ABL90 FLEX reference manual 8. Parameters
8-15
Derived parameters
In the Type column the following symbols are used:
ms for measured parameters
dv for derived parameters
in for input parameters
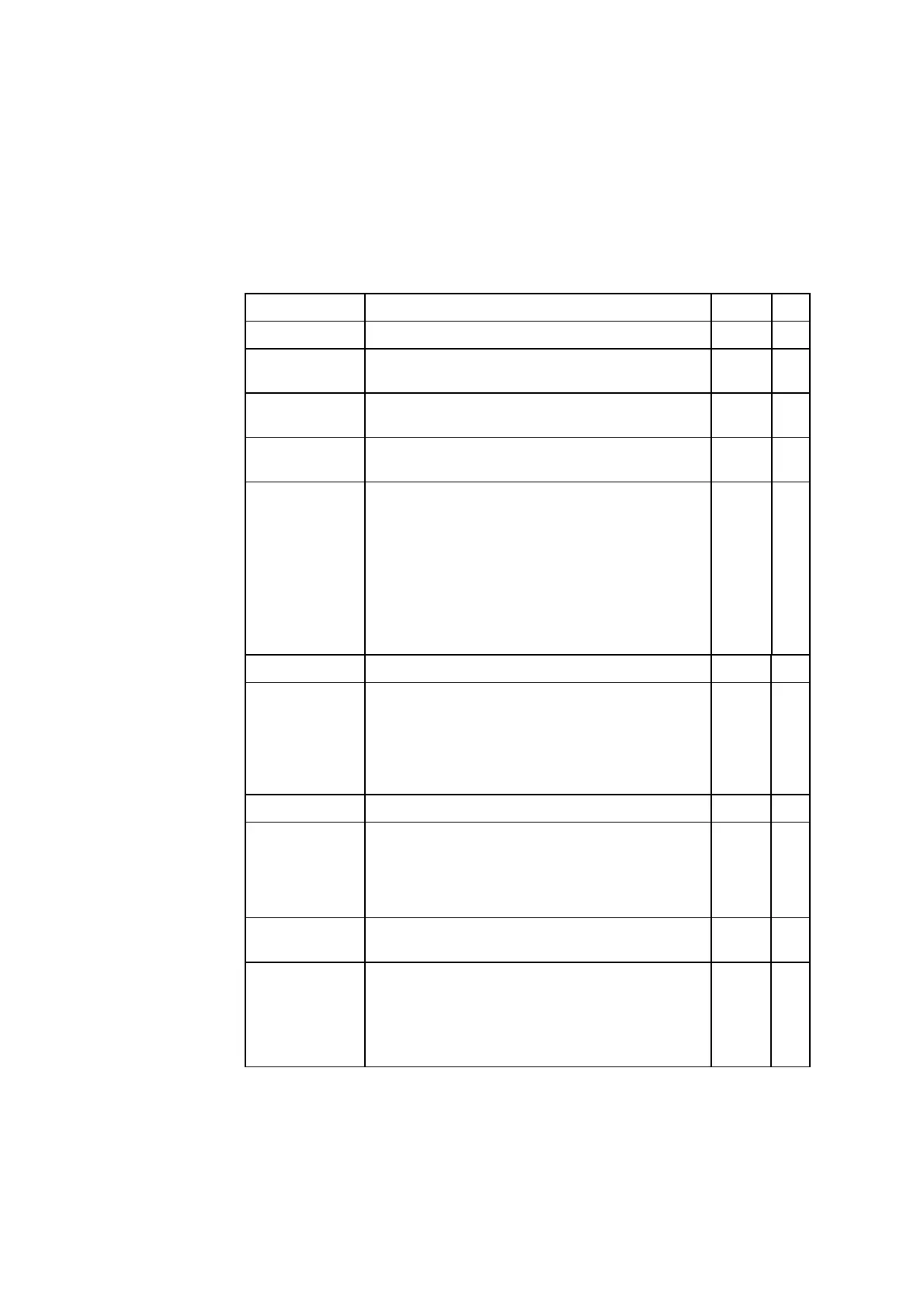
Symbol Definition Type Eq.
pH(T) pH of blood at patient temperature. dv 1
cH
+
(T) Concentration of hydrogen ions in blood at
patient temperature.
dv 2
pCO
2
(T) Partial pressure (or tension) of carbon dioxide
at patient temperature.
dv 3
cHCO
3
–
(P) Concentration of hydrogen carbonate in plasma
(also termed actual bicarbonate).
dv 4
cBase(B)
or ABE
Actual Base Excess, the concentration of titrable
base when the blood is titrated with a strong
base or acid to a plasma pH of 7.40, at pCO
2
of
5.33 kPa (40 mmHg) and 37 °C, at the actual
oxygen saturation [4,5,24].
Positive values (base excess) indicate a relative
deficit of non-carbonic acids; negative values
(base deficit) indicate a relative excess of non-
carbonic acids.
dv 5
cBase(B,ox) cBase(B) of fully oxygenated blood. dv 6
cBase(Ecf)
or SBE
Standard Base Excess, an in vivo expression of
base excess [5,6,24]. It refers to a model of the
extracellular fluid (one part of blood is diluted
by two parts of its own plasma) and is calcu-
lated using a standard value for the hemoglobin
concentration of the total extracellular fluid.
dv 7
cBase(Ecf,ox) cBase(Ecf) of fully oxygenated blood. dv 8
cHCO
3
–
(P,st) Standard Bicarbonate, the concentration of
hydrogen carbonate in the plasma from blood
that is equilibrated with a gas mixture with
pCO
2
= 5.33 kPa (40 mmHg) and
pO
2
13.33 kPa (100 mmHg) at 37 °C [4,5].
dv 9
ctCO
2
(P) Concentration of total carbon dioxide, (free CO
2
+ bound CO
2
) in plasma.
dv 10
ctCO
2
(B) Concentration of total carbon dioxide in whole
blood (also termed CO
2
content).
Calculated based on the total CO
2
concentrations in the two phases: plasma and
erythrocyte fluid [5].
dv 11
General
information
Acid-base
derived
parameters

 Loading...
Loading...