Inter-integrated circuit (I
2
C) interface RM0008
759/1128 DocID13902 Rev 15
26.3.6 SMBus
Introduction
The System Management Bus (SMBus) is a two-wire interface through which various
devices can communicate with each other and with the rest of the system. It is based on I
2
C
principles of operation. SMBus provides a control bus for system and power management
related tasks. A system may use SMBus to pass messages to and from devices instead of
toggling individual control lines.
The System Management Bus Specification refers to three types of devices. A slave is a
device that is receiving or responding to a command. A master is a device that issues
commands, generates the clocks, and terminates the transfer. A host is a specialized
master that provides the main interface to the system's CPU. A host must be a master-slave
and must support the SMBus host notify protocol. Only one host is allowed in a system.
Similarities between SMBus and I
2
C
• 2 wire bus protocol (1 Clk, 1 Data) + SMBus Alert line optional
• Master-slave communication, Master provides clock
• Multi master capability
• SMBus data format similar to I
2
C 7-bit addressing format (Figure 268).
Differences between SMBus and I
2
C
The following table describes the differences between SMBus and I
2
C.
SMBus application usage
With System Management Bus, a device can provide manufacturer information, tell the
system what its model/part number is, save its state for a suspend event, report different
types of errors, accept control parameters, and return its status. SMBus provides a control
bus for system and power management related tasks.
Device identification
Any device that exists on the System Management Bus as a slave has a unique address
called the Slave Address. For the list of reserved slave addresses, refer to the SMBus
specification version. 2.0 (http://smbus.org/).
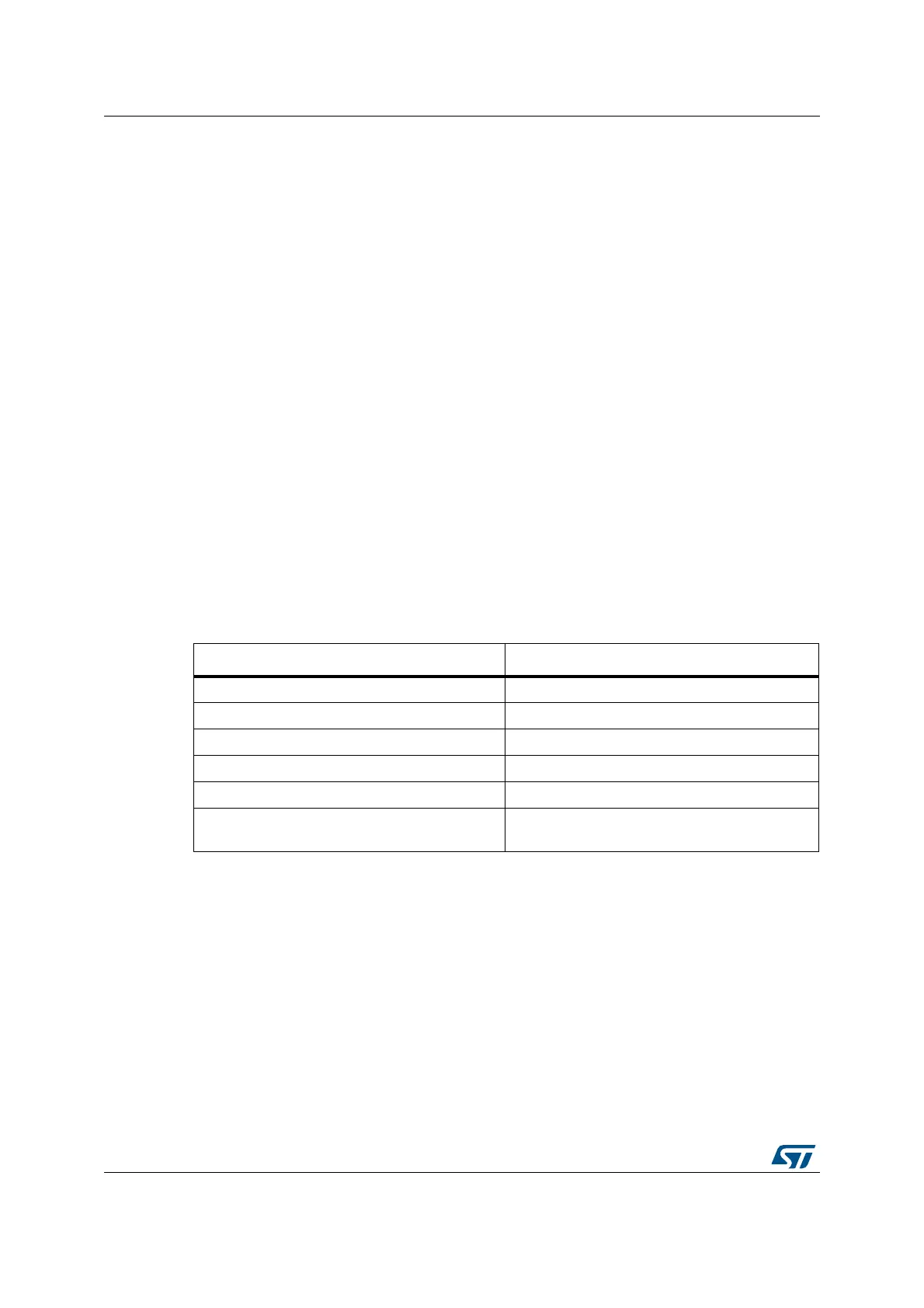
Table 188. SMBus vs. I
2
C
SMBus I
2
C
Max. speed 100 kHz Max. speed 400 kHz
Min. clock speed 10 kHz No minimum clock speed
35 ms clock low timeout No timeout
Logic levels are fixed Logic levels are V
DD
dependent
Different address types (reserved, dynamic etc.) 7-bit, 10-bit and general call slave address types
Different bus protocols (quick command, process
call etc.)
No bus protocols

 Loading...
Loading...