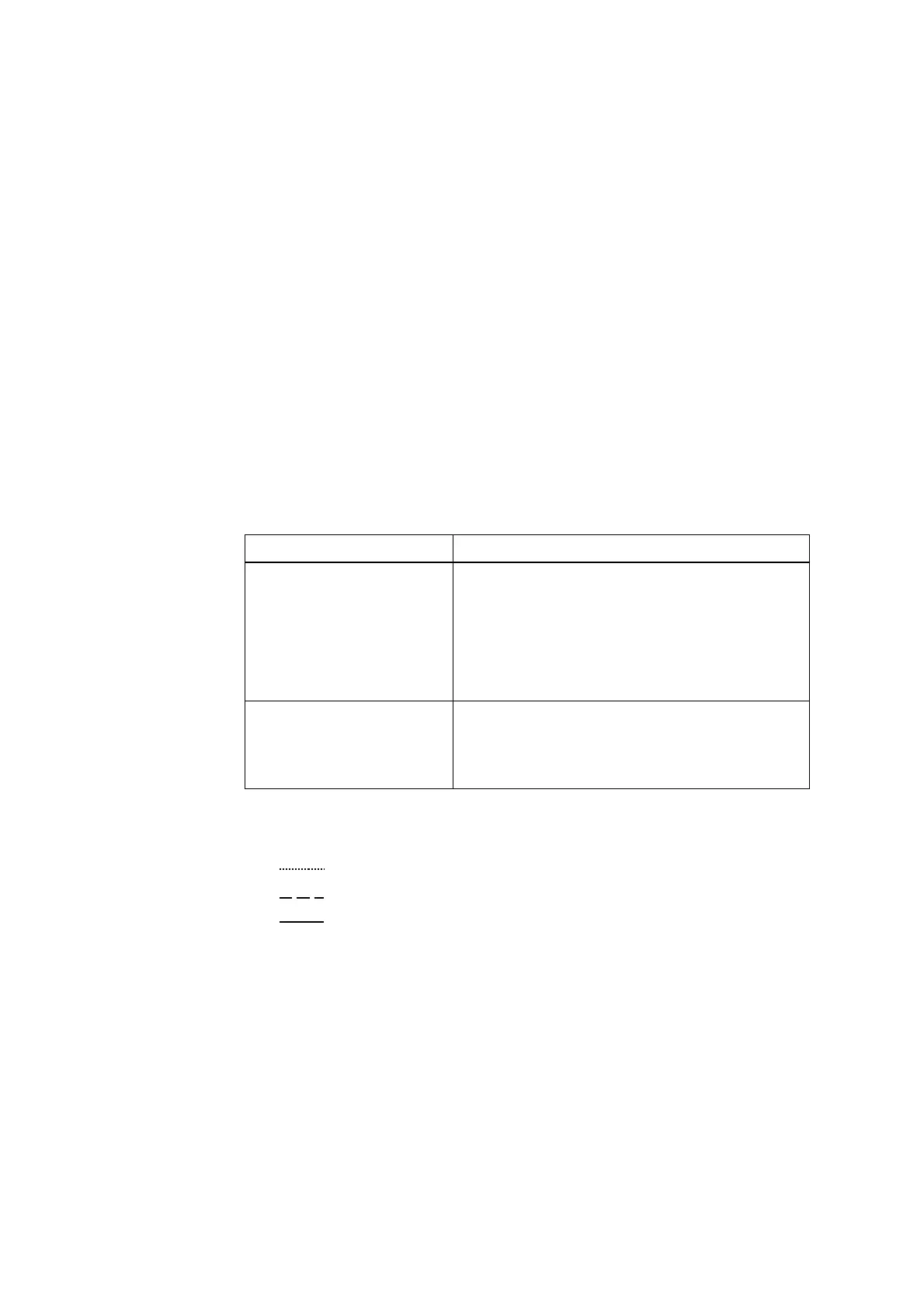
Westgard rule types Explanation
Warning rules Indicate that the next measurement should be
treated with care as the previous measurement
was outside the established ranges. It is
recommended to perform a second
measurement on a new ampoule of the same
level.
Rule 1
2s
is the only warning rule.
Rejection rules Indicate an error and require troubleshooting
your analyzer before analyzing blood samples.
Rules 1
3s
, 2
2s
, R
4s
, 4
1s
and 10
x
are rejection
rules.
The following lines are used in the plots:
Shows 3 SD ranges
Shows control ranges (2 SD)
Shows the mean value
The Westgard rules described in the following are selected for evaluation of
quality control measurement results. All six rules are applicable to manual QC.
Only four of the rules are applicable to built-in QC.
About
Westgard rules
Plot lines
 Loading...
Loading...