Oscilloscope Reference Math waveforms
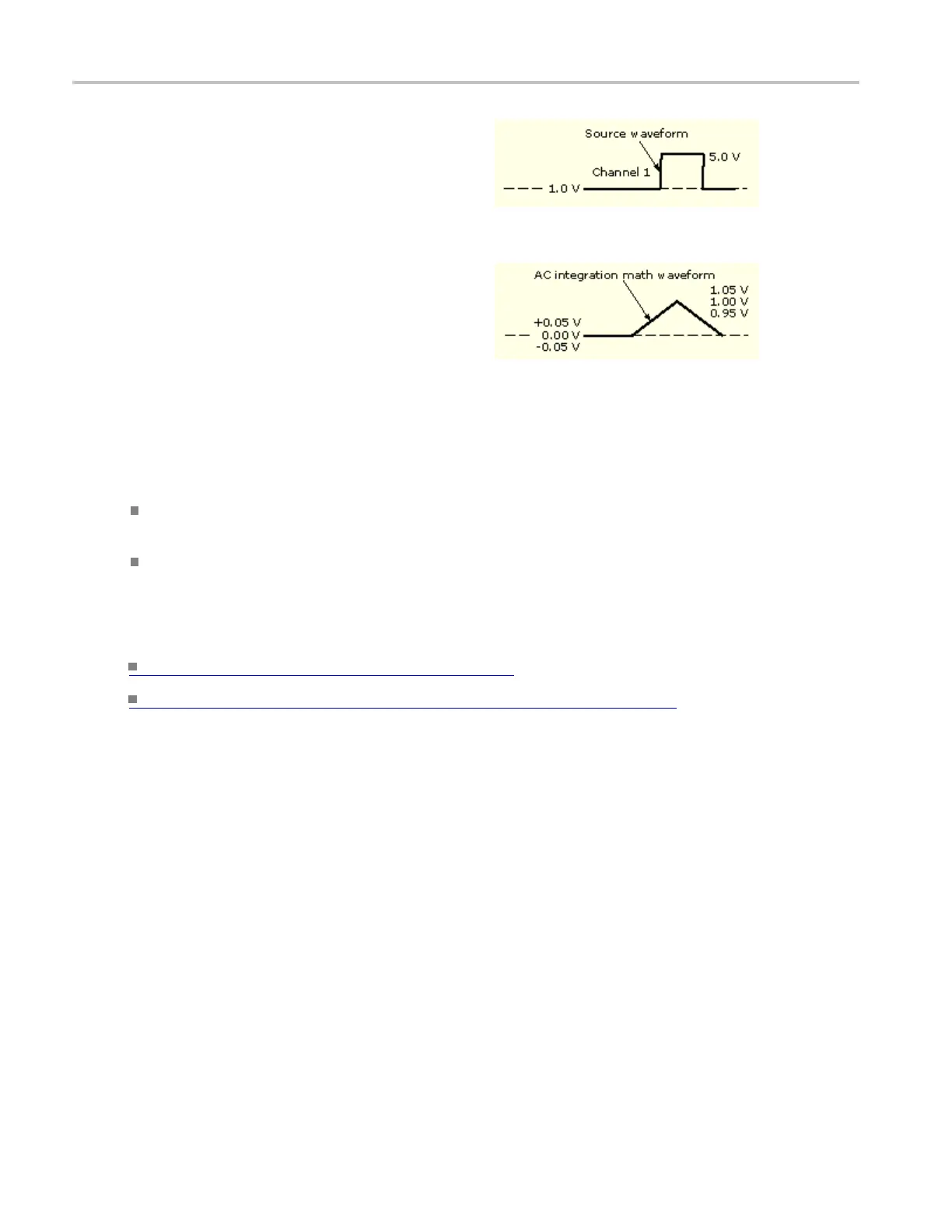
To simulate AC
coupling on this waveform:
Enter this expression:
Intg(Ch1-Avg(Ch1)), where Ch1 is the waveform shown
above Avg is t
he average function
And get this m
ath waveform:
xxx
Offset, position, and sca le
The setti
ngs that y ou make for offset, s cale, and position affect the math waveform you obtain. Here are
some tips for obtaining a good display:
Scale an
d position the source waveform so that it is contained on the screen. (Off-screen waveforms
may be clipped, resulting in errors in the derivative waveform.)
Use ver
tical position and vertical offset to position your source waveform. The vertical position
and offset will not affect your derivative waveform unless you position the source waveform off
screen so that it is clipped.
What do you want to do next?
Learn
about math waveform sources.
(see page 748)
Go to a step-by-step procedure for creating math waveforms. (see page 612)
Math waveforms
Once you have acquired waveforms or taken measurements on wave forms, the instrument can
mathematically combine them to create a waveform that supports your data-analysis task. For example,
yo
u might have a waveform clouded by background noise. You can obtain a cleaner waveform by
subtracting the background noise from your original waveform. Or, you can integrate a single waveform
into an integral math waveform as shown below.
744 DSA/DPO70000D, MSO/DPO/DSA70000C, DPO7000C, and MSO/DPO5000 Series

 Loading...
Loading...











